CASE Development in India (Part 2): Mobility
Mass adoption of connected cars, shared mobility partnerships and autonomous vehicle development
2021/02/10
- Summary
- Connected Vehicle
- Autonomous vehicle and ADAS development
- Shared Mobility
- Subscription service and car leasing
- Government guidelines for vehicle aggregator
Summary
 |
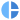
| MG Hector, India's first internet car (Source: MG Motor India) |
The Indian market is one which has traditionally been dominated by small cars and compared to other major automotive markets, is still significantly behind in terms of technological development. But in recent years, a change in this tradition can be seen with the emergence of new OEMs onto the Indian market and the advanced cars they have brought with them.
In the fiscal year 2019-20, India witnessed the mass adoption of connected cars with the launch of Hyundai Venue, Kia Seltos and MG Hector etc. Major OEMs also geared up to introduce autonomous vehicle technology. In addition, Indian OEMs established tie ups with shared mobility service providers like Uber, Ola, Meru etc. to gain their foothold in the connected market.
Connected vehicle technology is now gathering momentum in the Indian market as all leading OEMs offer it in their vehicles, especially in compact SUVs, SUVs and premium offerings. On the other hand, autonomous technology is yet to take off. No OEM is offering any model beyond autonomous Level 1, although a few OEMs have started R&D and tie ups for autonomous vehicles and ADAS related development.
Related reports:
CASE Development in India (Part 1): Electrification (Feb. 2021)
Tata and Jaguar Land Rover (Part 1): Turnaround Strategy and CASE Development (Oct. 2020)
Hyundai Motor Group: increasing electrified vehicle lineup with 44 models in 2025 (Jun. 2020)
Indian Auto Expo 2020: Indian and European OEMs announce new SUVs and electric models (Feb. 2020)
Indian Auto Expo 2020: GWM and Haima announce new entry into Indian market (Feb. 2020)
Free membership registration allows you to read the rest of the article for a limited time.

 AI Navigator
AI Navigator










 Japan
Japan USA
USA Mexico
Mexico Germany
Germany China (Shanghai)
China (Shanghai) Thailand
Thailand India
India