Adient plc (Formerly Automotive seating business division of Johnson Controls Inc.)
Company Profile
Business Overview
-The Company develops and manufactures seating systems and components for the automotive market, producing complete seating systems, frames, mechanisms, foam, head restraints, armrests, and trim covers.
-The Company is organized into three reportable segments based on geographical region: Americas, EMEA, and Asia.
-The Company was formerly the Automotive seating business of Johnson Controls, having completed its separation from Johnson Controls in October 2016.
Competitors
-Lear
-Toyota Boshoku
-Forvia
-Magna International
-Yanfeng Automotive Systems
Shareholders
-The Company is listed on the New York Stock Exchange.
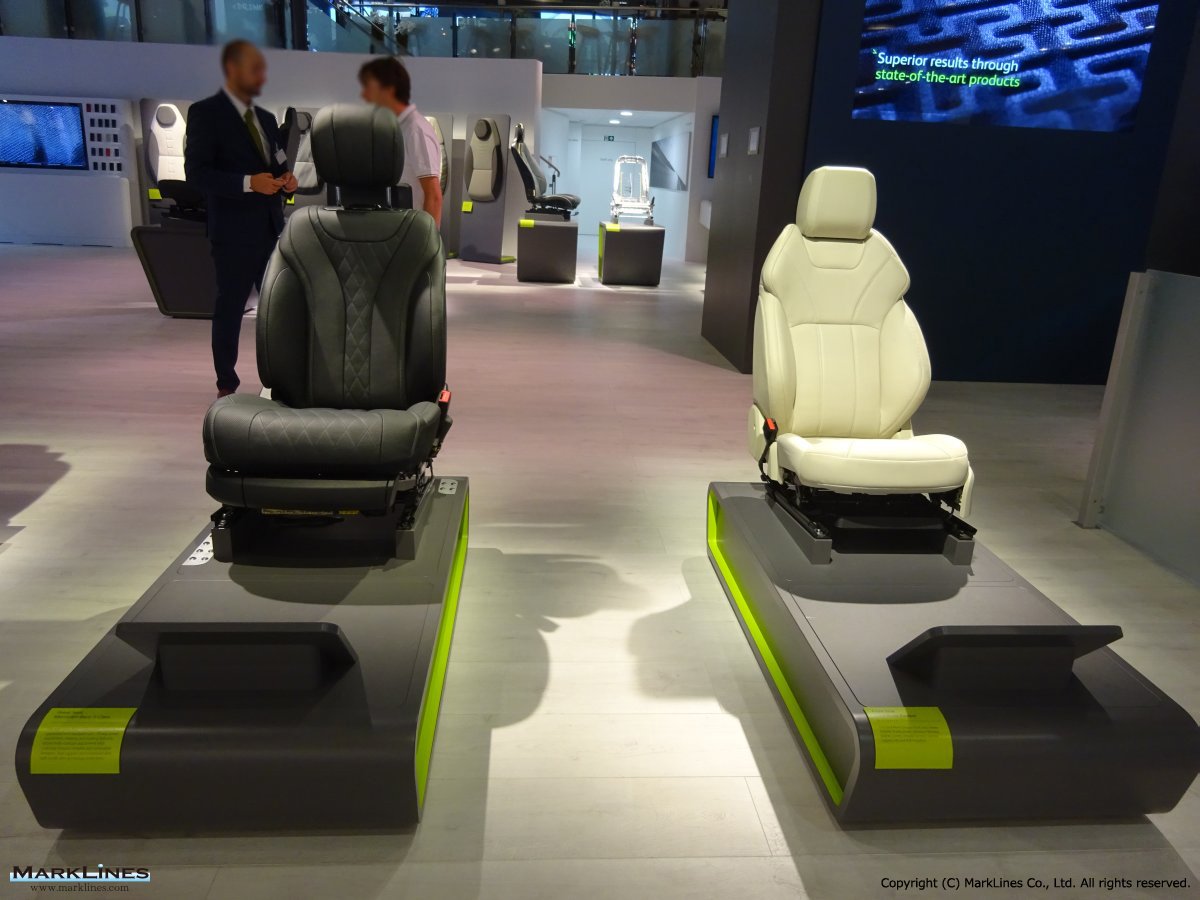
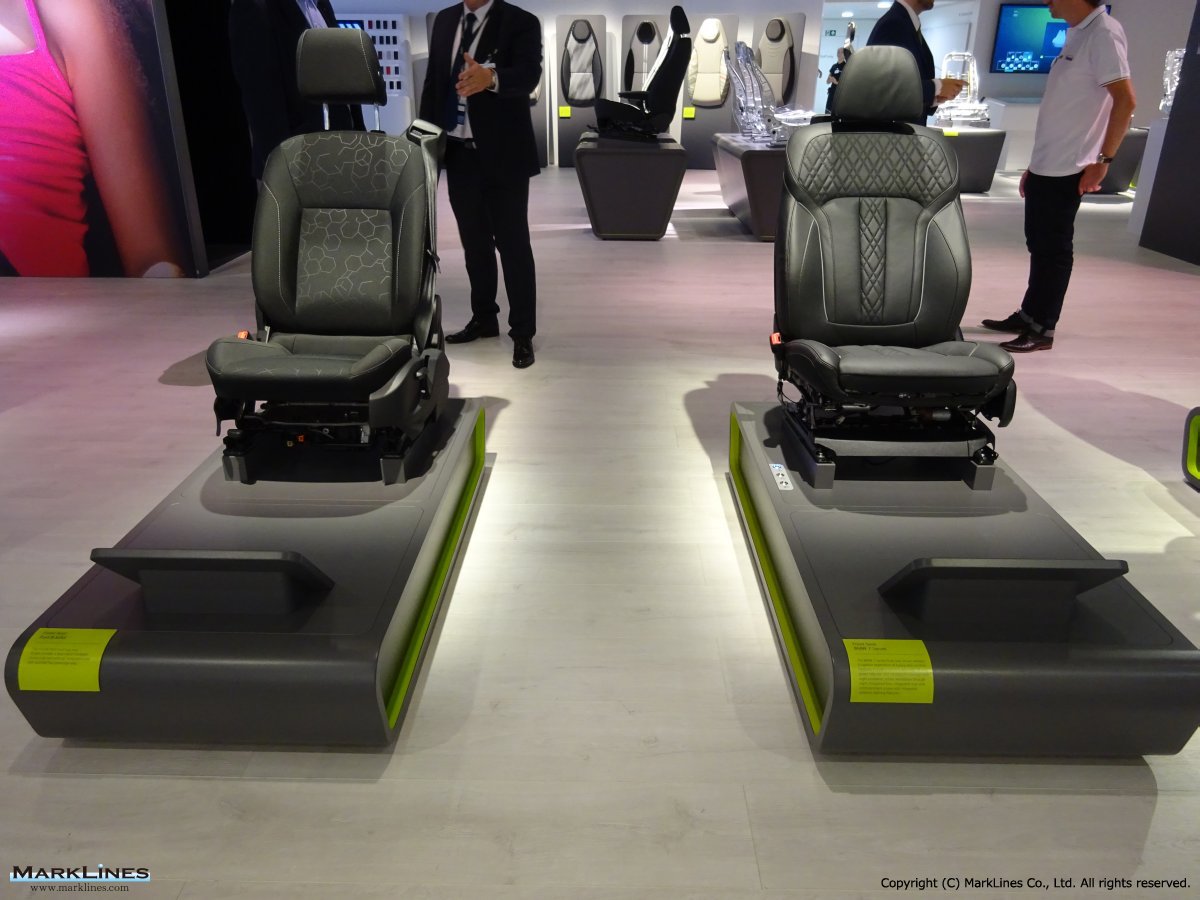
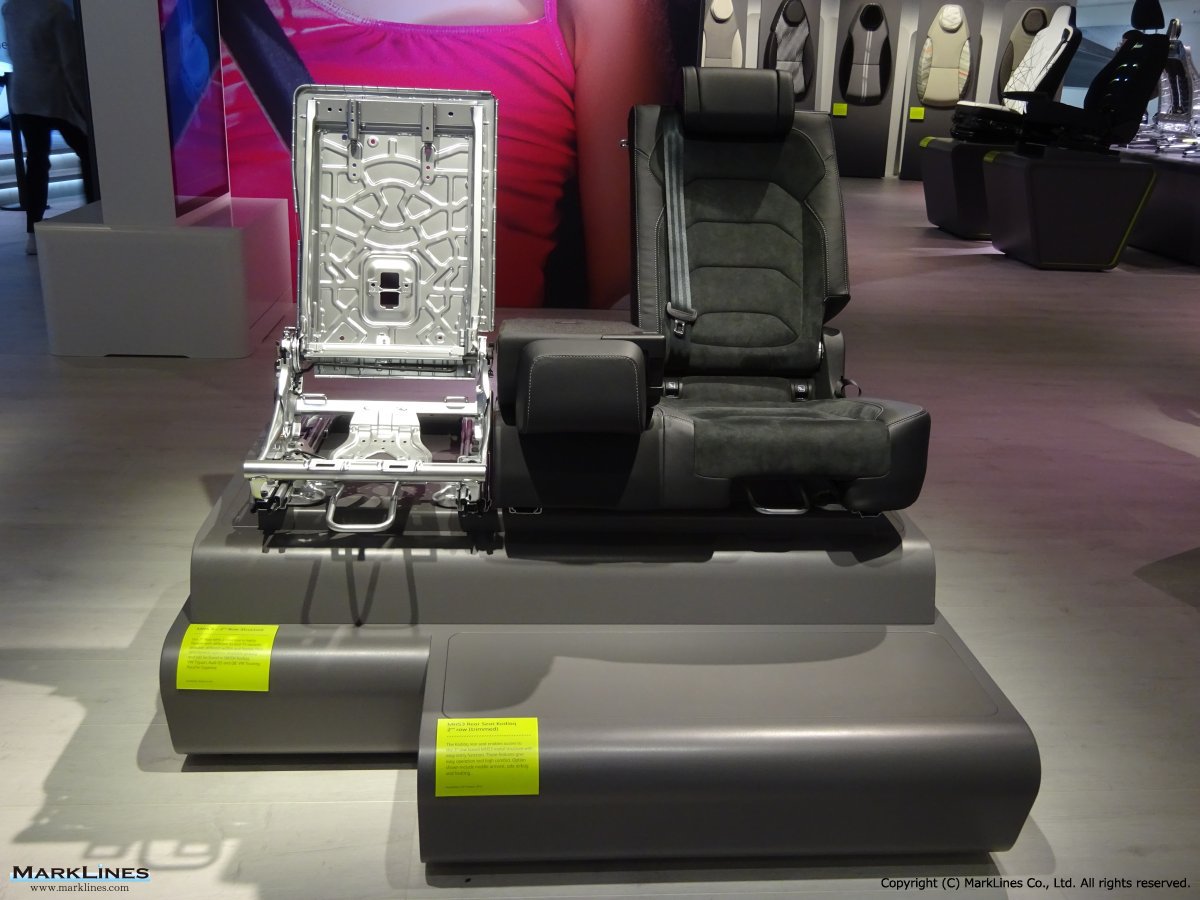
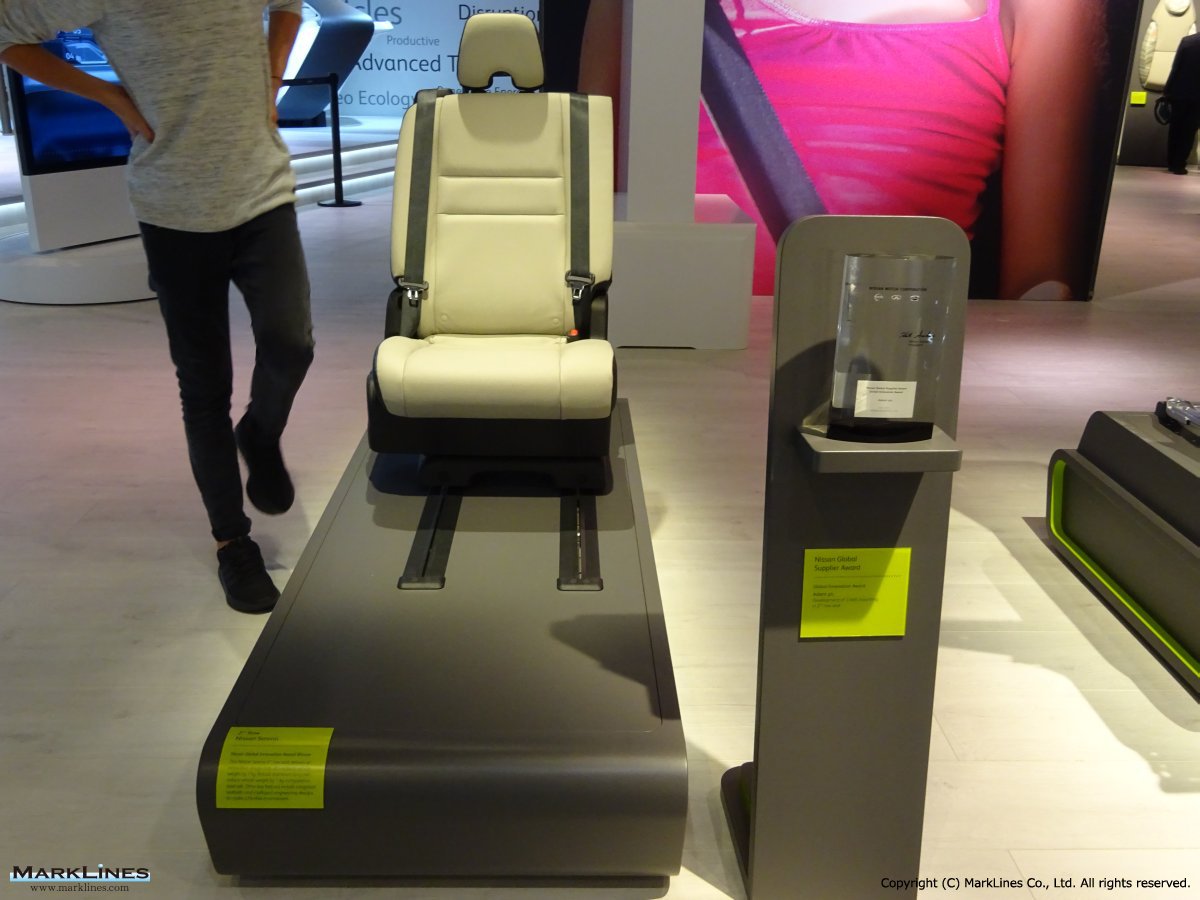
Products
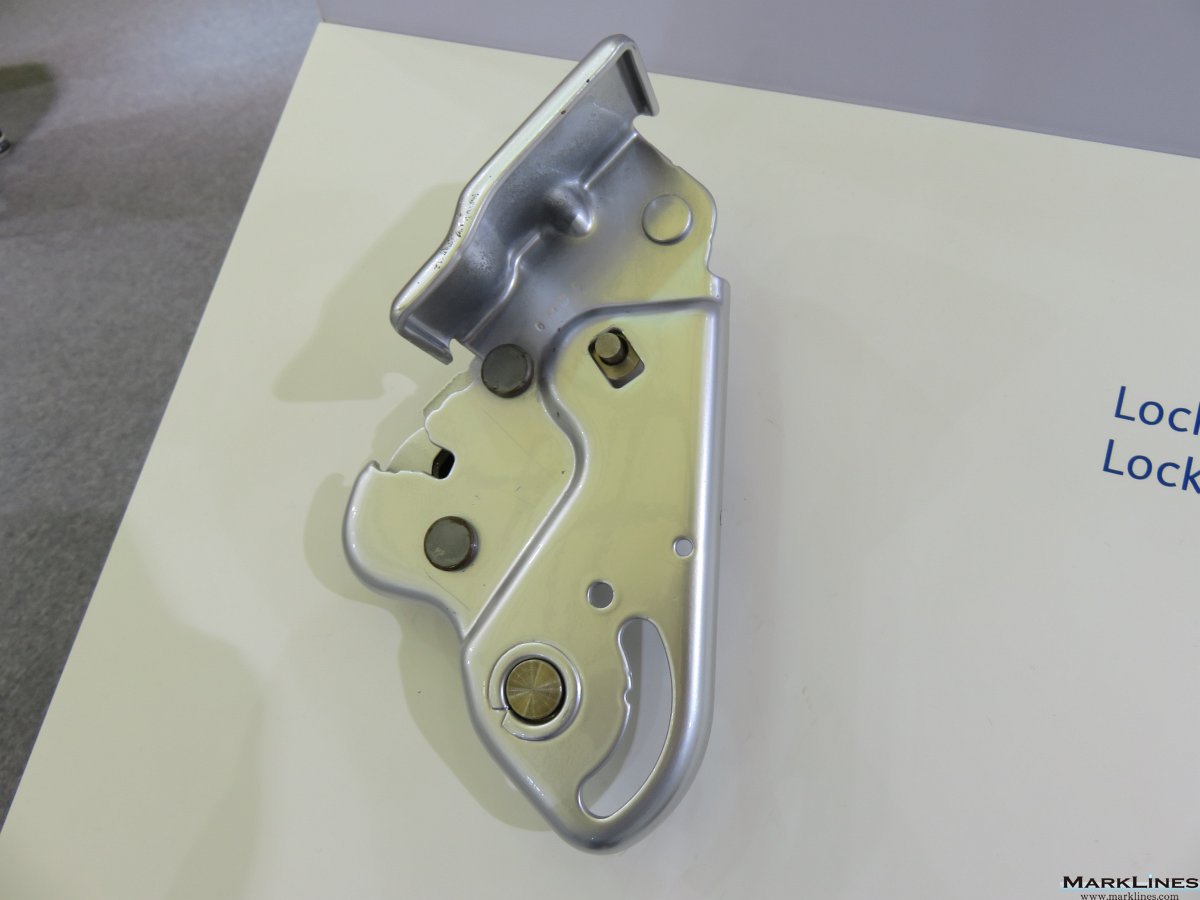
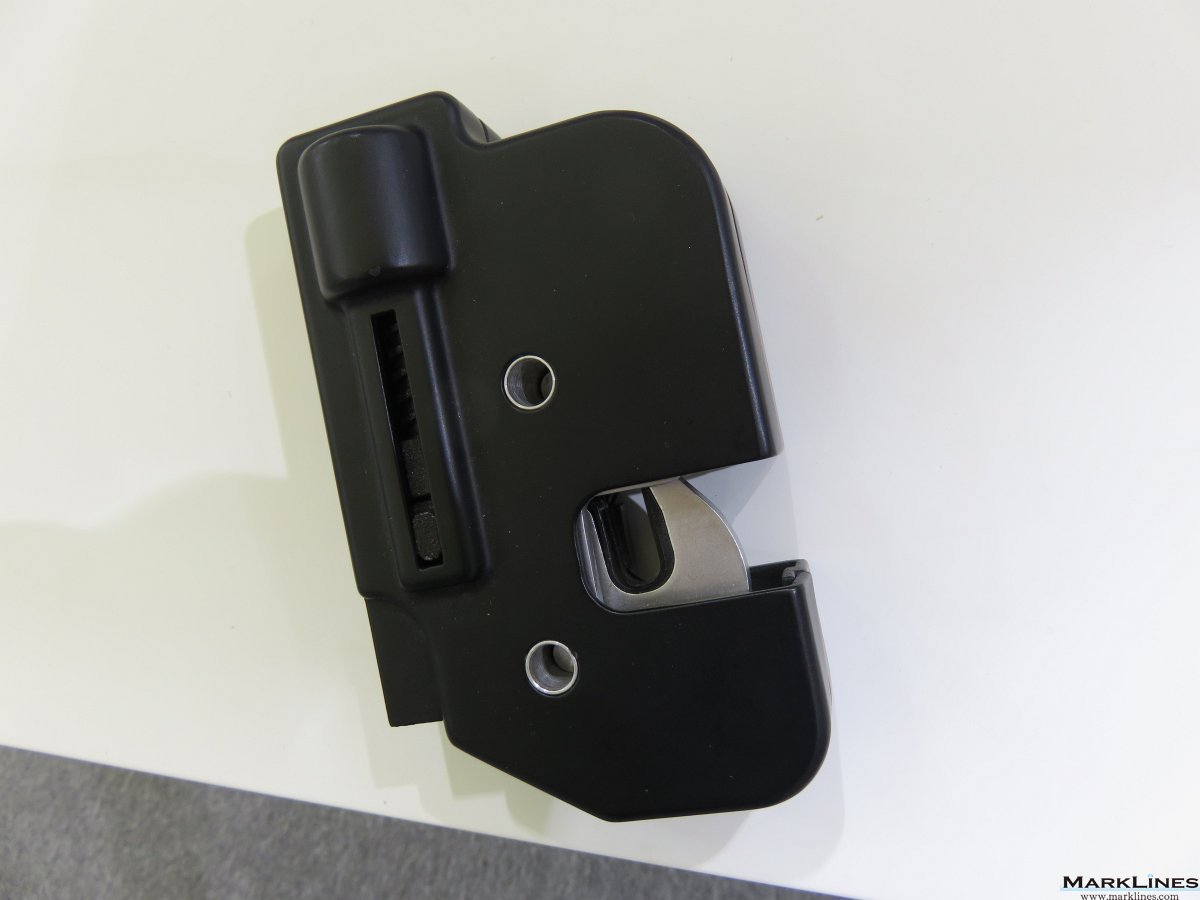
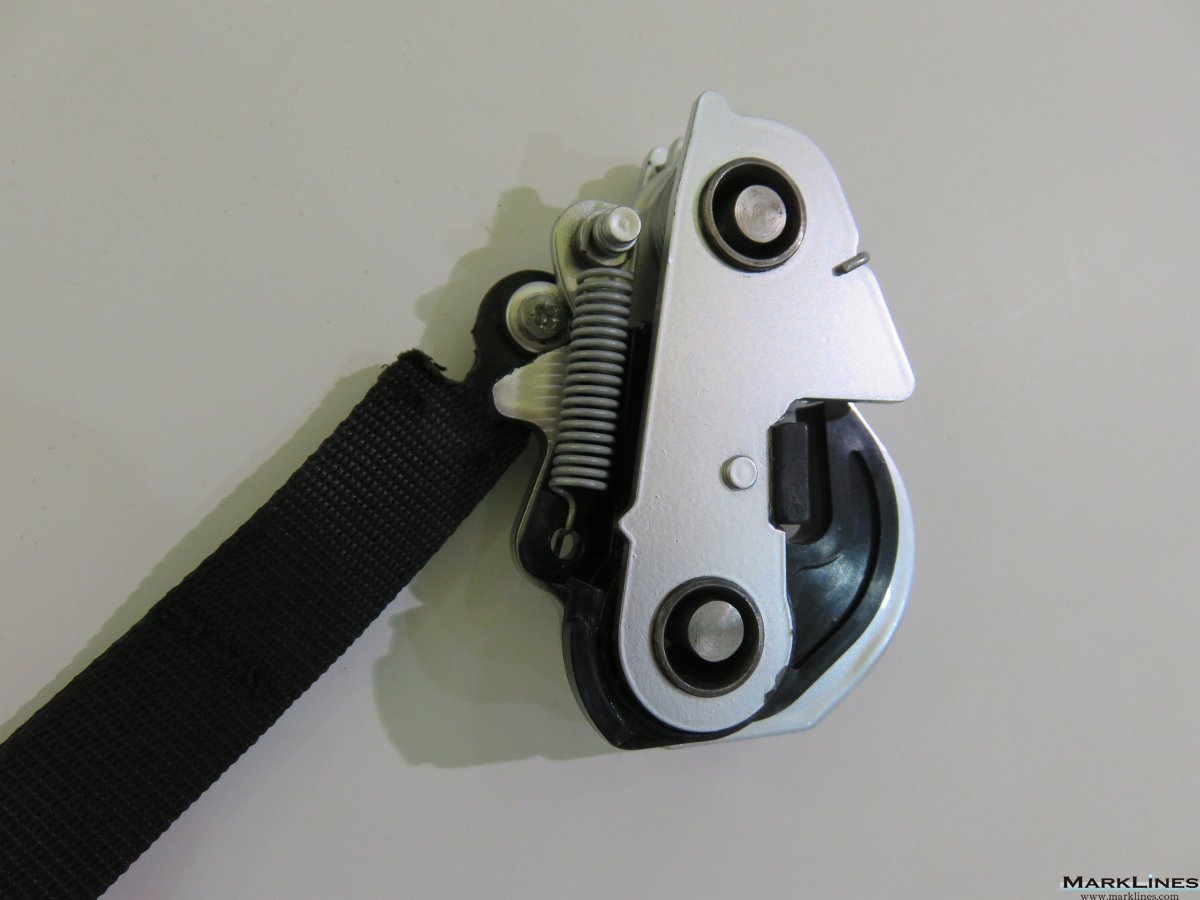
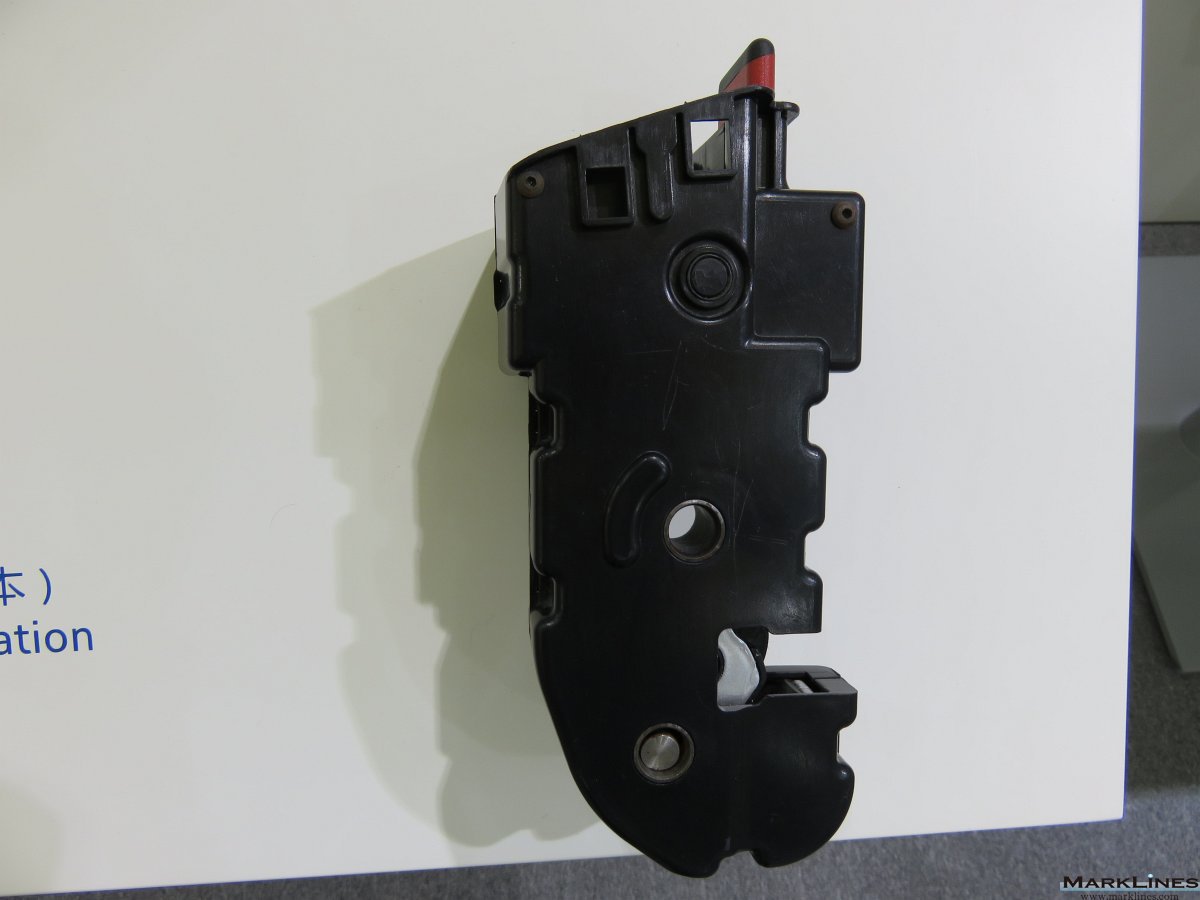
-Complete seats
-Commercial vehicle seats
-Structures & mechanisms
-Foam
-Trim
-Soft Back Panel sustainable component with up to 70% recycled PET
-Soft Side Valance sustainable component with up to 70% recycled PET
History
| 1883 | Warren S. Johnson, a professor at the State Normal School in Whitewater, Wisconsin, received a patent for the first electric room thermostat. His invention launched the building control industry and was the impetus for a new company. |
| 1885 | Johnson and a group of Milwaukee investors incorporated the Johnson Electric Service Company to manufacture, install and service automatic temperature regulation systems for buildings. Between 1885 and 1911, Professor Johnson delved into many other areas, including electric storage batteries, steam and gas powered automobiles, huge pneumatic tower clocks and wireless telegraph communication. |
| 1902 | Name changed to Johnson Service Co. |
| 1910 | Opened first European sales offices. |
| 1911 | Johnson died, and the Company decided to focus solely on its temperature control business for nonresidential buildings. |
| 1940 | Johnson Service Co. securities first listed on what is today the NASDAQ exchange. |
| 1965 | Johnson Service Co. securities listed on the New York Stock Exchange. |
| 1974 | The Company renamed Johnson Controls, Inc. |
| 1978 | Acquired Globe-Union, Inc., a Wisconsin-based manufacturer of automotive batteries for both the replacement and original equipment markets, and the Company entered automotive battery business. |
| 1985 | Acquired Michigan-based Hoover Universal, the source of its automotive seating and plastics machinery businesses. At the time, the seating business primarily manufactured individual components, like frames, tracks or cushions, according to the automakers' specifications. |
| 1990s | Expanded its presence within cars and light trucks by offering interior components such as headliners and door trim. |
| Jul. 1996 | Acquired Prince Automotive and expanded its automotive interior systems business. Prince is known for its innovation, from the first lighted vanity mirror in 1972 to the integration of electronics into interior systems. |
| Feb. 1997 | Divested Plastic Container Division with annual sales of USD 135 million, for USD 6.5 billion to Schmalbach-Lubesca AG/Continental Can Europe. |
| Jul. 1998 | Acquired Becker Group, a manufacturer of interior components with annual sales of USD 1.3 billion, for USD 548 million, plus the assumption of approximately USD 372 million of debt. |
| Sep. 1998 | Sold off the Plastic Machinery Division to Miracron Inc. for USD 190 million. The division generates USD 190 million per year. |
| Oct. 1998 | Established a technical center in Yokohama, representative office in Aichi in Japan. |
| Jan. 1999 | Sold off its eight injection molding facilities and other two manufacturing plants, which had been owned by Becker Group, to Becker Ventures. |
| Feb. 1999 | Acquired Commerfin S.p.A, an Italian manufacturer of door panels/ floor consoles and metal mold casting products with annual sales of USD 100 million. The Company started to supply to Fiat. |
| Mar. 1999 | Sold off its industrial battery division with annual sales of USD 87 million, for USD 135 million to Abcde. With this transaction, the Company focused on the automotive battery business. |
| Mar. 1999 | Formed a joint venture, named TrimQuest L.L.C., with Plastech Engineered Products (Michigan) to manufacture overhead systems. The production of overhead systems for the Ford/LS 2000 model is scheduled to begin from August 1999. |
| May 1999 | Acquired a seat trim cover facility in Kentucky, from TechnoTrim, a joint venture with Tachi-S since 1996. |
| May 1999 | Production began at Saltillio facility of TechnoTrim, a joint venture with Tachi-S, in Mexico. This plant will supply seat covers to GM, Nissan and Ford. |
| Sep. 1999 | Acquired a head liner plant and the Uberherrn plant from Benecke-Kaliko AG, the largest manufacturer of head liners in Germany and fourth largest manufacturer of automotive roof systems in Europe. Benecke also manufactures head air bags, and interior pillars. |
| Dec. 1999 | Launched a joint-venture with Araco Corporation, an auto-body maker affiliated with Toyota, to produce car seat covers for France's Renault SA at a new sewing plant in Slovakia. Araco holds a 49% stake, and the Company holds 51%. By April 2001 the joint-venture called Trim Leader was producing more than 800 seat covers a day for Renault Clio, Renault Twingo, Toyota Avensis and Toyota Corolla. The company employs 867 people. |
| Jun. 2000 | In order to support a contract with Mercedes-Benz for the supply of cockpits for the Mercedes-Benz C-Class in South Africa, the Company opened a cockpit facility, 1.5km away from DaimlerChrysler's plant in Port Elizabeth. The plant reached full production in mid-2001. The Company will also supply headliner modules to the C-Class from this new plant. |
| Jun. 2000 | Announced that it had opened a new interiors facility in Warren, Michigan (USA). The just-in-time facility manufactures door trim panels for several DaimlerChrysler cars and trucks, which are supplied to the carmaker's plants in Michigan and Ohio. The Company invested USD 35 million in the plant, which will employ 335 people. |
| Sep. 2000 | Acquired approximately 90% of the outstanding shares of Ikeda Bussan Co. Ltd. (Ikeda), a Japanese supplier of automotive seating systems and the primary supplier of seating systems to Nissan Motor Company. |
| Oct. 2000 | Announced that it was investing in new capacity to make headliners and optional cargo organizers for DaimlerChrysler's 2001 minivans. The Company is building two new facilities in Missouri (USA), one in Tecumseh (Canada) and expanding its existing facilities in Graz (Austria). |
| Nov. 2000 | Purchased stock in the Donnelly Corporation, a Michigan based supplier of automotive rearview mirror systems, modular window systems and handle products. |
| Nov. 2000 | Acquired Gylling Optima Batteries AB, a manufacturer of spiral-wound lead-acid batteries, and MC International, a leader in refrigeration and air conditioning systems and services in Europe. These acquisitions had a combined purchase price of approximately USD 200 million. |
| Jan. 2001 | Partnered with Volvo Cars to develop seating and interior systems for the automaker's safety concept car. |
| Apr. 2001 | Announced the planned investment of EUR 56.65 million in a production line in Romania. The exact location will depend on a number of contracts with Romanian carmakers. |
| Jul. 2001 | Will build a new manufacturing plant in Canton, Miss., to supply automotive seat systems for three 2004 model year vehicles assembled by a new Nissan Motor Co. plant two miles away. Construction of the Company's 120,000-square-foot plant is set to begin in early 2002. |
| Sep. 2001 | Agreed to license the North American technical, manufacturing and commercial rights to its seat cooling technology to a German supplier, W.E.T. Automotive Systems AG of Odelzhausen, Germany, which is a developer and manufacturer of seat heating products and related technologies in North America and Europe. |
| Oct. 2001 | Acquired the automotive electronics software and systems engineering division of Sagem SA and the German automotive battery manufacturer Hoppecke Automotive GmbH & Co. KG. |
| Oct. 2002 | Acquired the automotive battery business of Varta Automotive Battery Division (Varta). Varta is a major original equipment supplier to BMW, DaimlerChrysler, Ford, PSA and Volkswagen. |
| 2003 | Acquired Borg Instruments AG (Borg), an automotive electronics company with headquarters in Germany. Also acquired Varta Automotive GmbH and 80% majority ownership in VB Autobatterie GmbH. |
| 2005 | Acquired Delphi's global battery business. |
| Dec. 2009 | Johnson Controls has signed a global strategic agreement with Geely Holding Group in China. |
| 2011 | Acquired the C. Rob. Hammerstein Group (CRH). CRH, headquartered in Solingen, Germany, develops and manufactures seat structures, seat adjusters, steering column adjusters, and other products. |
| Signed a purchase agreement to acquire Keiper Recaro Group's automotive business. | |
| Acquired the automotive division of Romanian Spumotim S.A. | |
| Acquired an additional 35% equity share in JP Foam Manufacturing, a joint venture with Proseat of Germany, making it its wholly owned subsidiary. | |
| 2012 | Acquired a 24.9% share in its Novo Mesto, Slovenia joint venture called TPV Johnson Controls, making the Company the majority shareholder in the joint venture. |
| May 2013 | Made Tata Johnson Controls, which was a 50-50 joint venture with Tata AutoComp, a wholly owned subsidiary. |
| Sep. 2013 | Divested HomeLink product group to Gentex. |
| Nov. 2013 | Acquired 90% ownership of Colombian battery supplier, MAC S.A. |
| May 2014 | Signed agreement to form automotive interiors joint venture with Yanfeng Automotive Trim Systems Co., Ltd. |
| Jul. 2014 | Signed agreement with Shanghai Yanfeng Industry and Commerce Co., Ltd., and Anhui Yansheng Automotive Trim Co. Ltd. to form a fabrics joint venture in Huainan City, China. The new JV is named Anhui New Nangang Johnson Controls Automotive Trim Co., Ltd. |
| Completed divestiture of automotive electronics business to Visteon. | |
| Jul. 2015 | Transferred its interior business to Yanfeng Automotive Interiors Co., Ltd., a joint venture with a wholly-owned subsidiary of Huayu Automotive Systems Co., Ltd (HUAYU). |
| Plans to pursue a tax-free spin-off of its Automotive Experience business. Following the separation, the Automotive Experience business will be named "Adient" and will operate as an independent, publicly traded company, effective Oct. 12, 2016. The new company will be listed on the New York Stock Exchange. | |
| Sep. 2015 | Signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Beijing Hainachuan Automotive Parts Co. Ltd. (BHAP), an auto parts subsidiary of Beijing Automotive Industry Group Co., Ltd. (BAIC Group), to set up automotive battery sales and manufacturing joint ventures in China. |
| Apr. 2016 | Adient Ltd. files SEC Form 10 for planned spin-off from Johnson Controls. |
| Oct. 2016 | Completed separation from Johnson Controls. The Company's shares begin trading on the New York Stock Exchange. |
| Nov. 2016 | Opened business office in San Jose, California which will also serve as a research and development hub focused on connected and autonomous vehicles. |
| Jan. 2017 | Opened a new corporate office in Shanghai, China. |
| Jun. 2017 | Opened new plant for production of automotive seating covers in the technologically developing zone in Strumica, Macedonia. |
| Nov. 2017 | Announced the groundbreaking of a state-of-the art automotive seating prototyping and testing facility in Pune, India. |
| Mar. 2018 | Formed the joint venture Adient Arvind Automotive Fabrics with Arvind, to develop and manufacture automotive fabrics in India. |
| Jan. 2020 | Recaro Automotive Seating announced it was sold by Adient to Raven Acquisitions LLC, a Detroit based, privately owned investment corporation. |
| Oct. 2020 | Sage Automotive Interiors completed its agreement to acquire the automotive fabric business of Adient. |
| Mar. 2021 | Ended the joint venture with Yanfeng Automotive Interiors Co., Ltd. |
| Aug. 2024 | Zhejiang Tiancheng Controls Co., Ltd. completed acquisition of the Company’s entire 48% equity in the joint venture Changsha Adient Automotive Components Co., Ltd., changing the name to Changsha Huacheng Automotive Components Co., Ltd. |
Supplemental Information 1
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2006
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2007
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2008
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2009
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2010
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2011
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2012
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2013
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2014
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2015
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2016
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2017
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2018
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2019
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2020
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2021
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2022
>>>Business Report FY ended Sep. 30, 2023
Archives of Past Exhibits
Note:
-A figure in brackets ( ) indicates a loss
-This report includes information of Johnson Controls Inc. through the fiscal year ended September 30, 2015, prior to its spin-off.
>>>Johnson Controls official site

 AI Navigator
AI Navigator






























 Japan
Japan USA
USA Mexico
Mexico Germany
Germany China (Shanghai)
China (Shanghai) Thailand
Thailand India
India