Toyota Industries Corporation
Company Profile
Business Overview
-The Company is the founding company of the Toyota Group.
-Its main business activities include manufacturing and sales of automobiles, industrial vehicles, textile machinery and other products, and logistics.
-The main business activities of its automotive division include assembling cars; and developing and producing automotive components such as car air-conditioning compressors, automotive electric components and devices, batteries and stamping molds.
-The Company has the world’s highest market share in three product areas, i.e., forklifts, automotive air-conditioner compressors, and air-jet looms. (Based on Company’s own study)
2030 Vision (Announced in April 2019)
-The targets for FY2030 are as follows. Operating profit: more than JPY 400 billion, operating profit margin: 10%.
<Major developments in the automotive segment>
1. Compressors
- Invest in automatic products that offer excellent performance in terms of low magnetic-noise and quietness, destined for Europe and China.
- Strengthen organization to increase capabilities in stages through making minimum investments in unit production in terms of fixed-capacity, adjustable capacity, and automation.
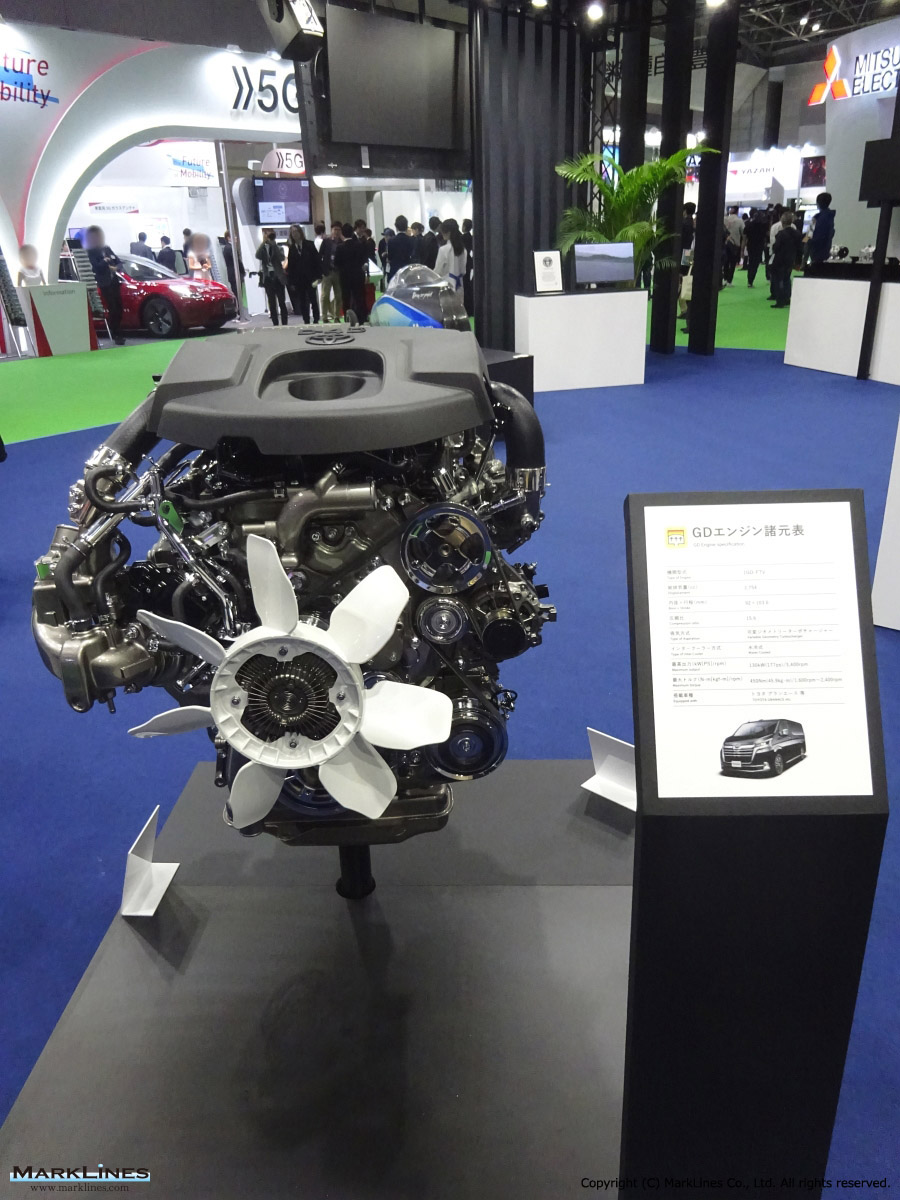
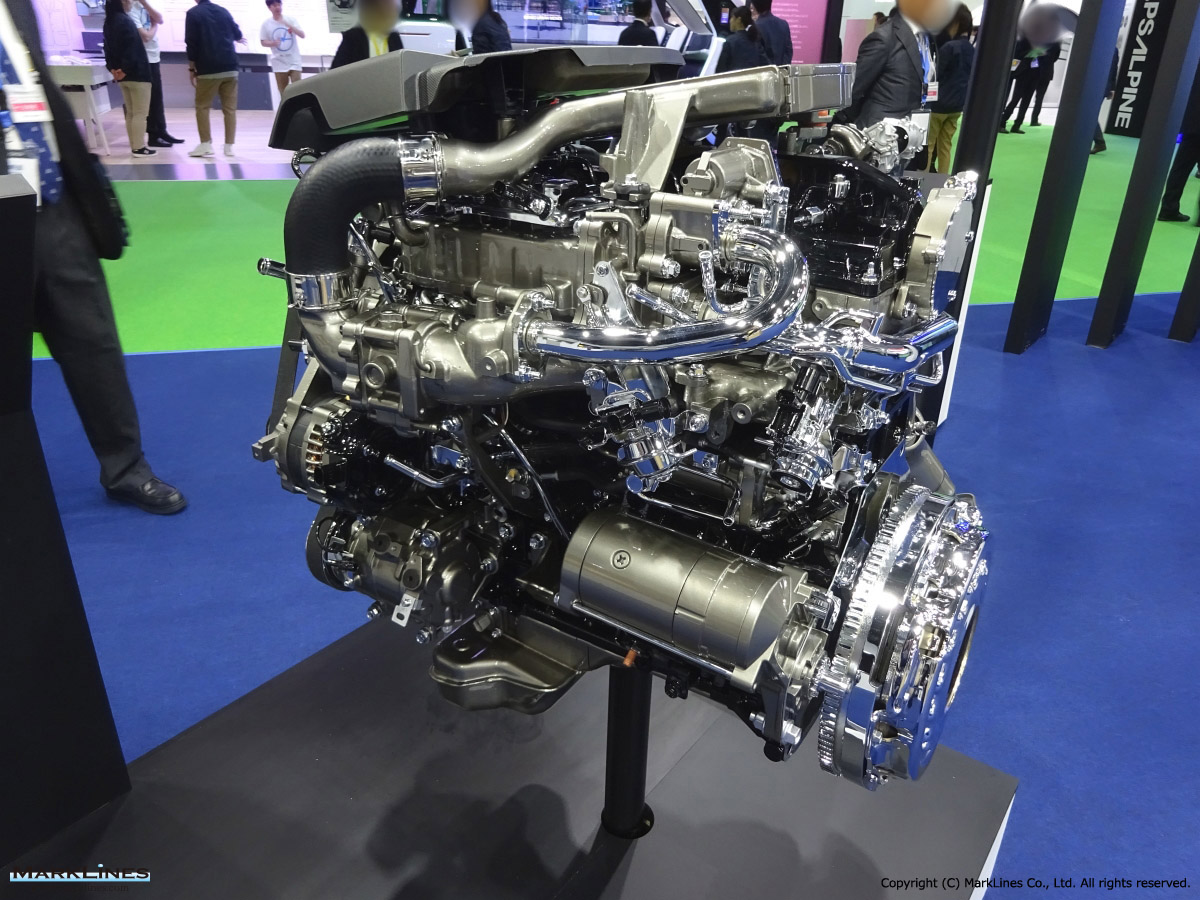
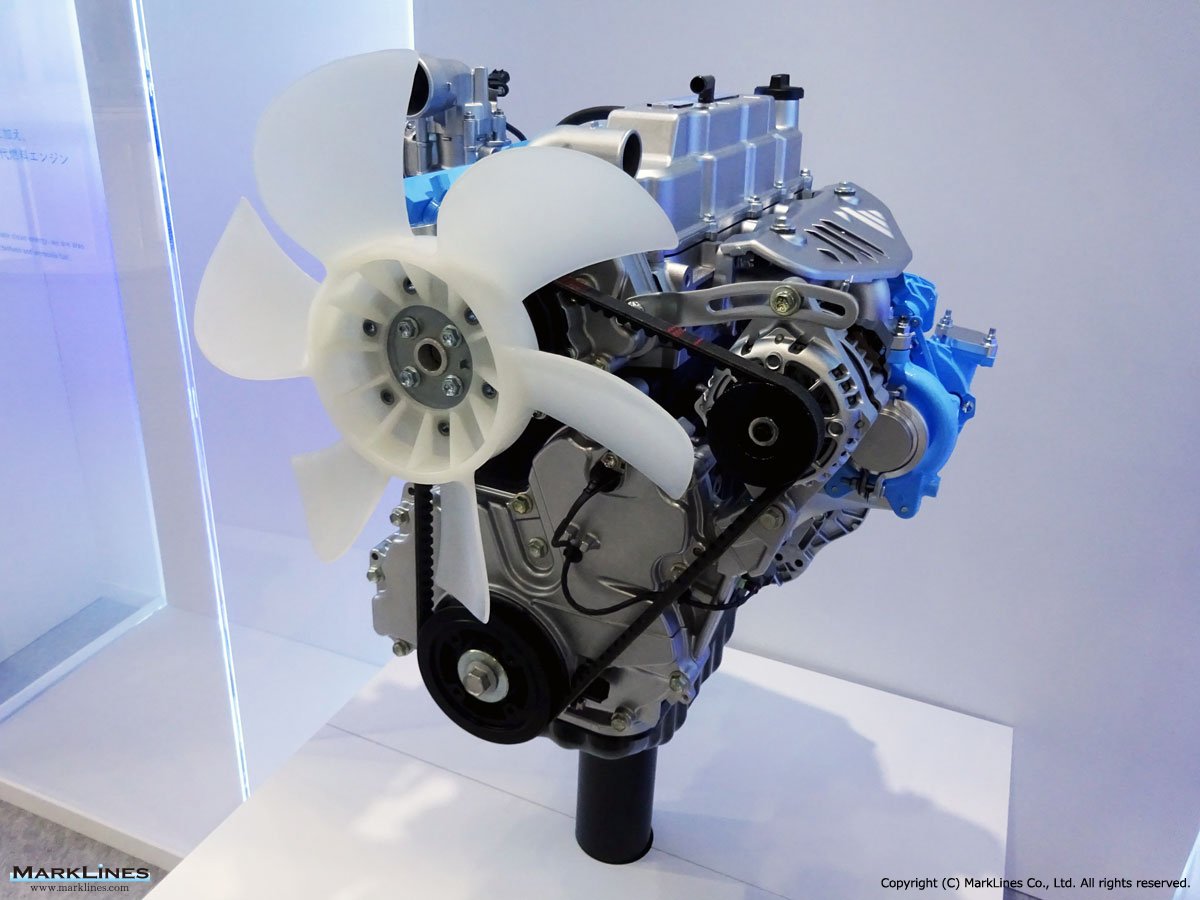
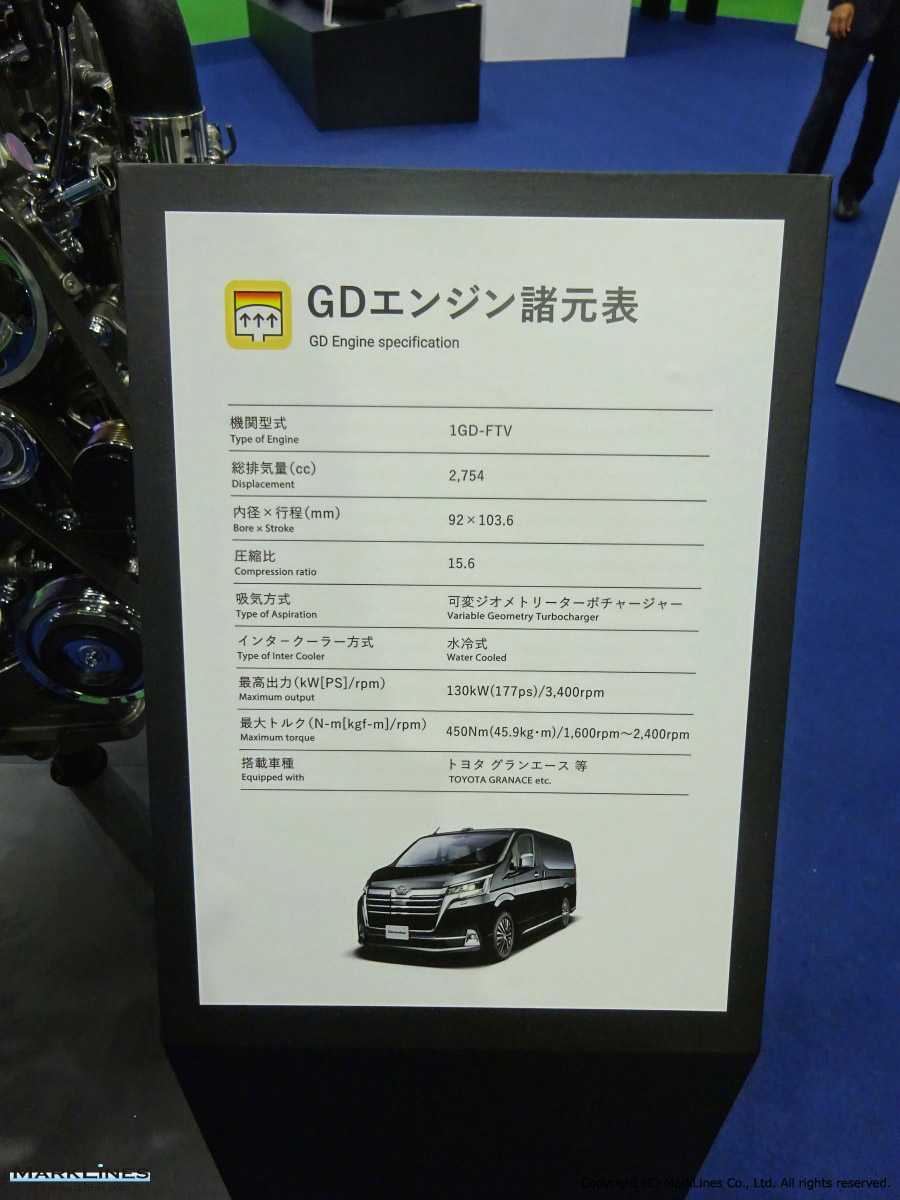
2. Engines
- Diesel Engines
- Respond to the deep-rooted demand especially for commercial vehicles and SUVs in emerging countries.
- Expand production capacity of GD engines.
- Enhance development and production efficiencies by consolidating businesses from Toyota
- Develop next-generation engines that target zero emissions.
- Turbo Engines
- Increase the types of vehicles equipped with diesel engines
- Launch turbo engines for gasoline engines
- Increase sales to more than Toyota vehicles
- Differentiate through R&D achievements reflected in company-built engines
- Gasoline Engines
- Increase unit production of TNGA engines that are the successors of the AR engines.
- Challenge taking up development activities.
Shareholders
| -Listed on the Prime Market of the Tokyo Stock Exchange and the Premium Market of the Nagoya Stock Exchange. | (As of Mar. 31, 2025) |
| Name or Company Name | Investment ratio (%) |
| Toyota Motor Corp. | 24.59 |
| The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Ltd. (Trust Account) | 9.53 |
| TOYOTA FUDOSAN CO., LTD. | 5.41 |
| Toyota Tsusho Corporation | 5.07 |
| Denso Corporation | 4.92 |
| Custody Bank of Japan, Ltd. (Trust Account) | 3.38 |
| Nippon Life Insurance Co. (Standing proxy The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Ltd.) | 2.18 |
| Aisin Corporation | 2.18 |
| STATE STREET BANK AND TRUST COMPANY 505001 (Standing proxy Mizuho Bank, Ltd. Yen Settlement Sales Section) | 1.66 |
| Aioi Nissay Dowa Insurance Co., Ltd. (Standing proxy The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Ltd.) | 1.30 |
| Total | 60.22 |
Products
Vehicles
-RAV4
Engines
Engines for Automobiles
-Diesel engines
-Gasoline engines
Foundry Parts
-Cylinder blocks
- Cylinder blocks for NASCAR racing
- Aluminum cylinder blocks for A25A gasoline engines
-Cylinder heads
- Aluminum cylinder heads for GD diesel engines
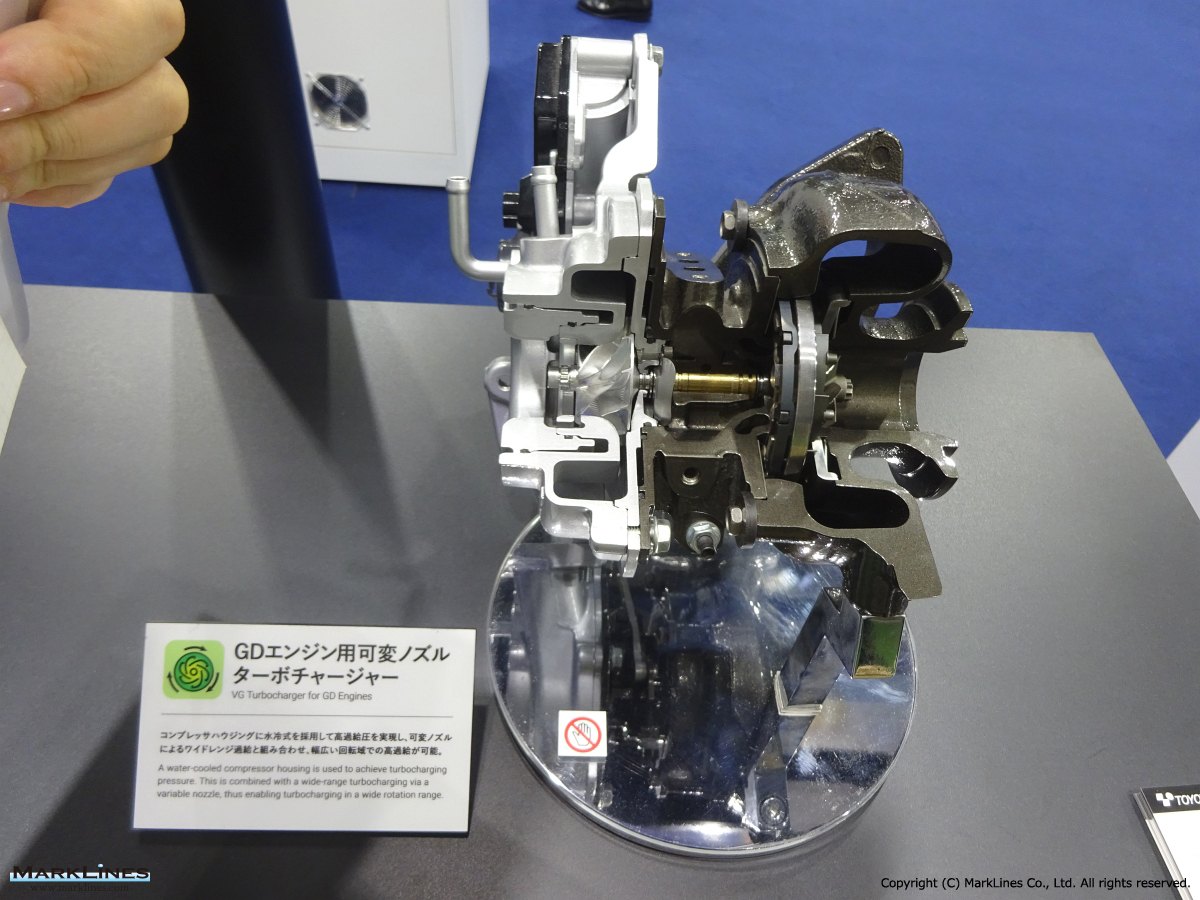
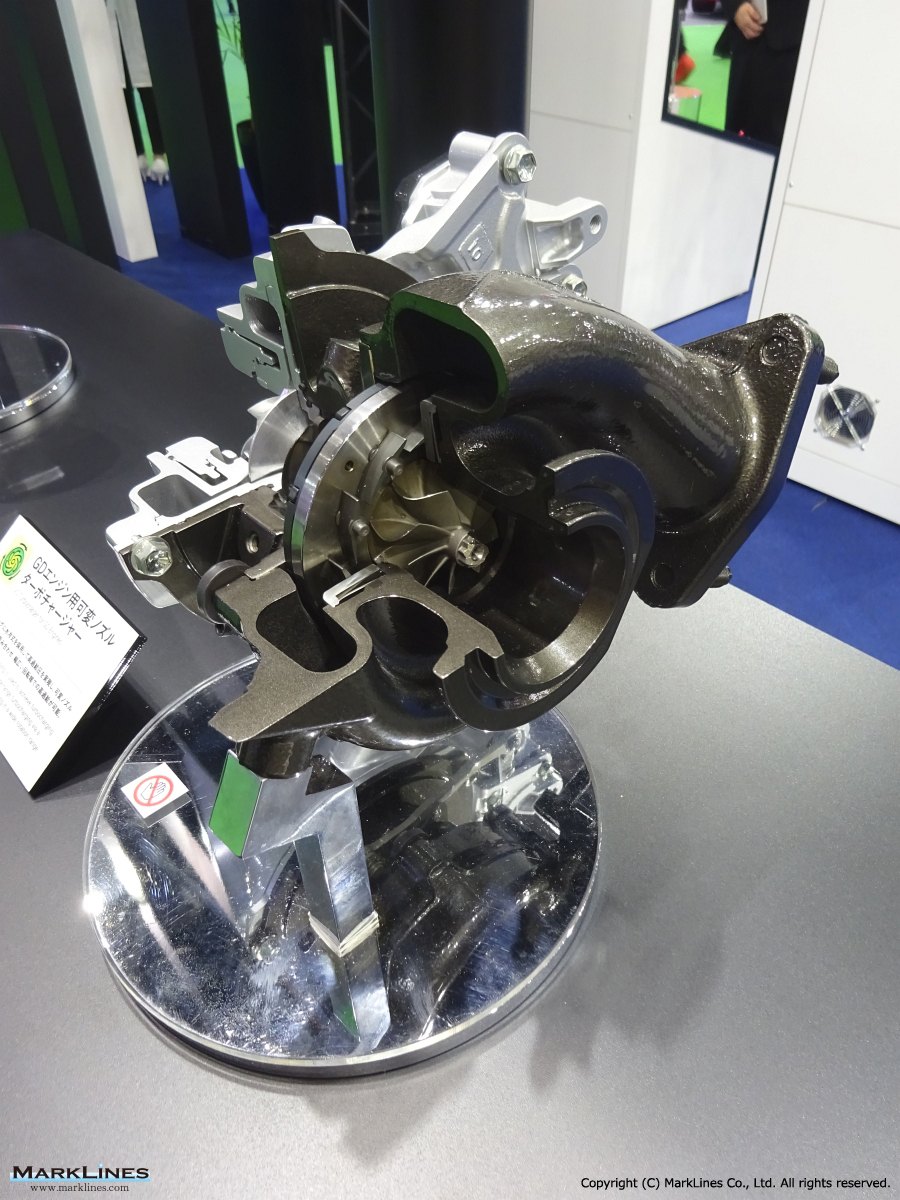
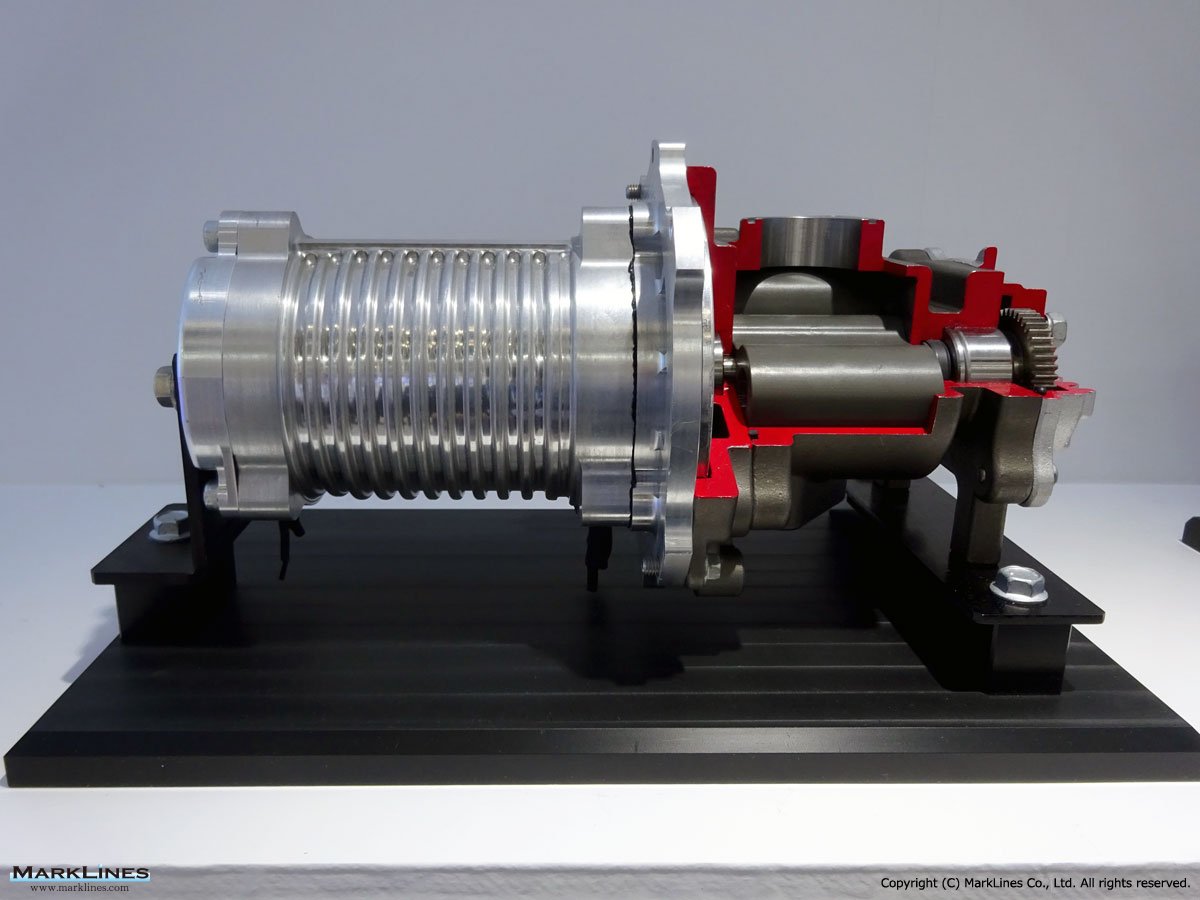
Turbochargers
-Two-way twin turbocharging system for F33A Diesel Engine
-Variable Geometry Turbocharger for GD diesel engine
-Wastegate Turbocharger for the AR Gasoline Engine
-Waste gate Turbocharger for T24A Gasoline Engine
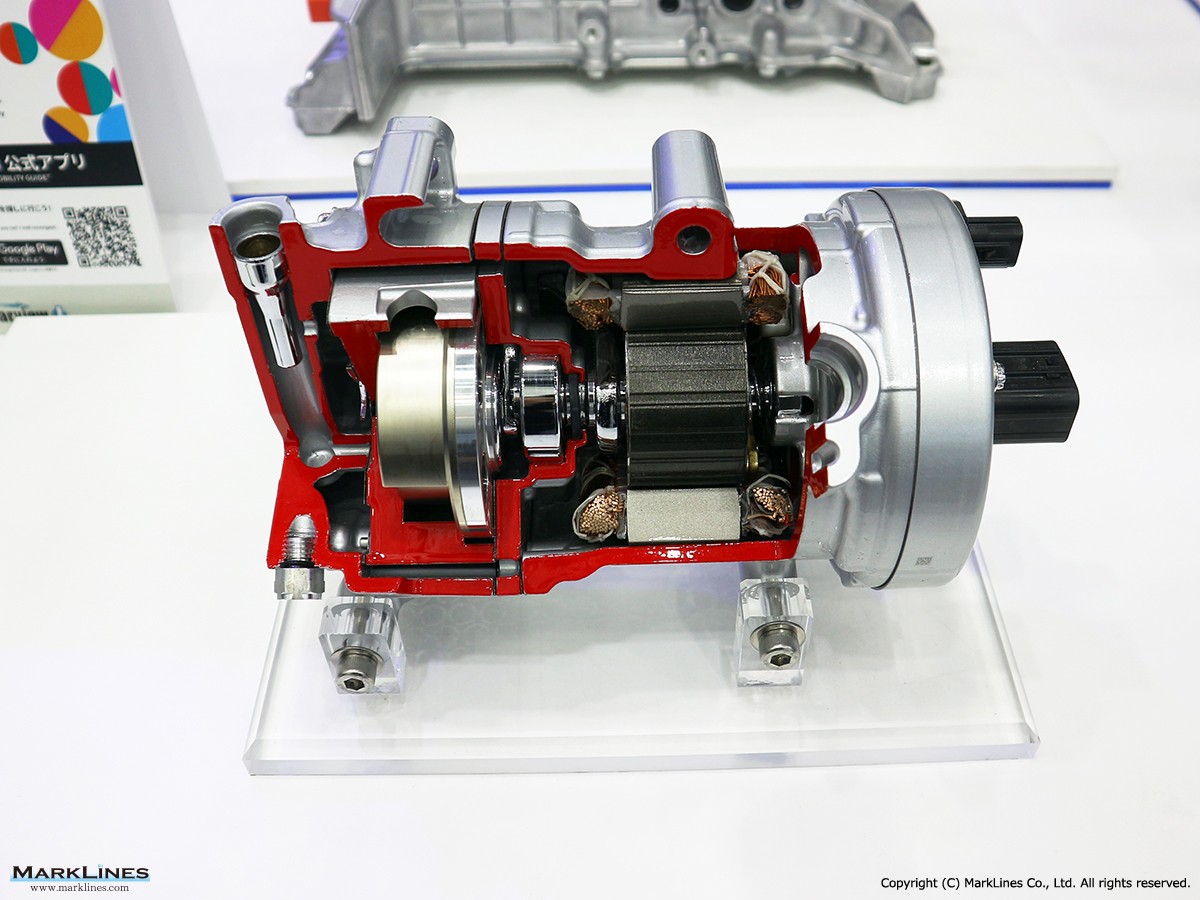
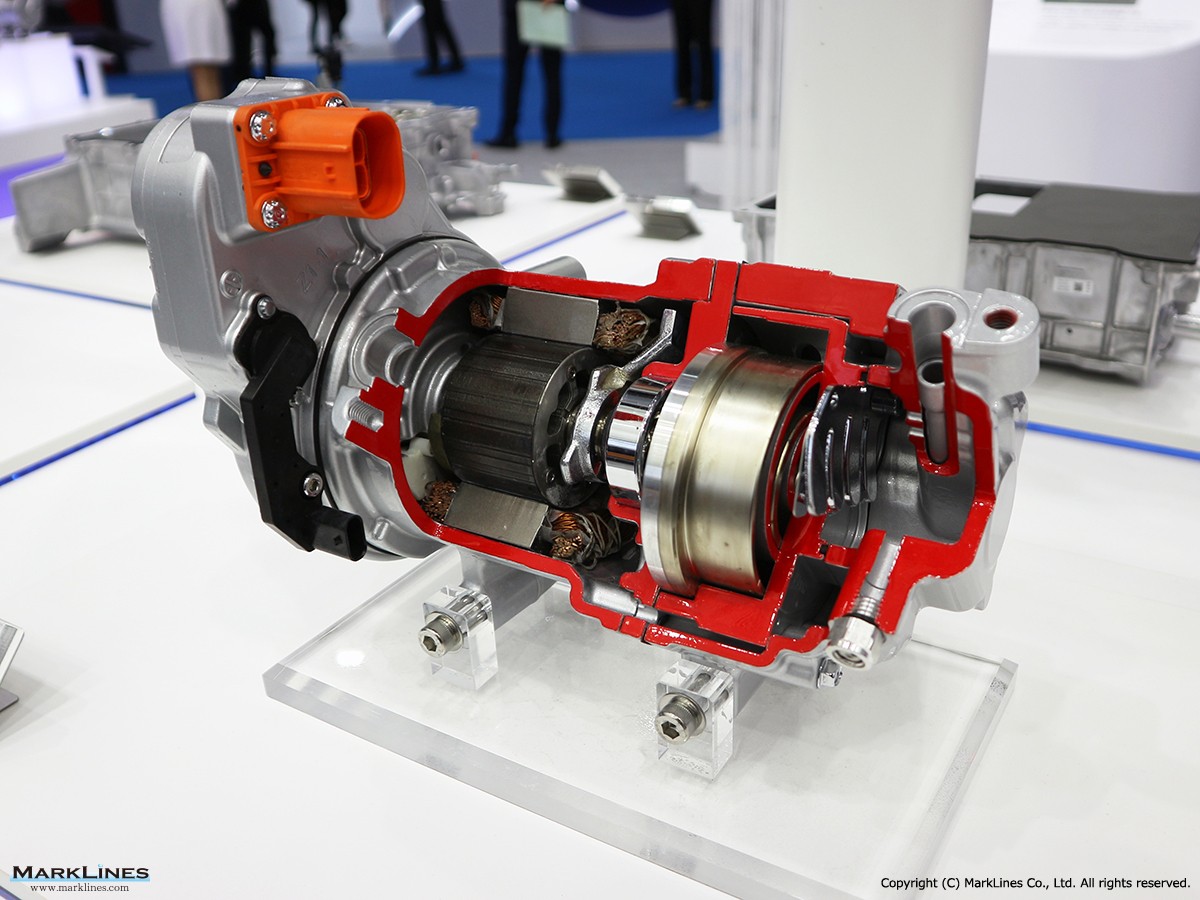
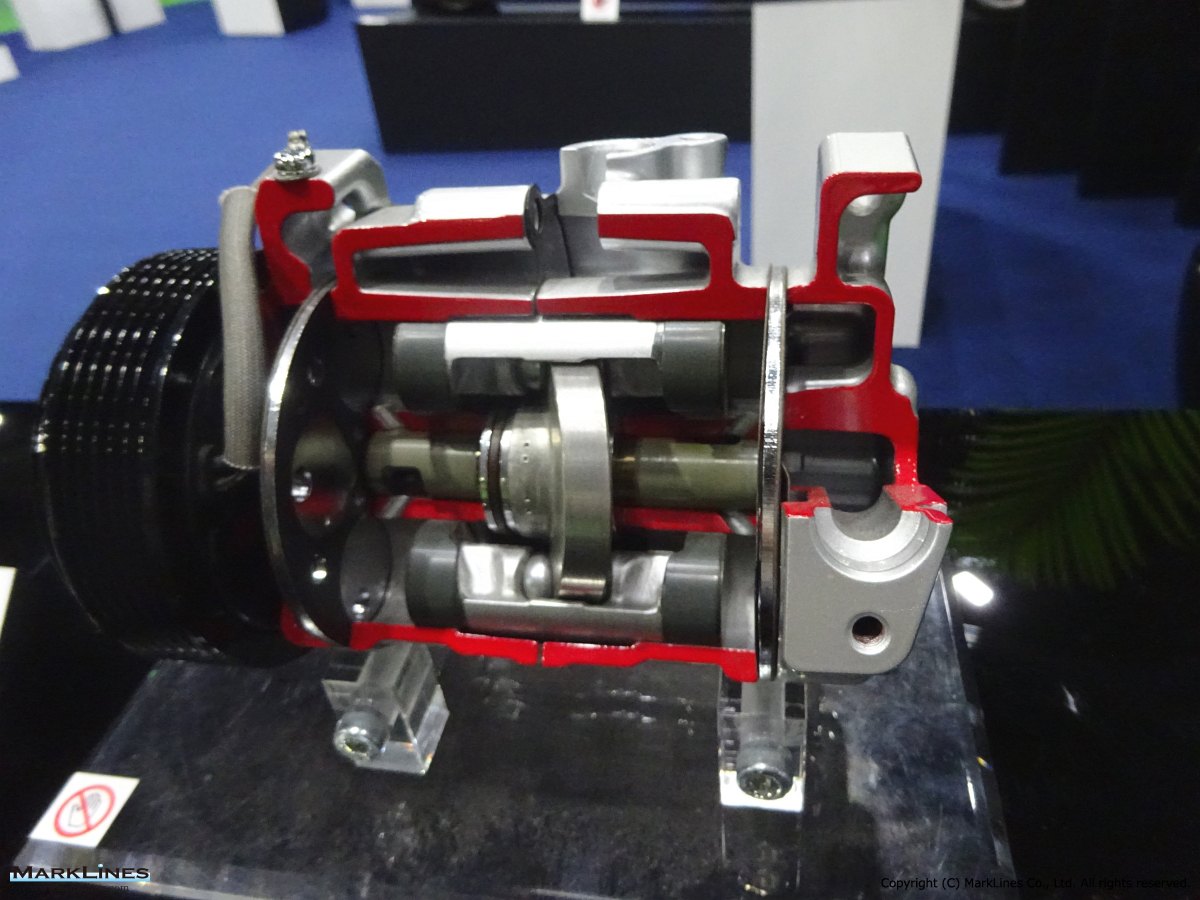
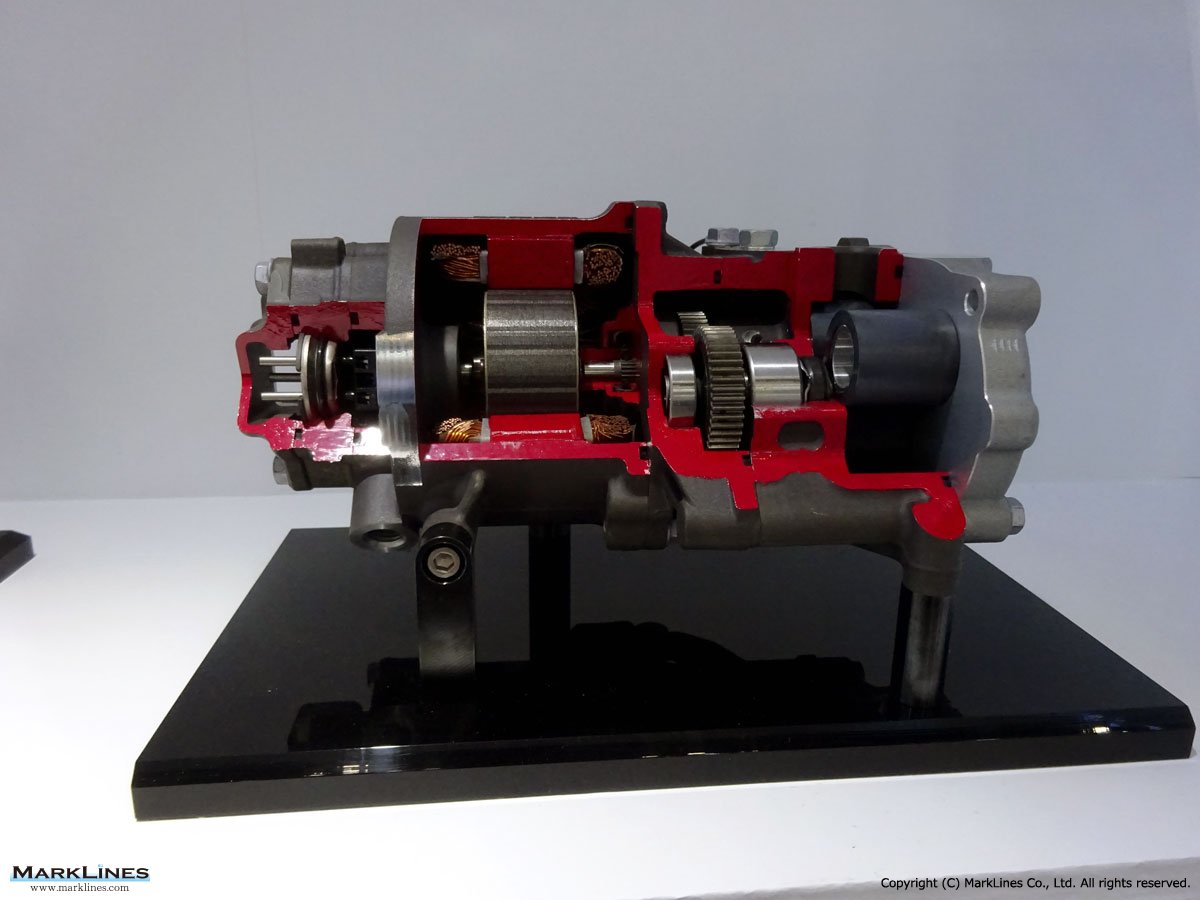
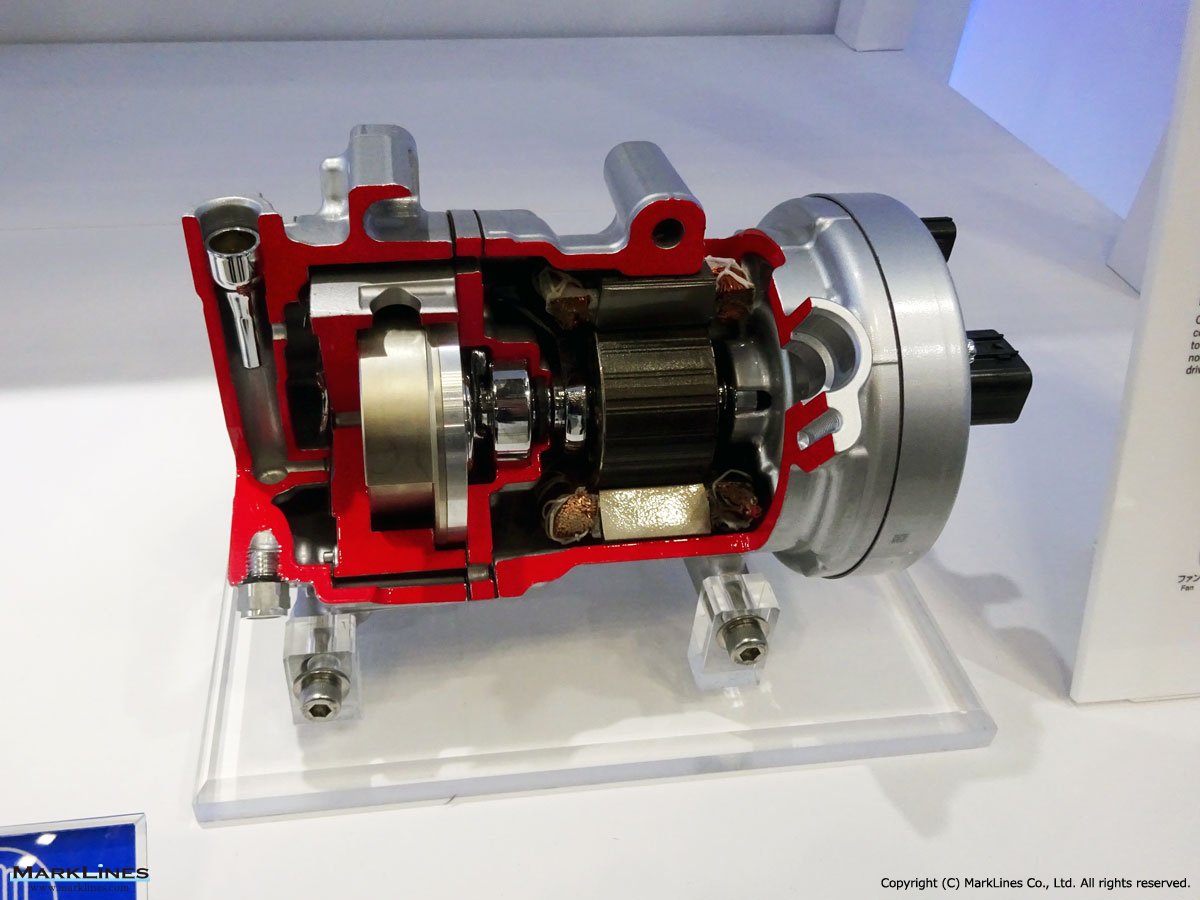
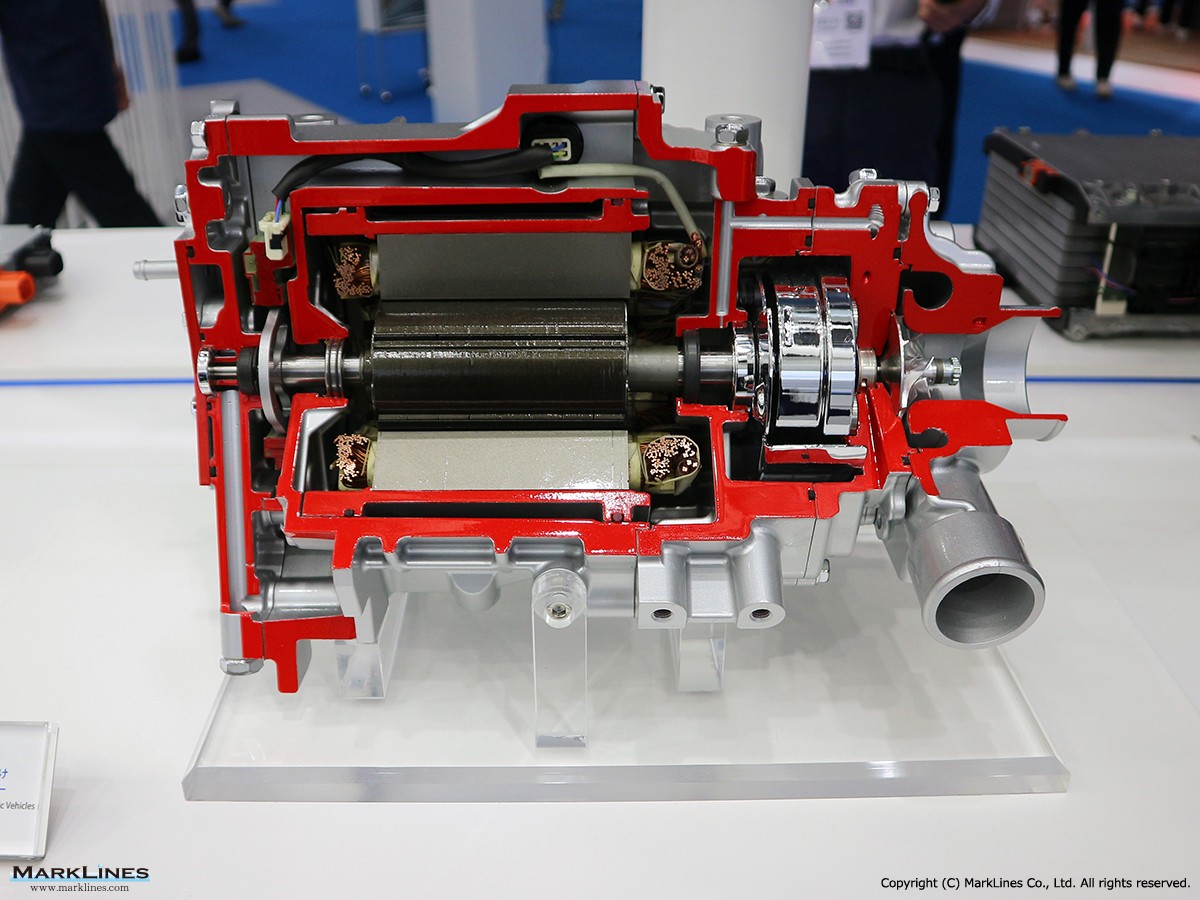
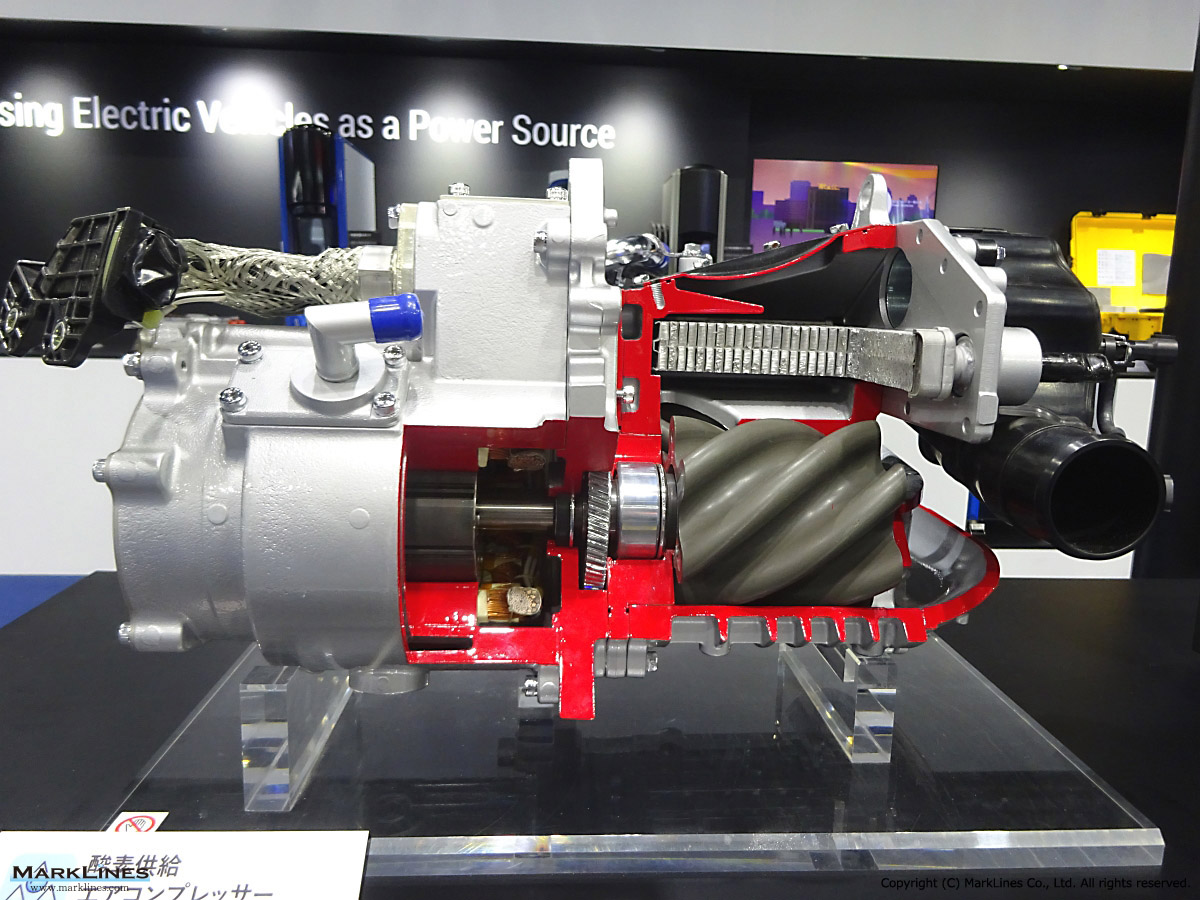
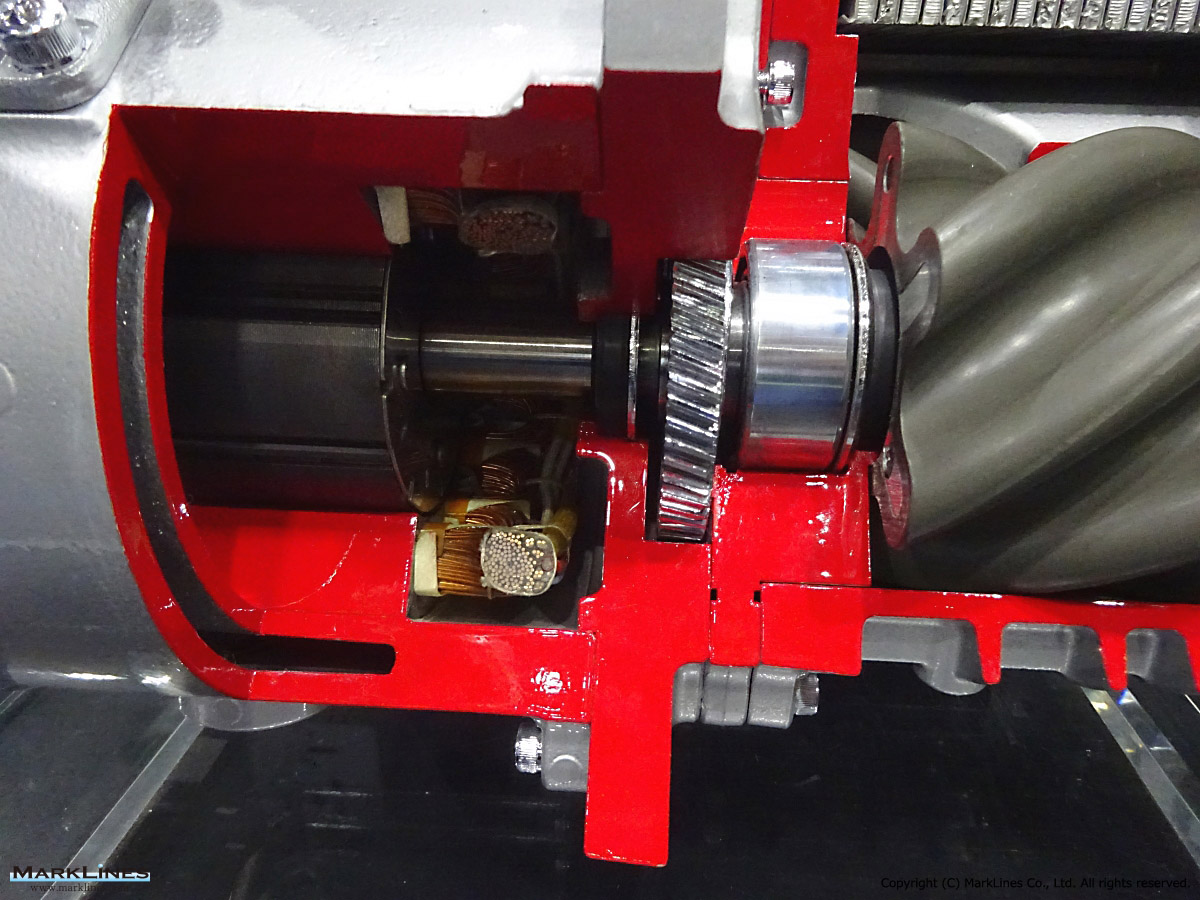
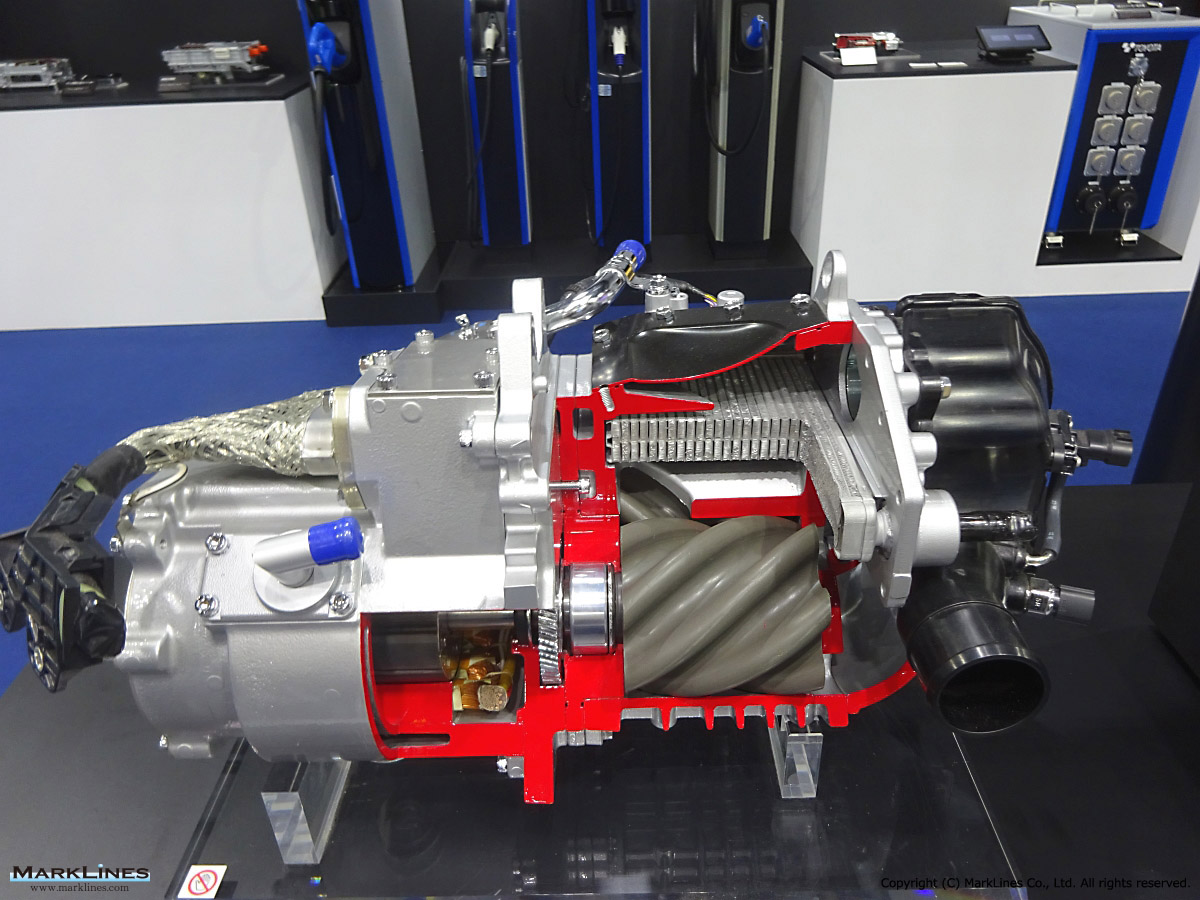
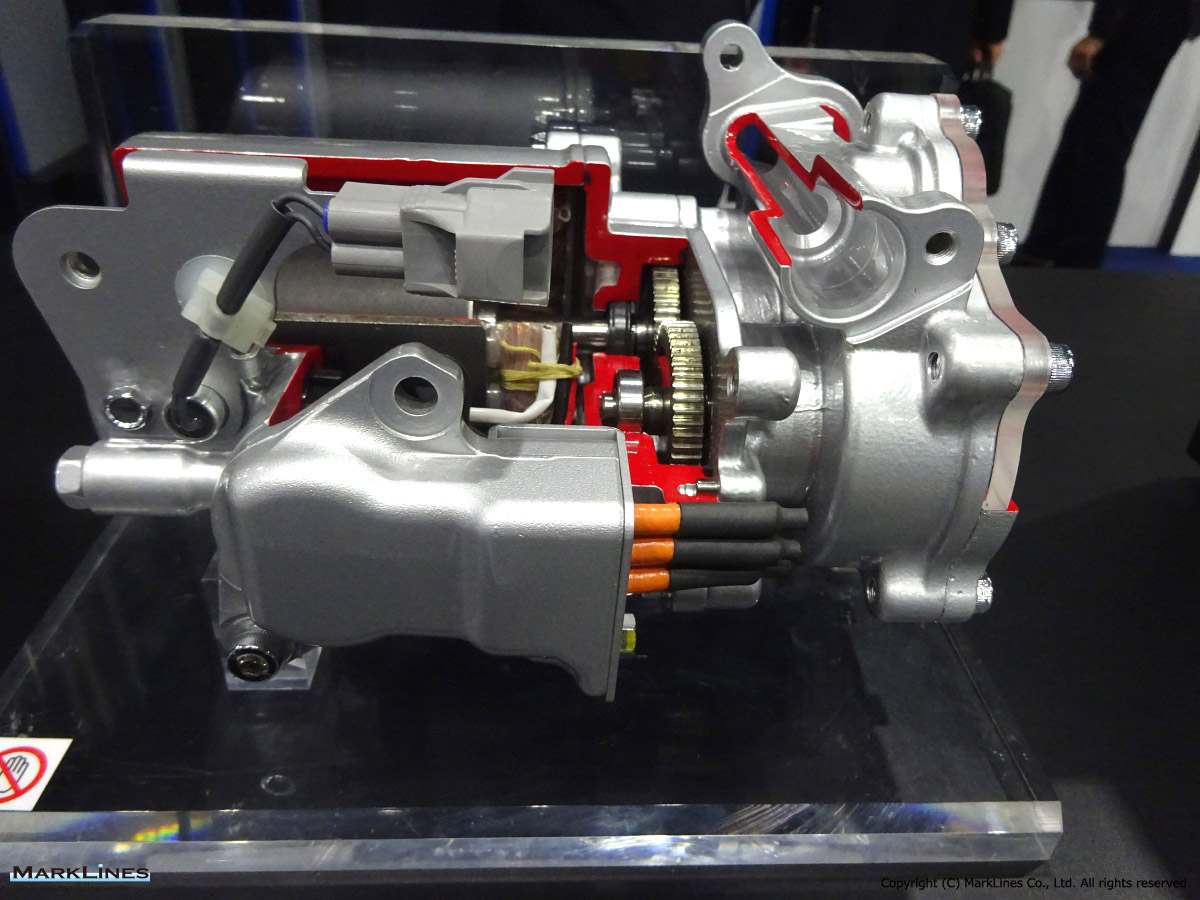
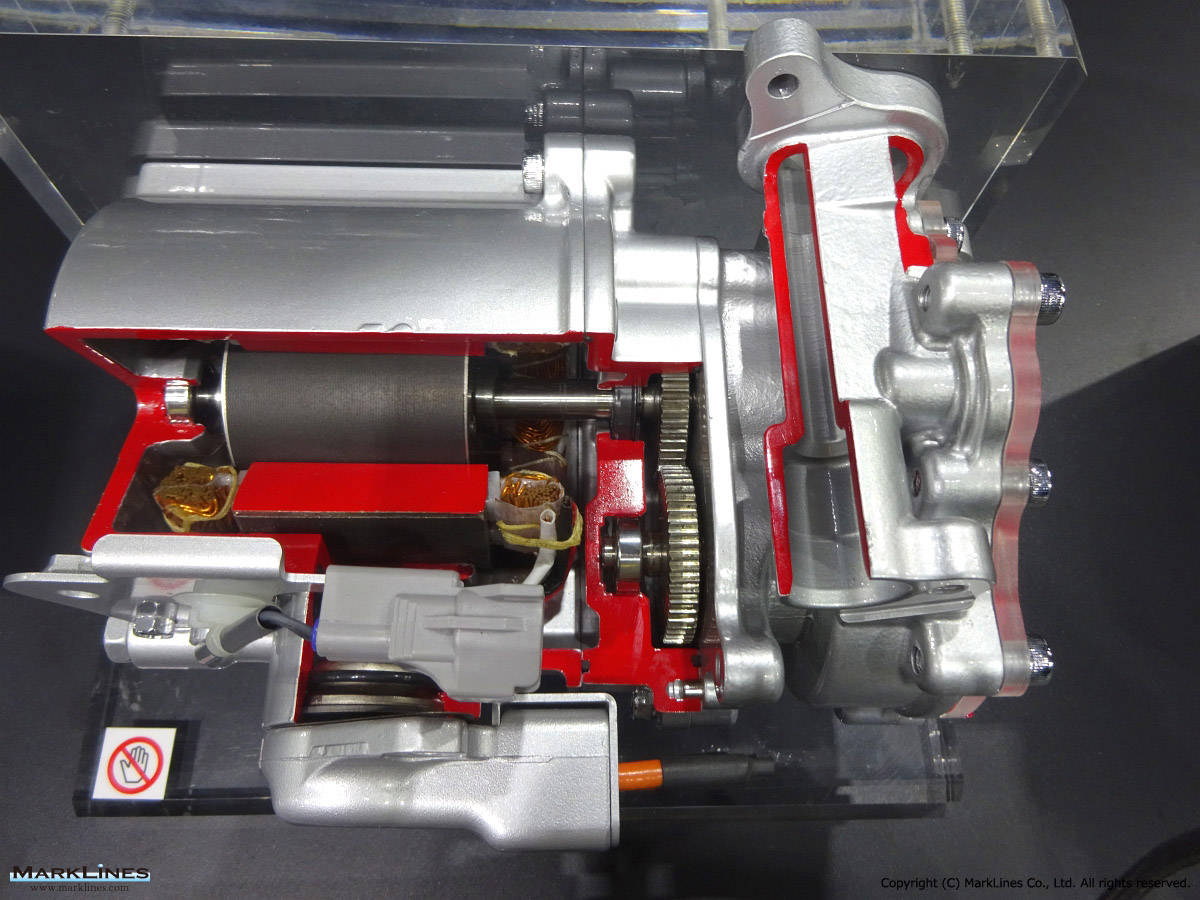
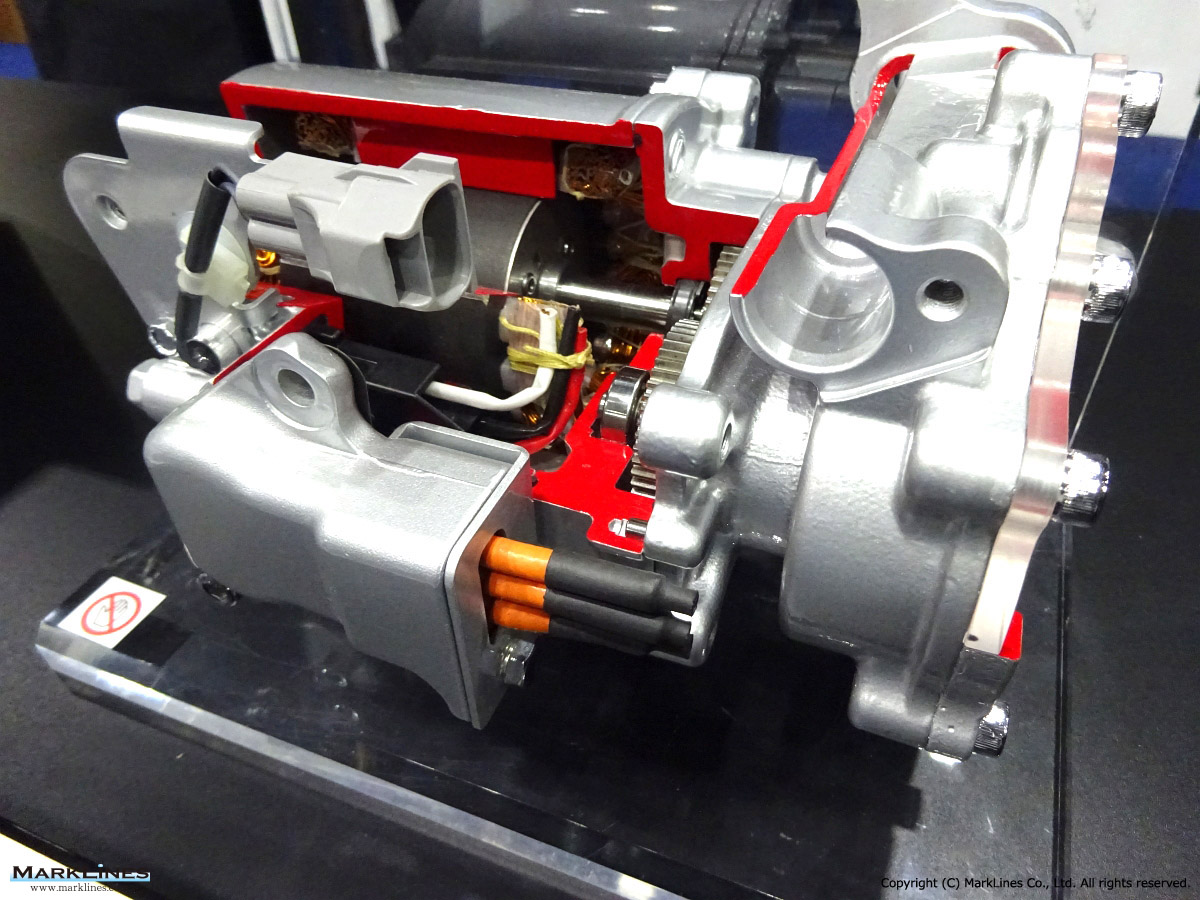
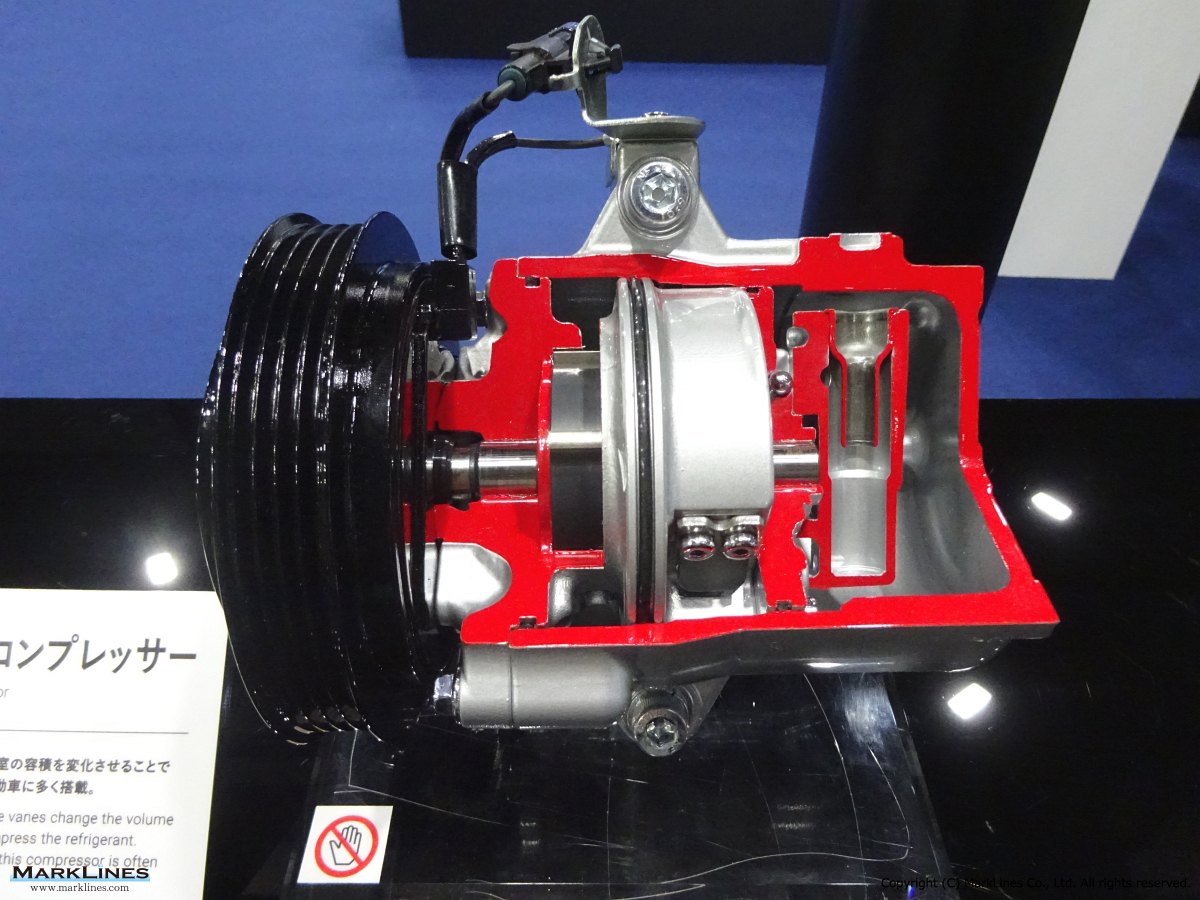
Car Air-Conditioning Compressors
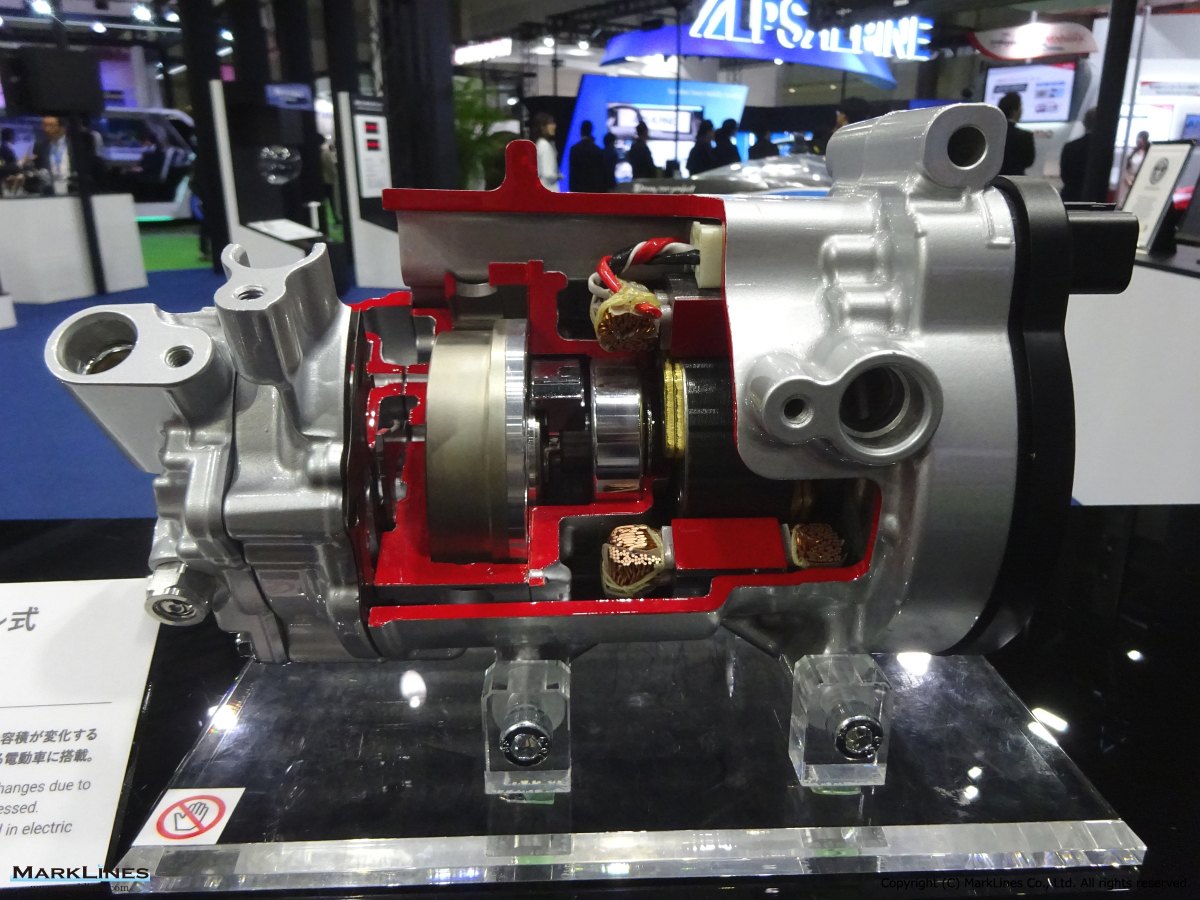
Electrically-Driven Compressors
Continuous Variable-Displacement Type Compressors
-One-way swash plate internally-controlled type
-One-way swash plate externally-controlled type
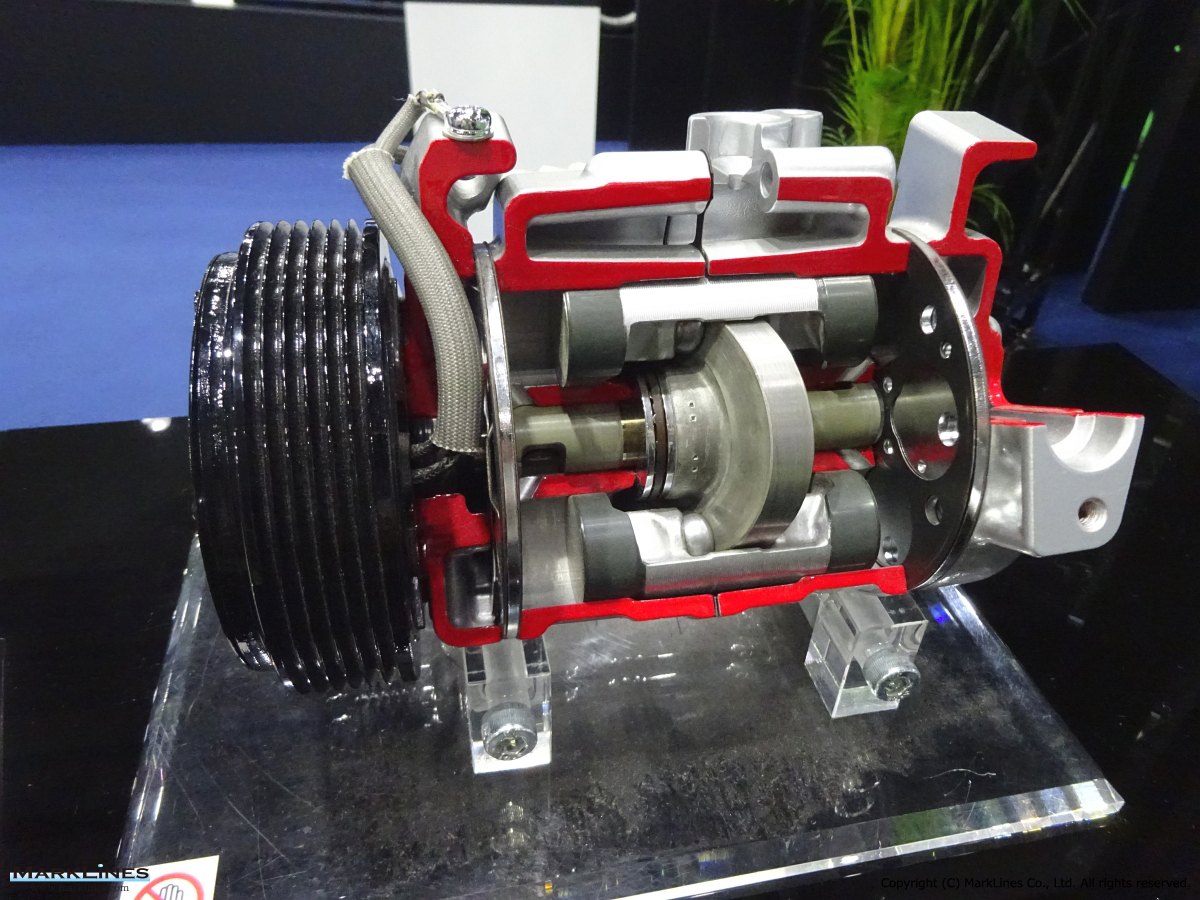
Fixed-Displacement Type Compressors
-Swash Plate Type
-Vane Type
-Scroll type
Aluminum Die-Cast Products
-Compressor cylinders
-Compressor housings
-Motor housings for electric compressors
-Compressor pistons (T6 treatment)
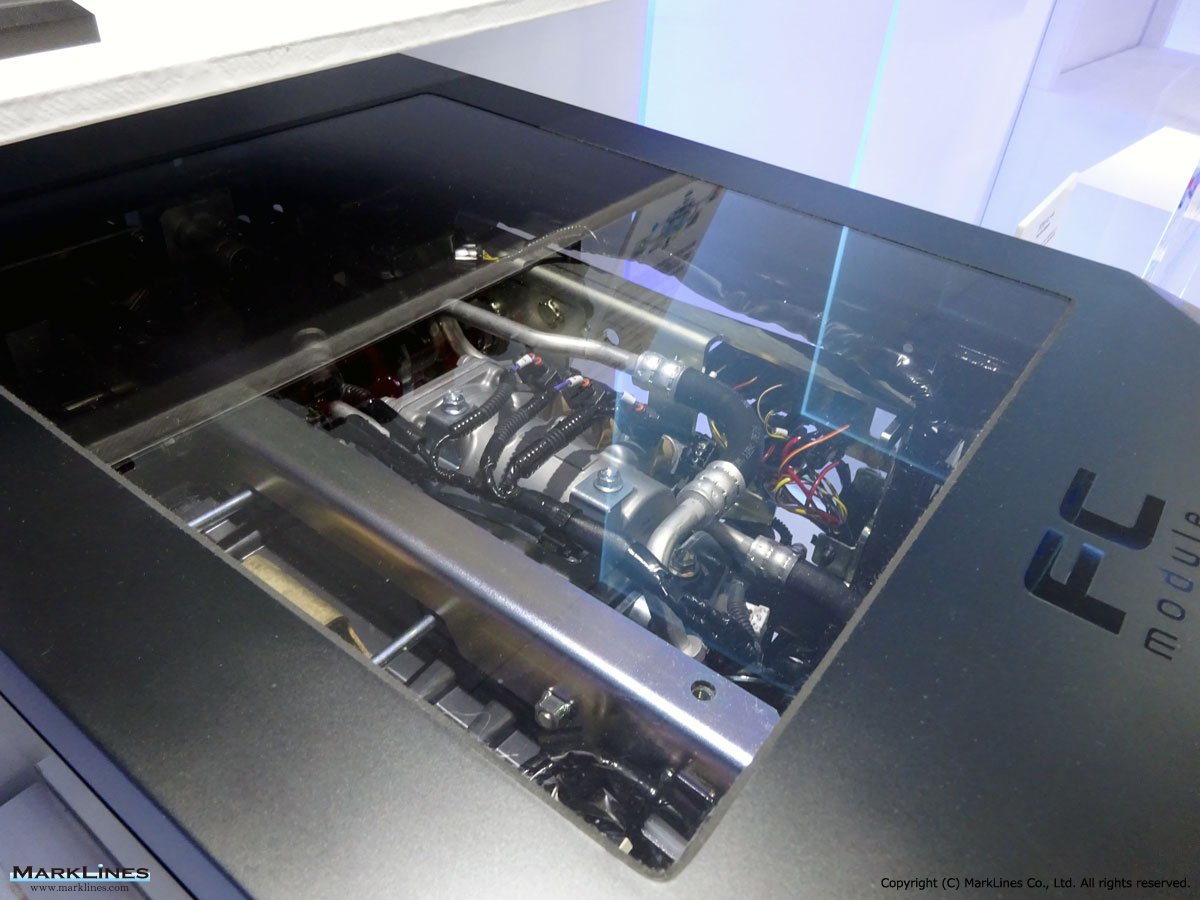
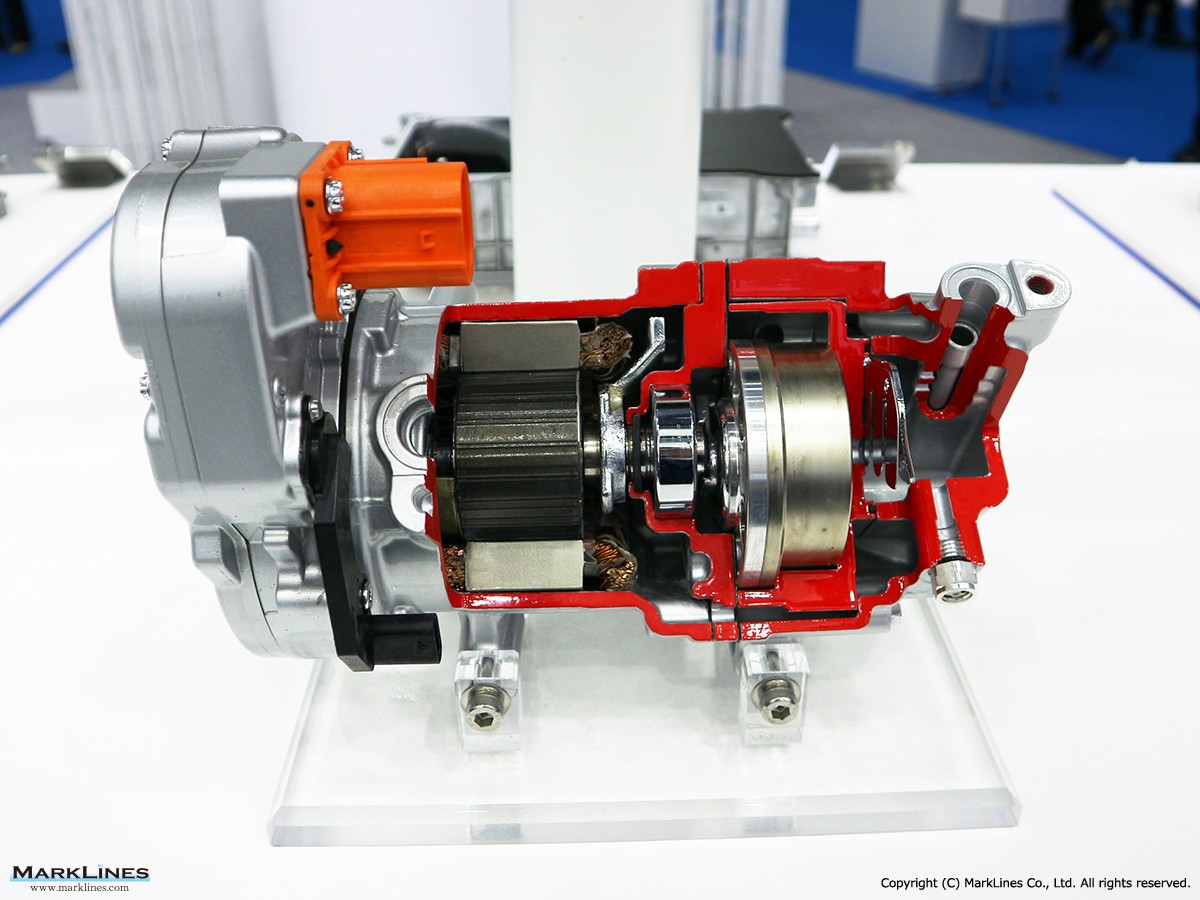
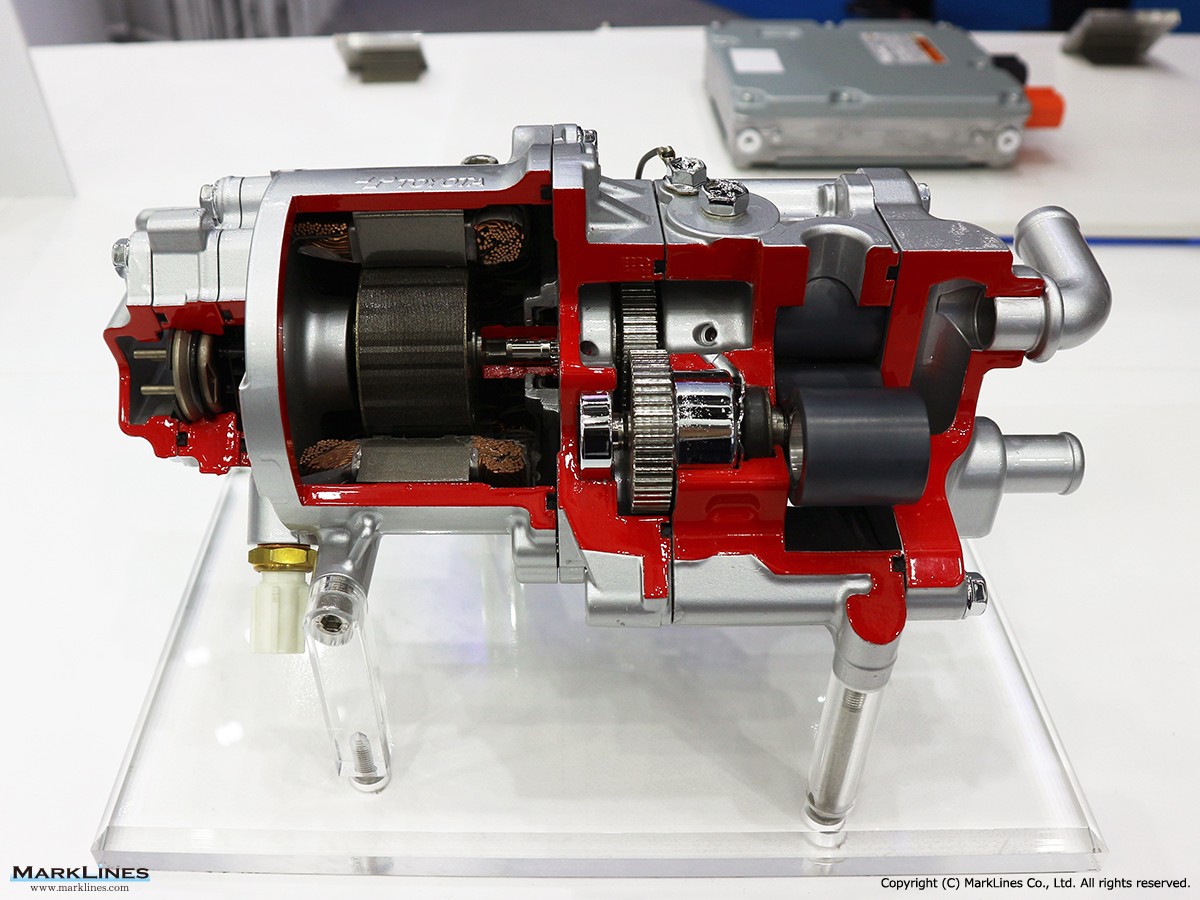
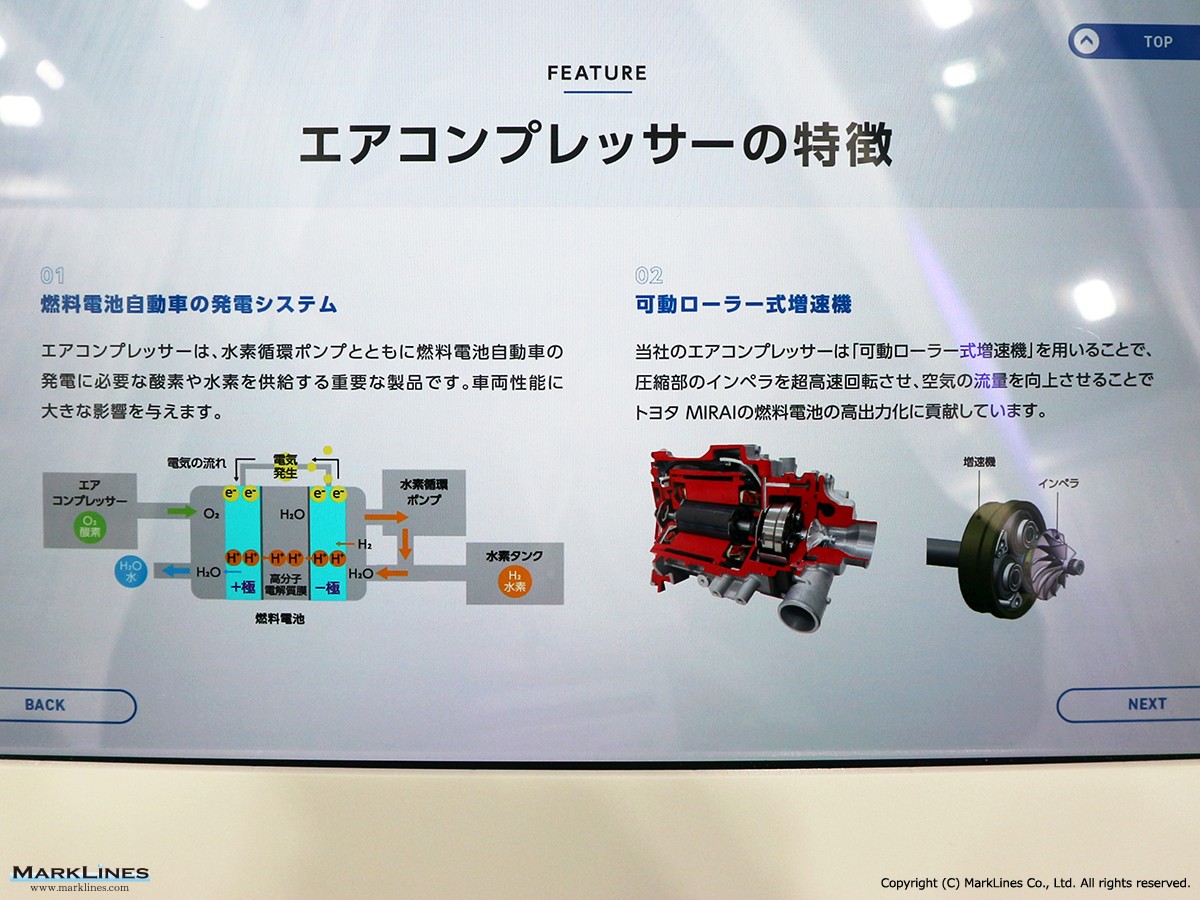
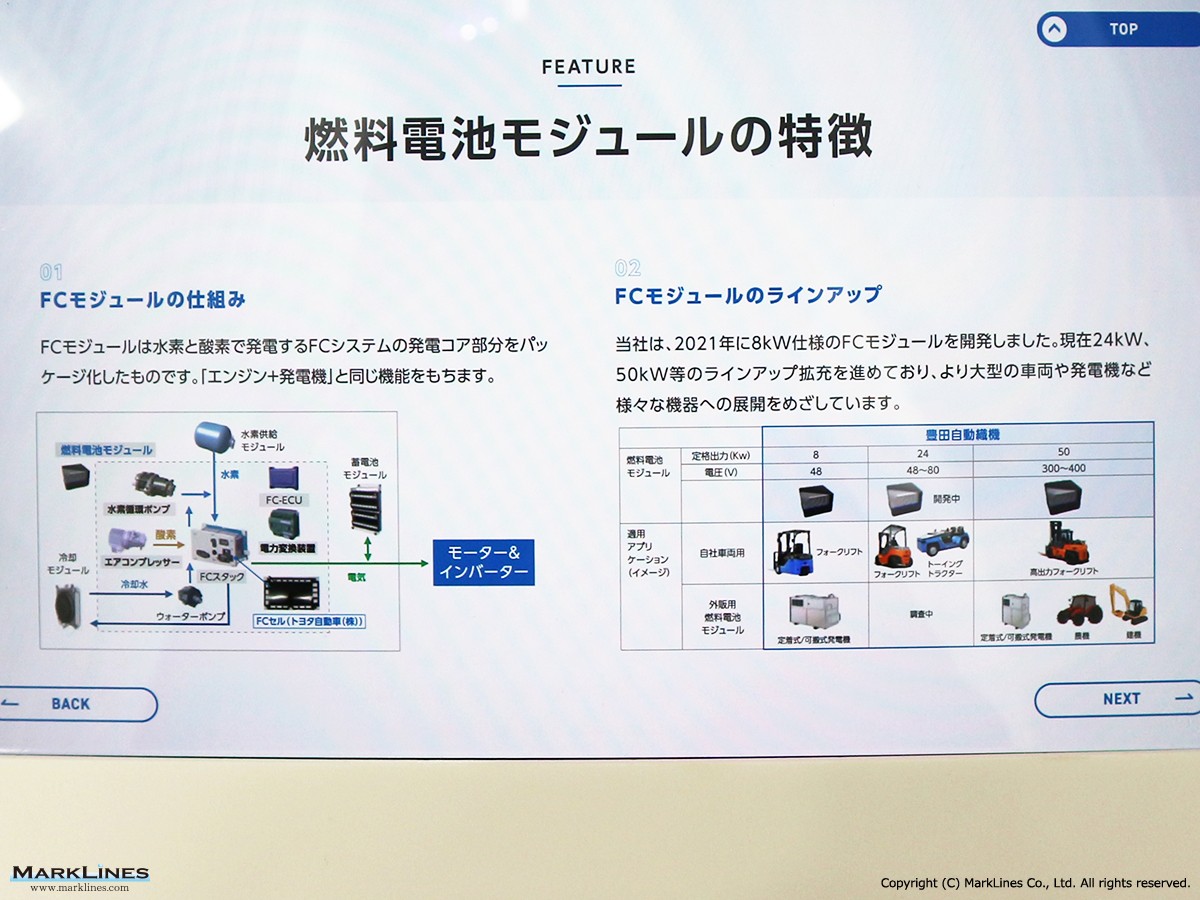
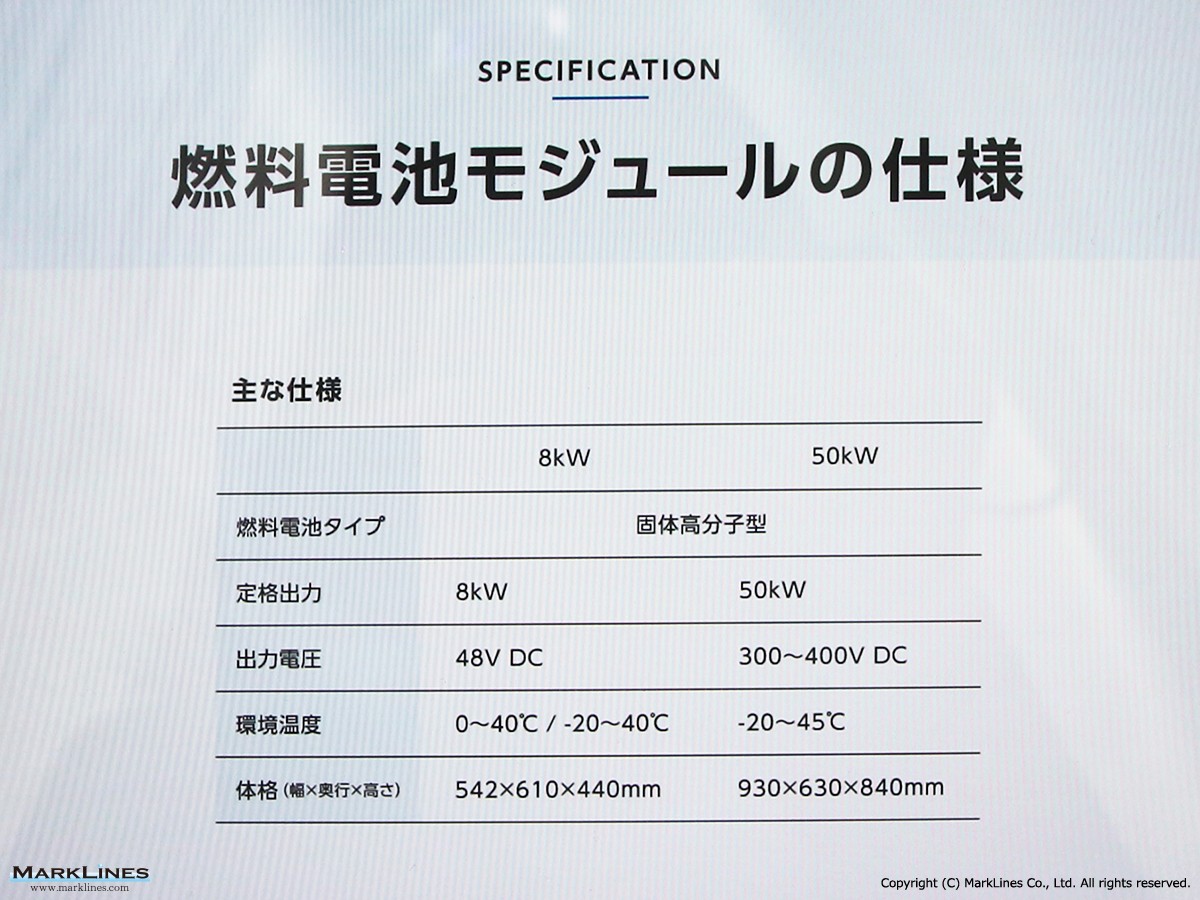
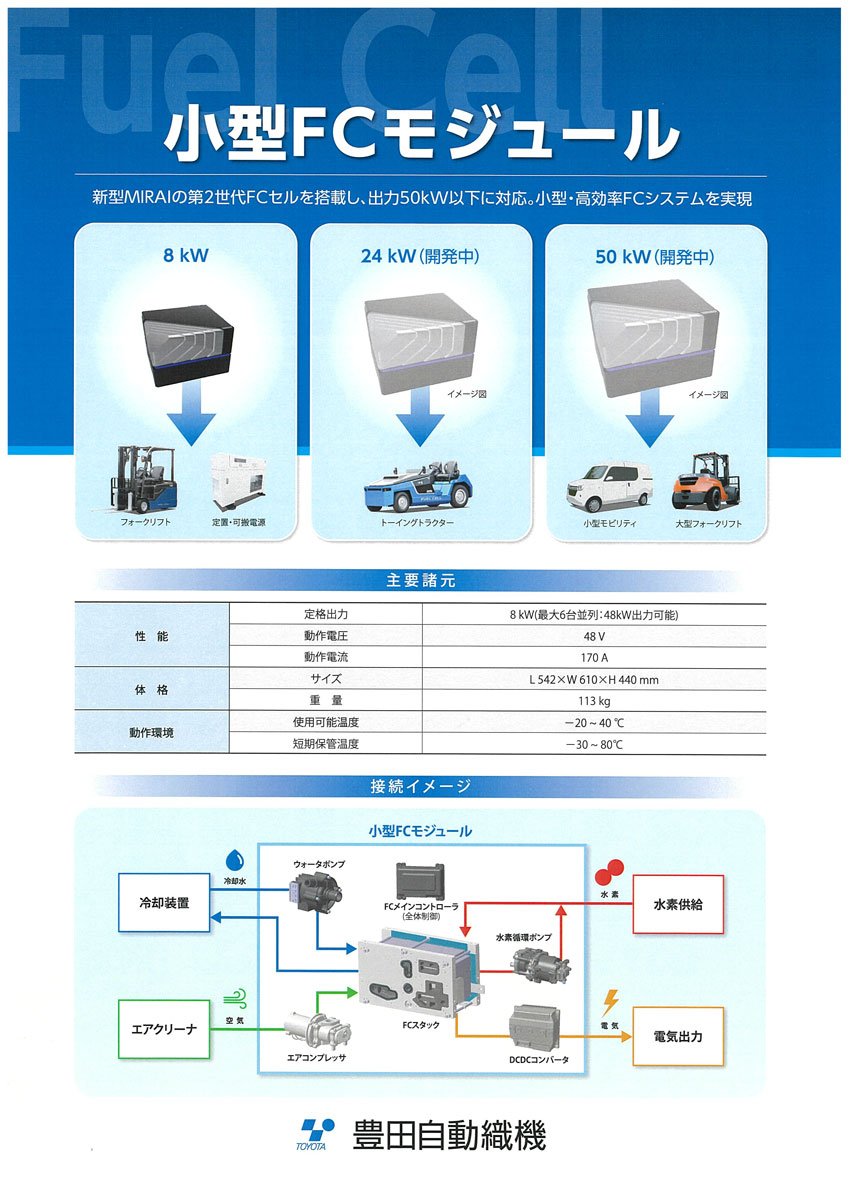
FCEV Products
-Air compressors for FCV
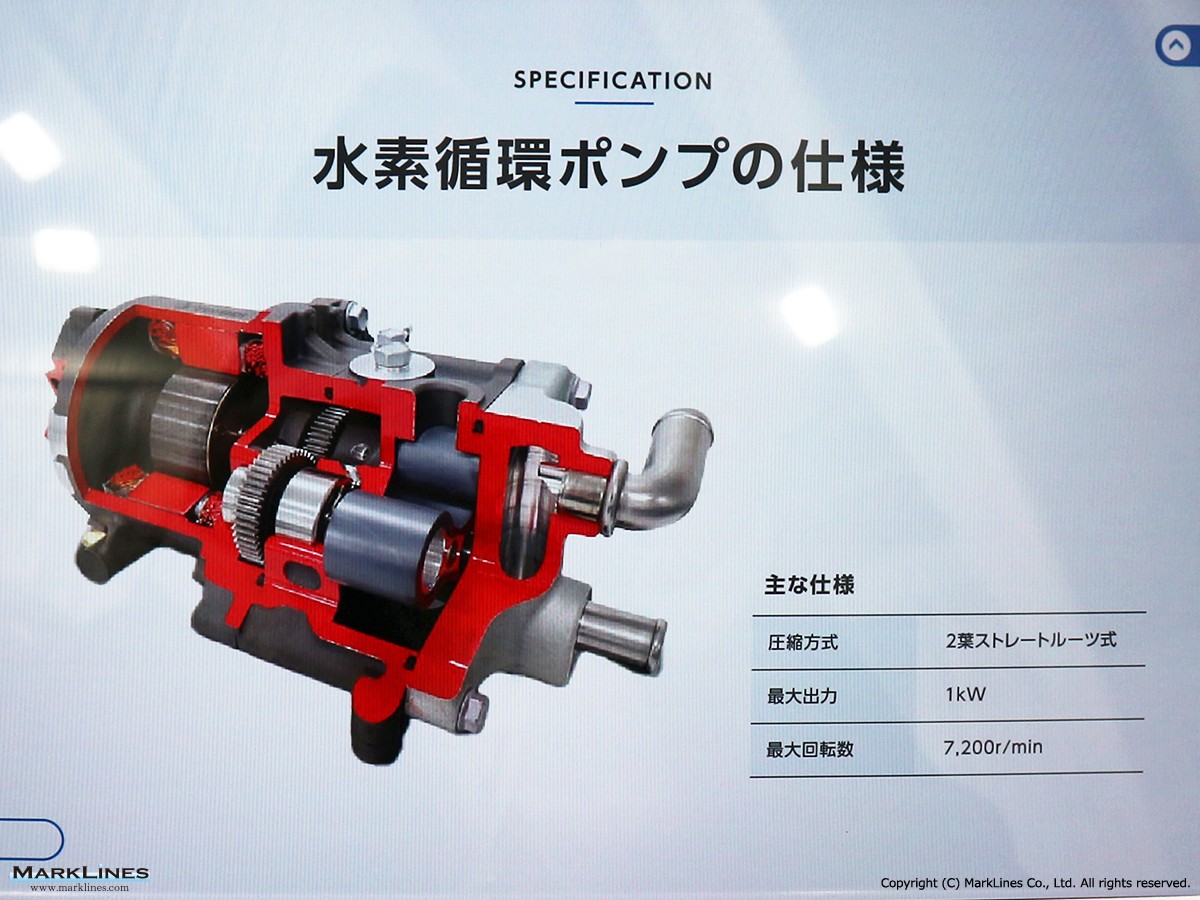
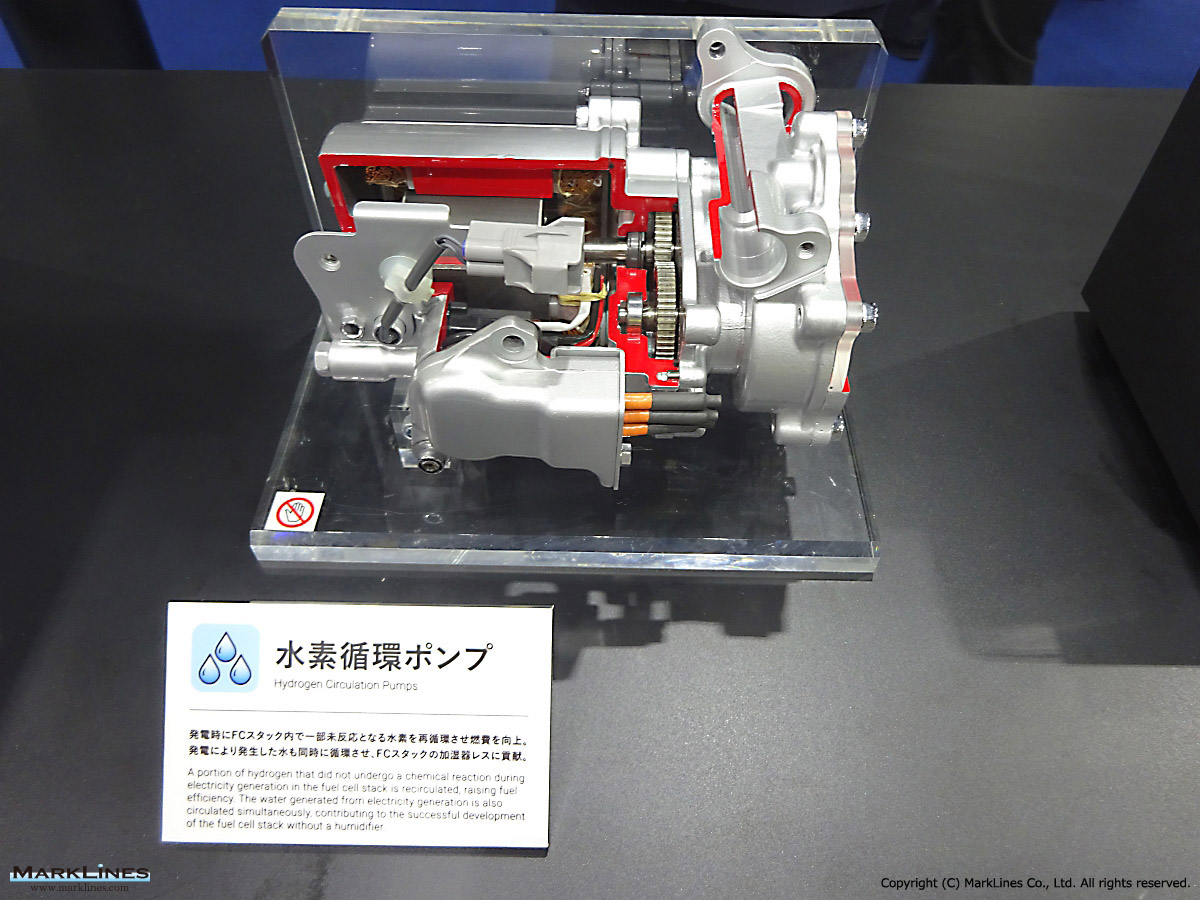
-Hydrogen circulation pumps for FCV
-Viscous Type Power Heaters
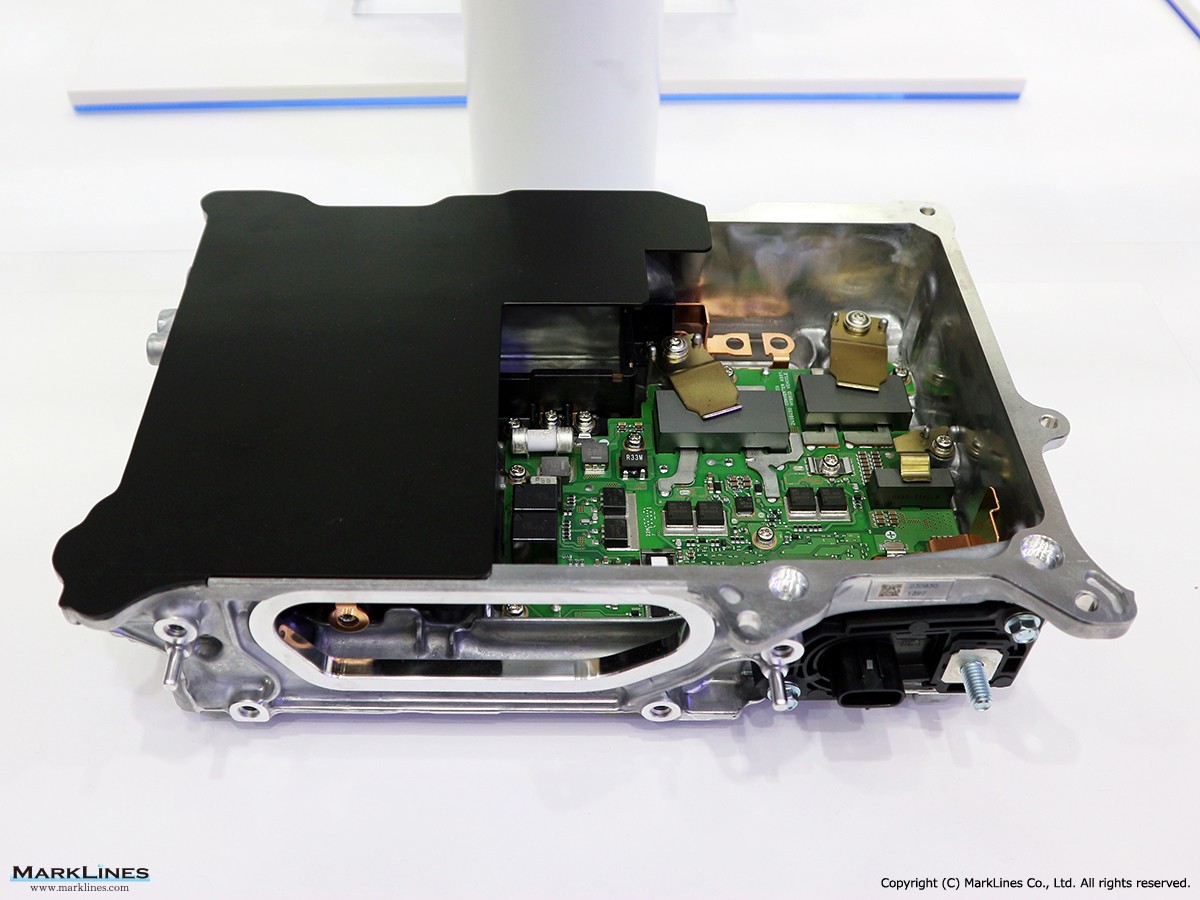
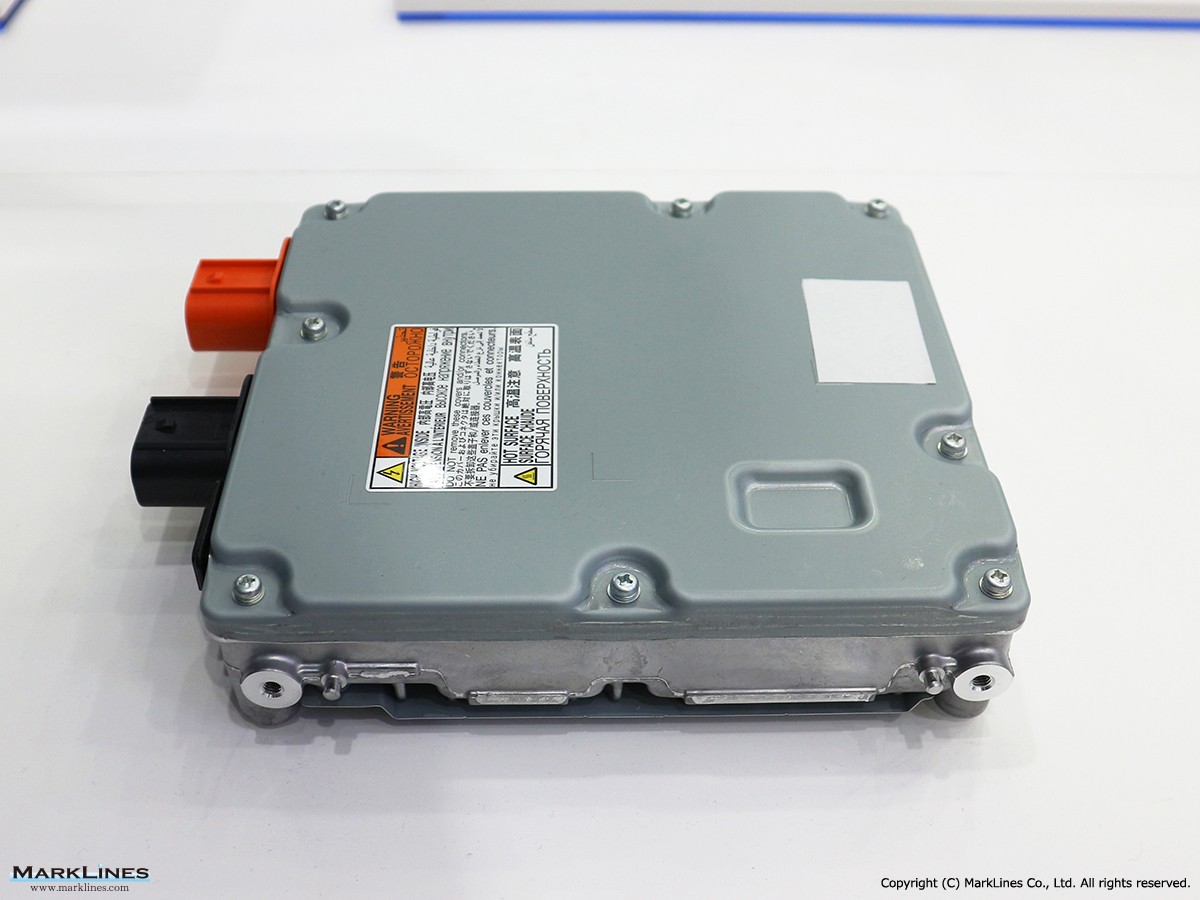
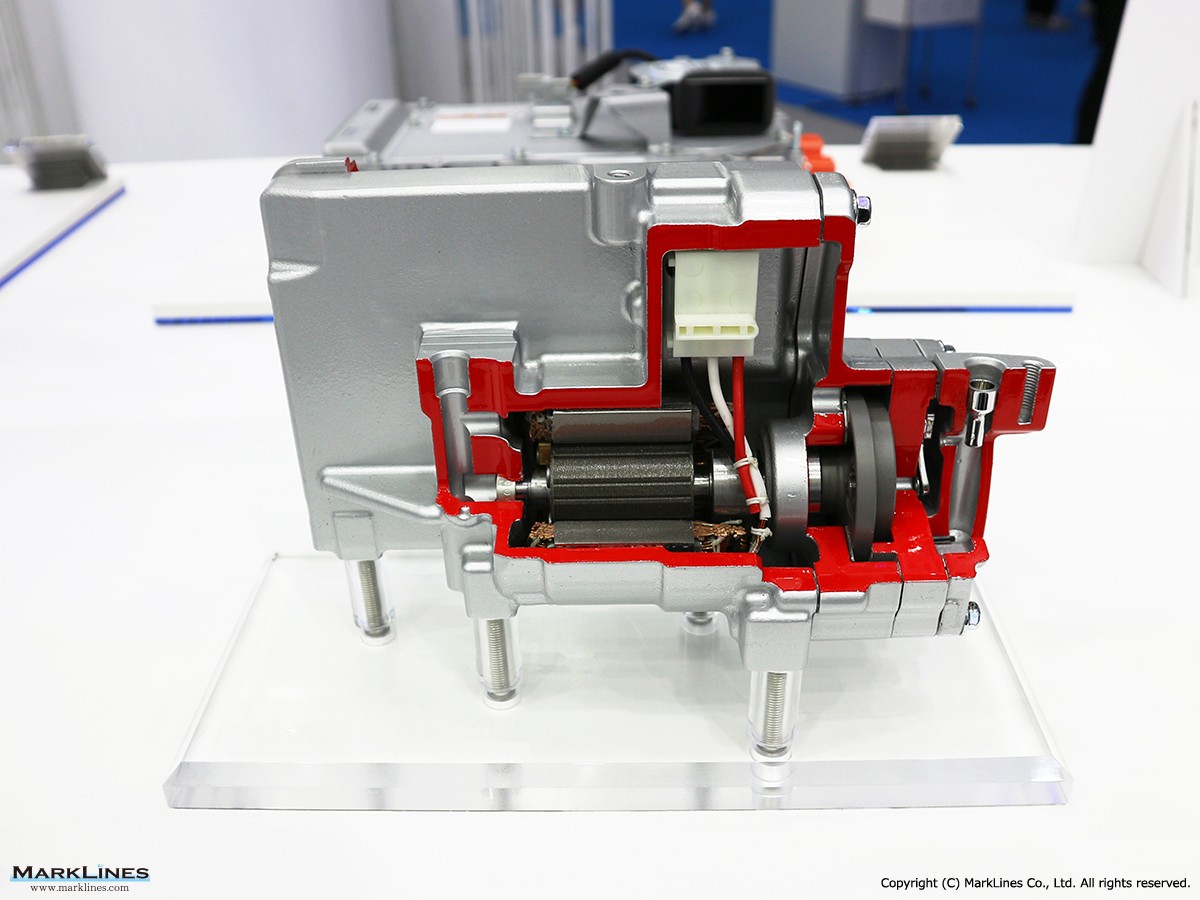
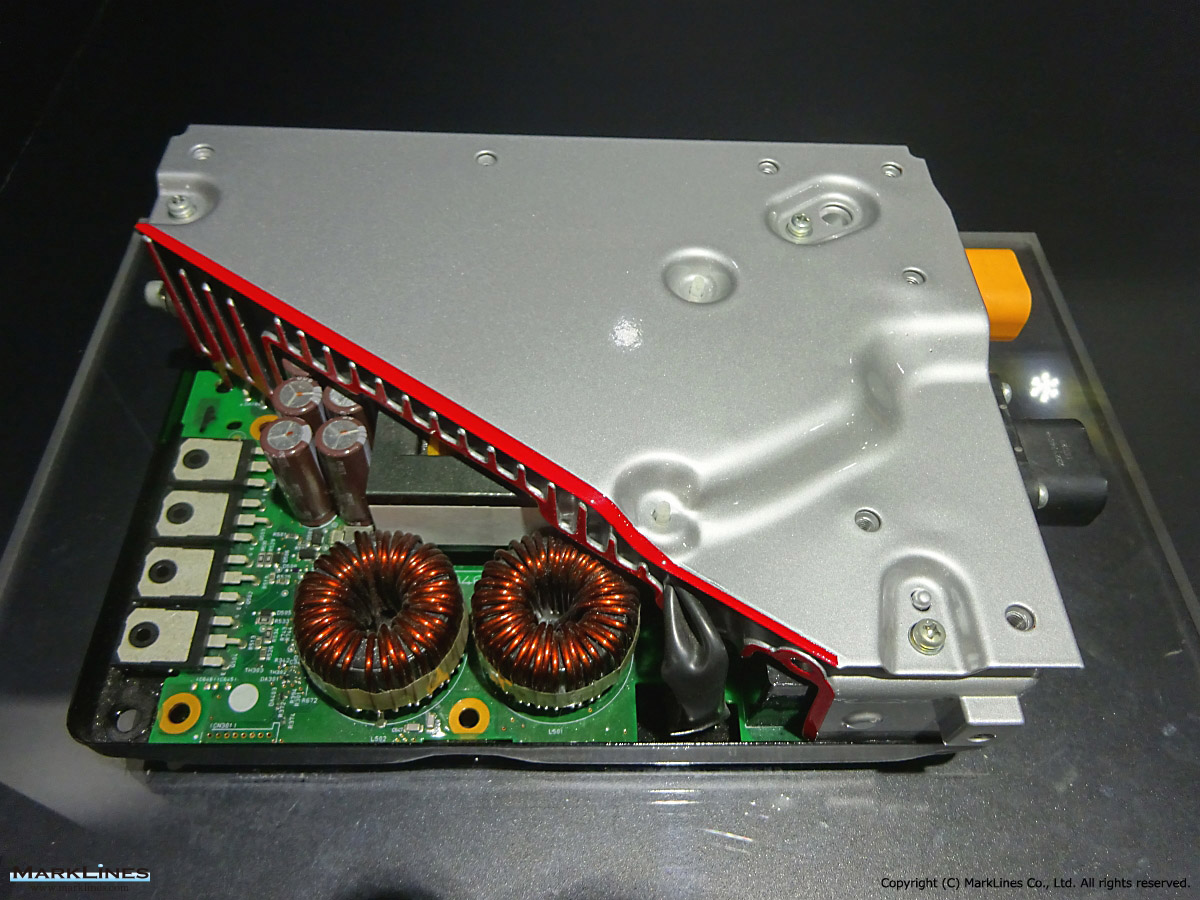
Car Electronics
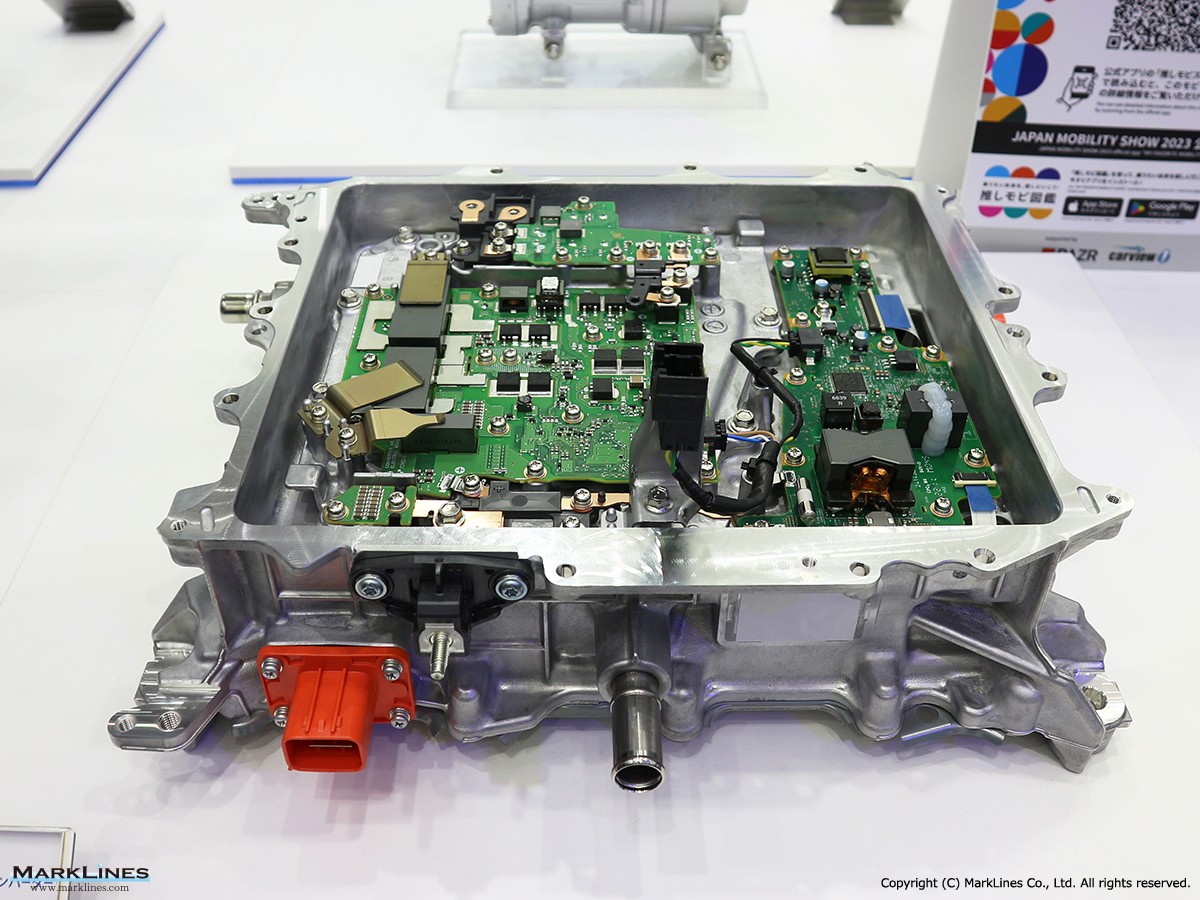
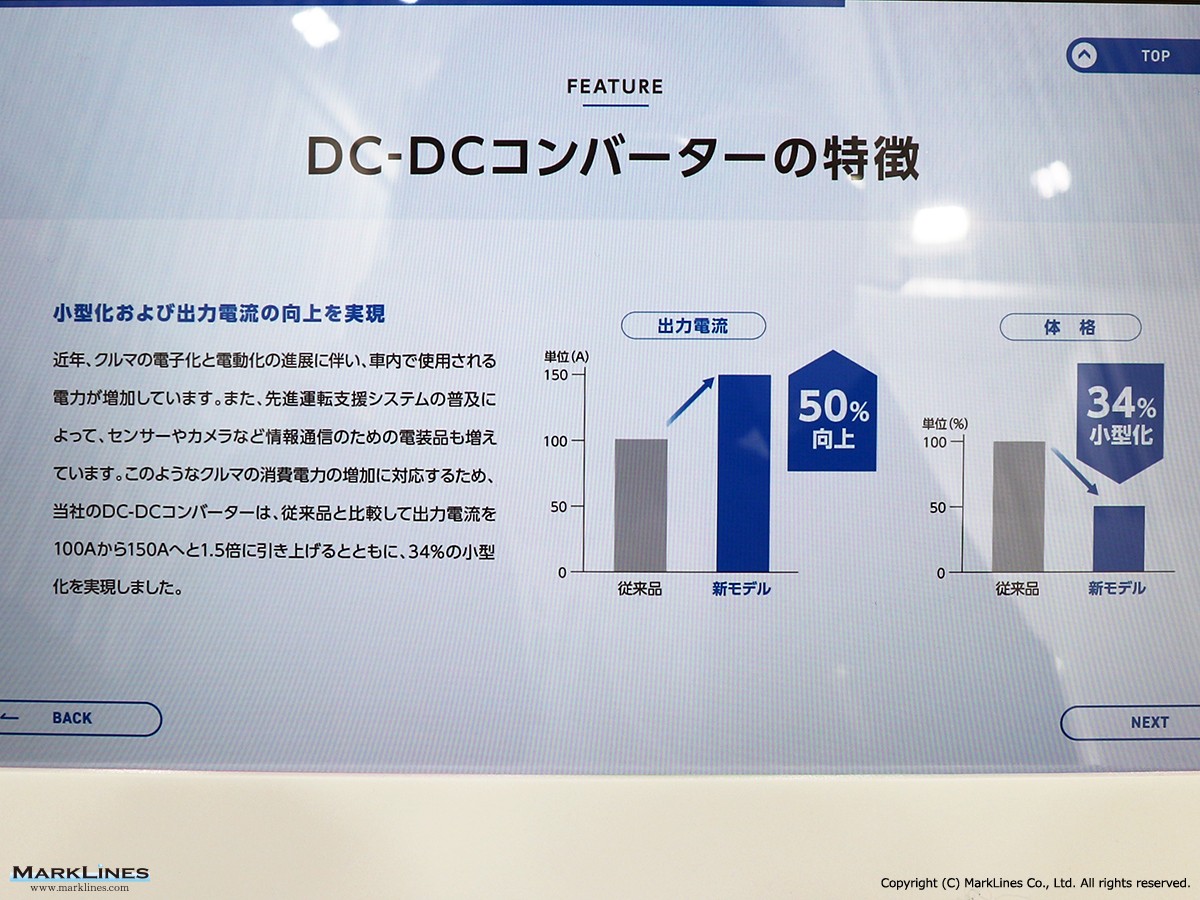
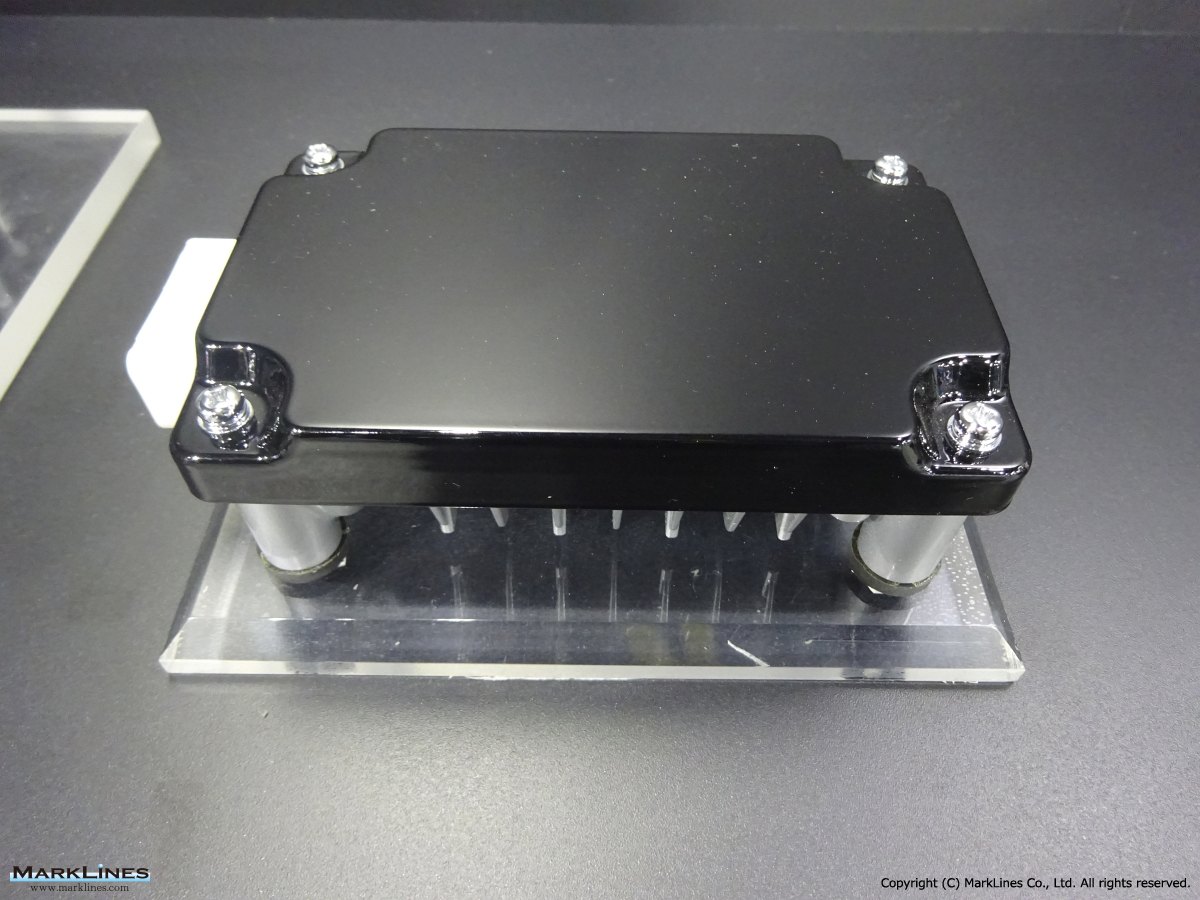
DC-DC converter (Converters)
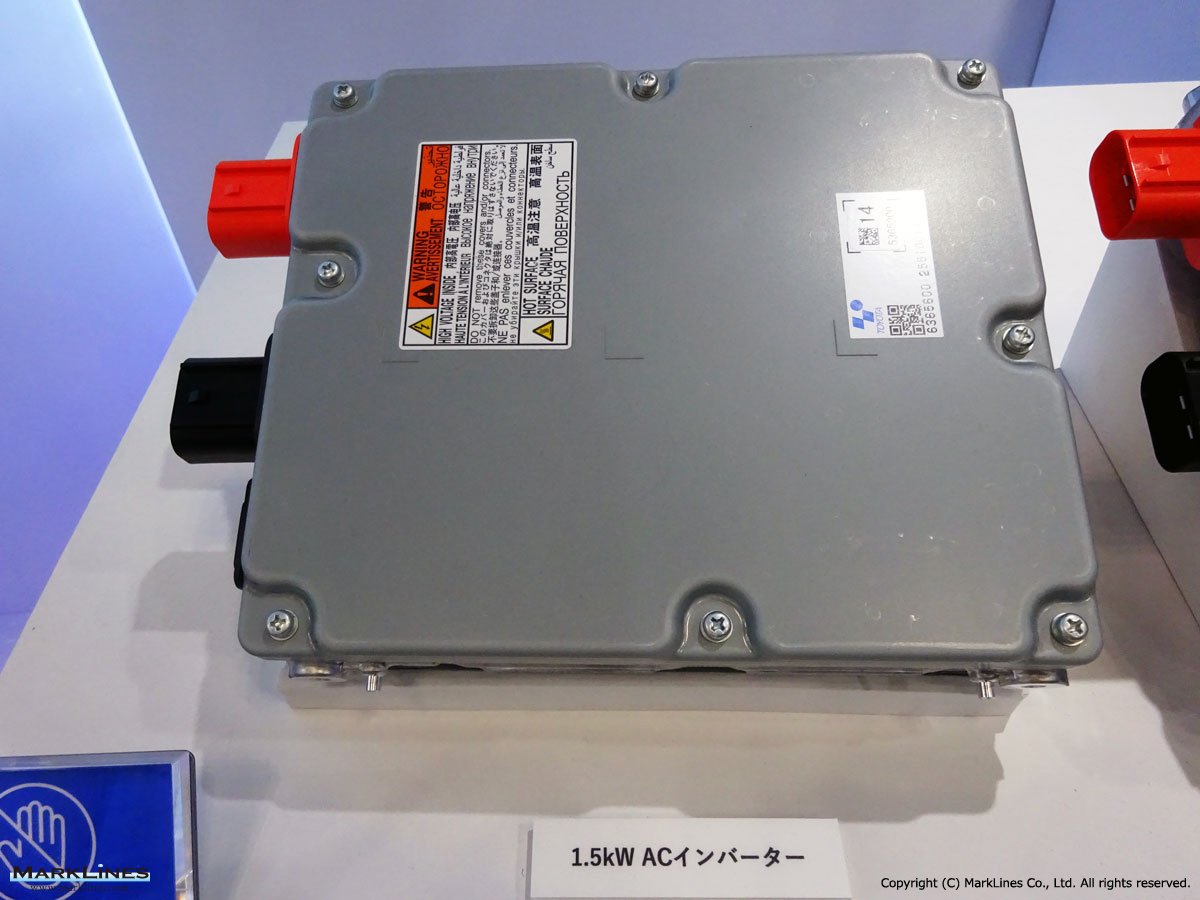
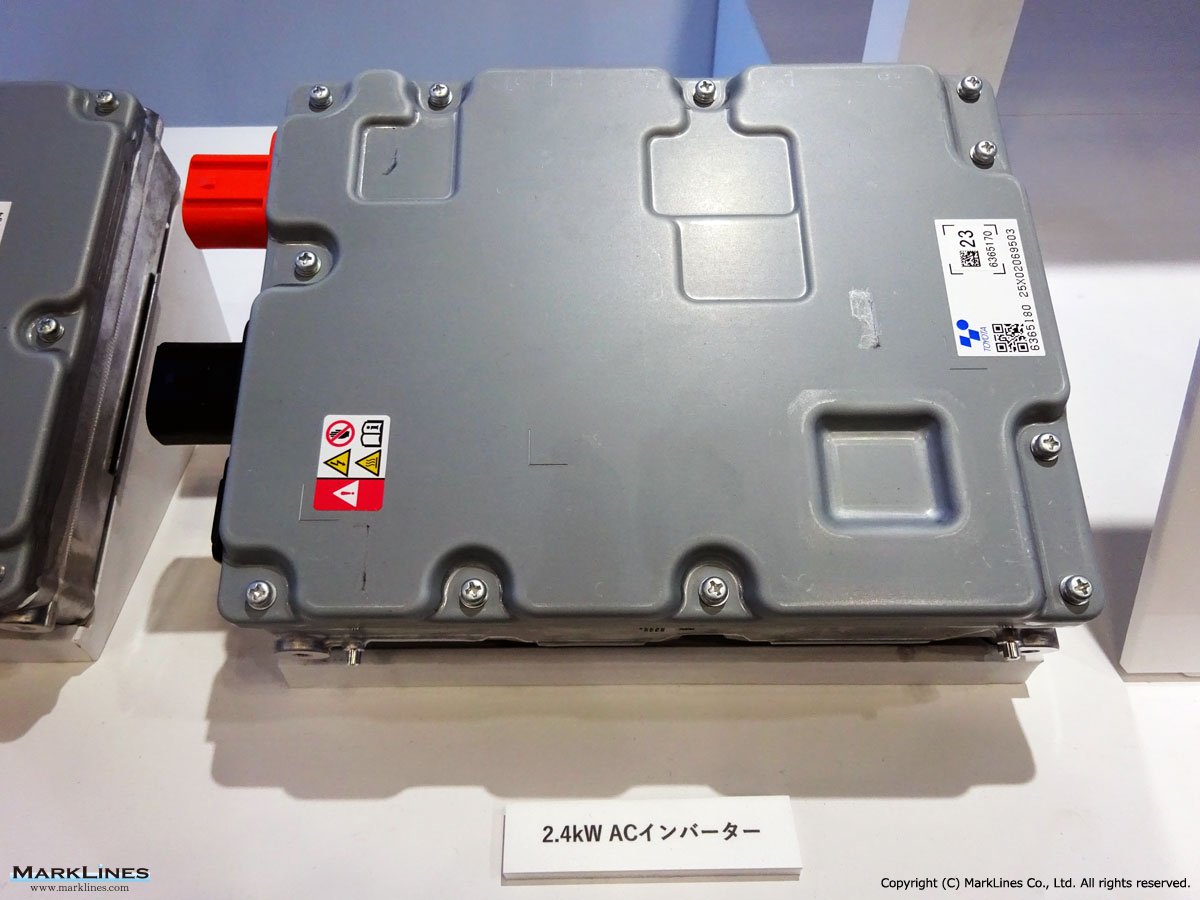
AC Inverters
-2400W DC-AC inverters
-1.5kW DC-AC inverters
-400W DC-AC inverters
-150W DC-AC inverters
-100W DC-AC inverters
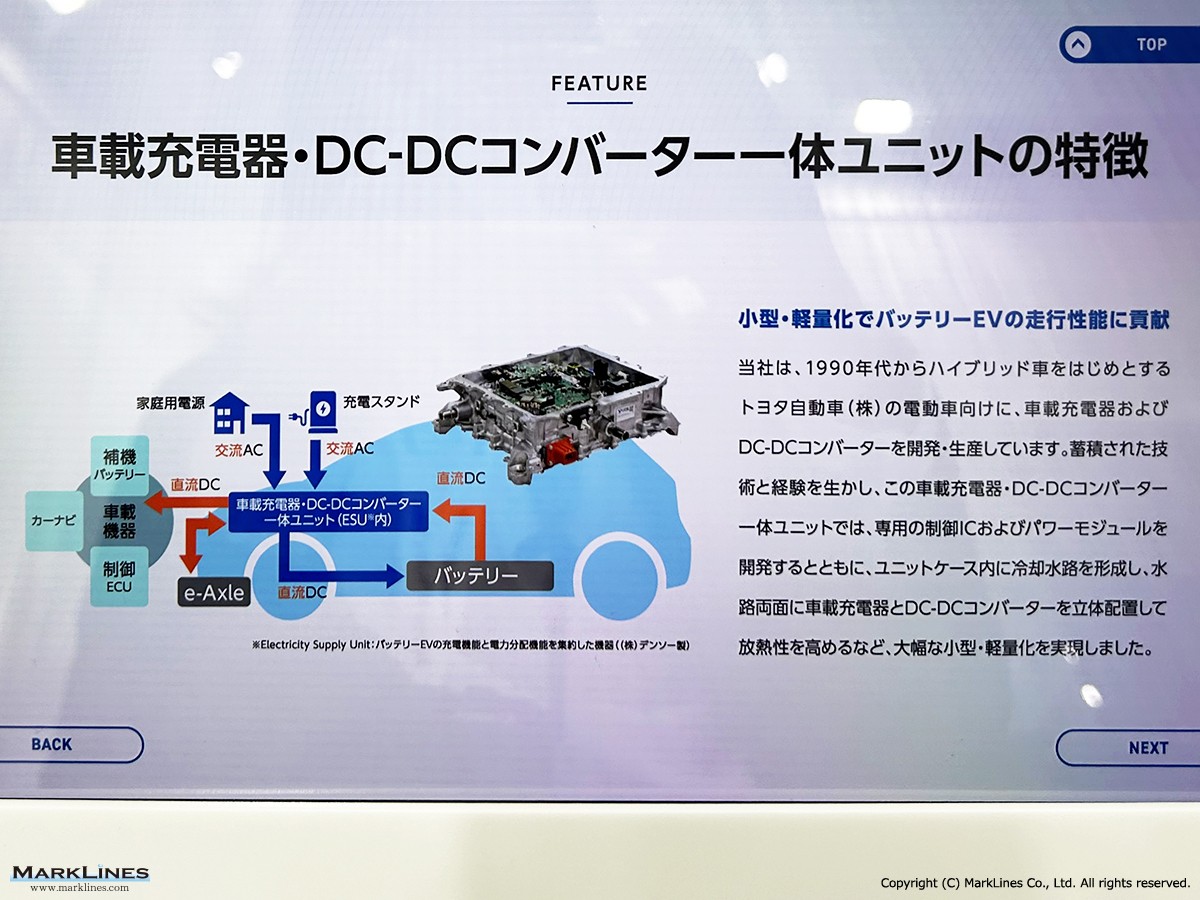
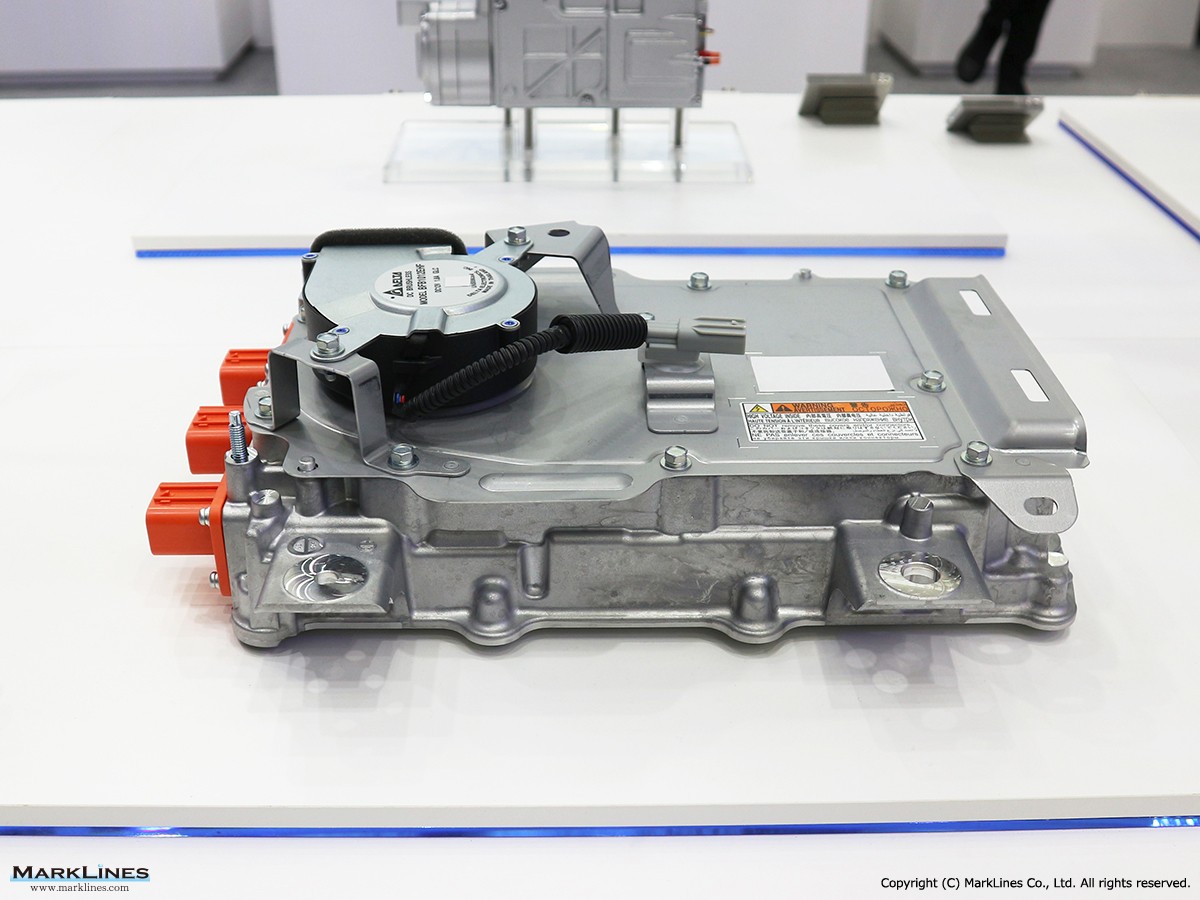
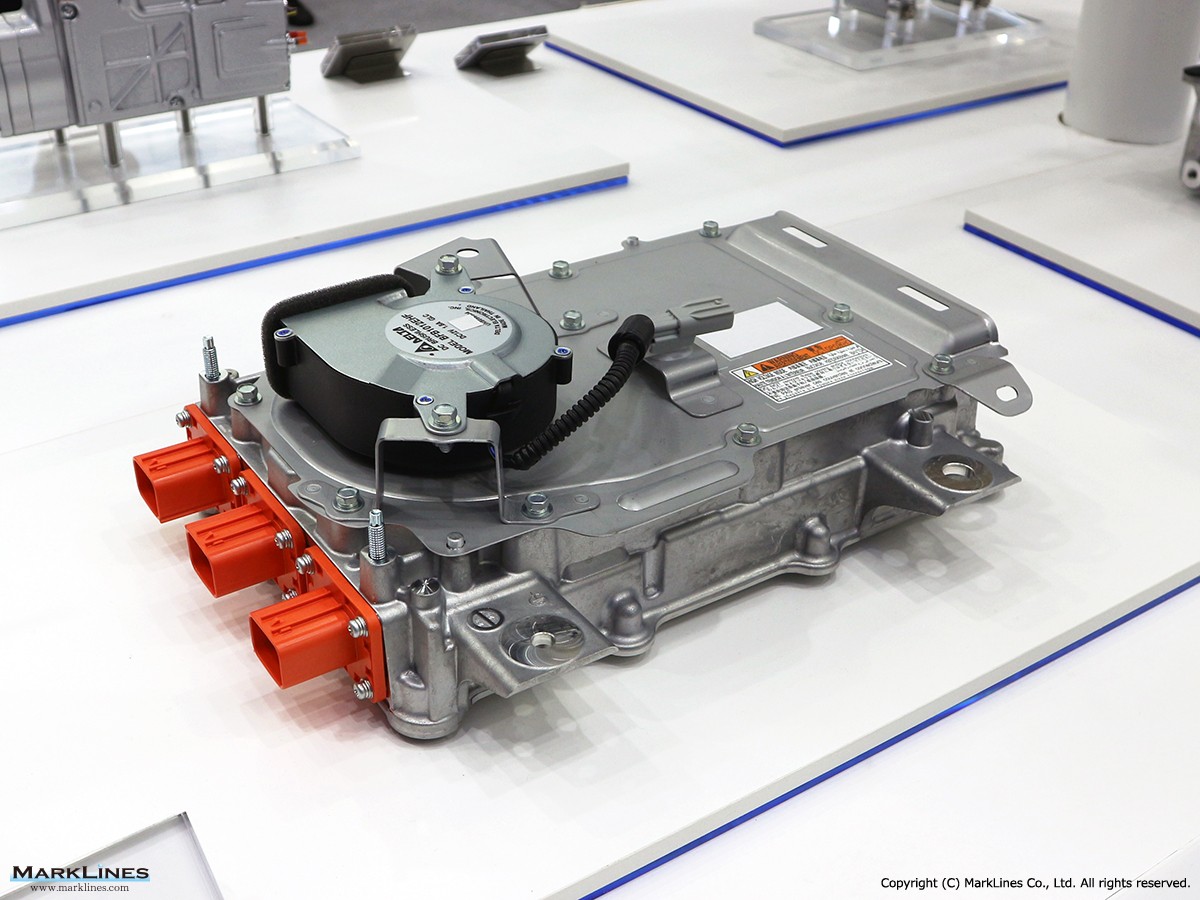
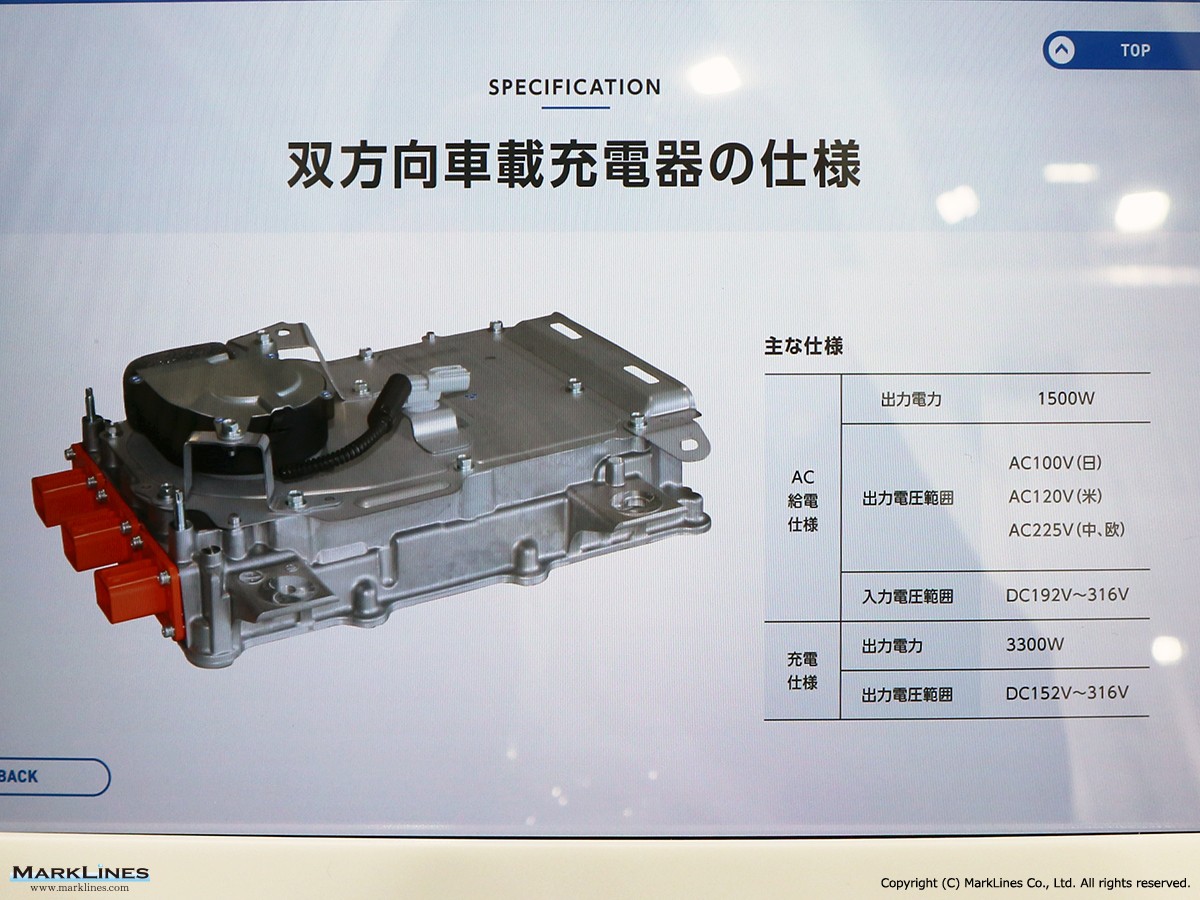
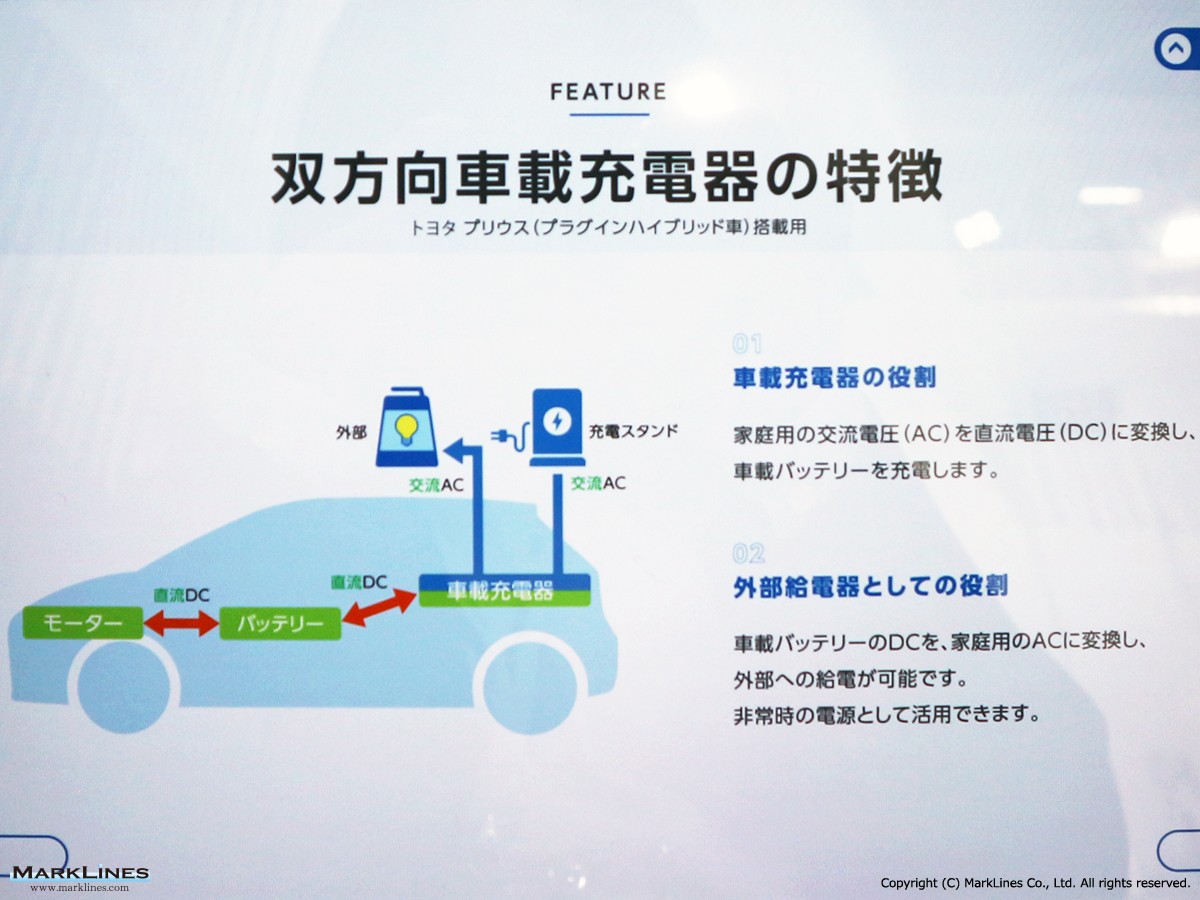
On-Board Chargers
-On-Board Chargers
-Integrated On-Board Charger and DC-DC Converter Units
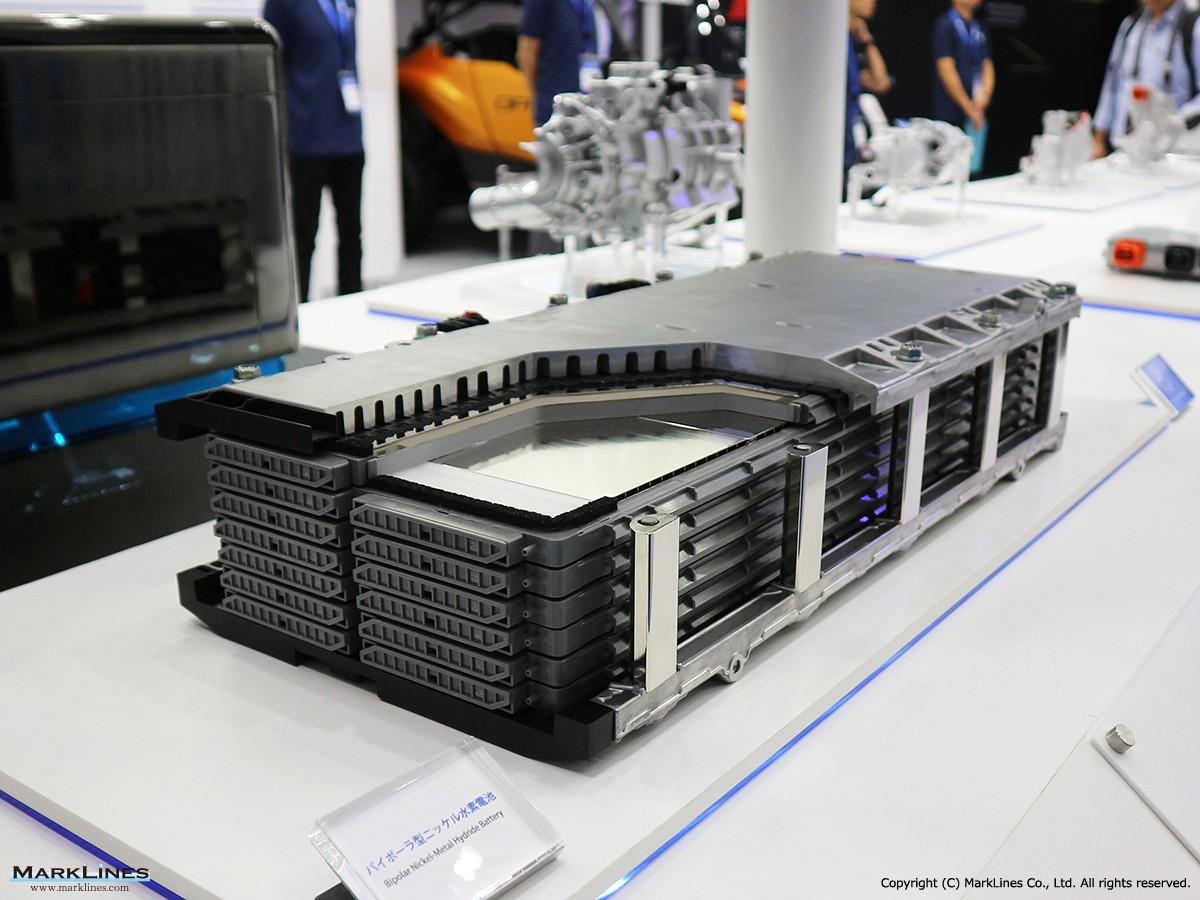
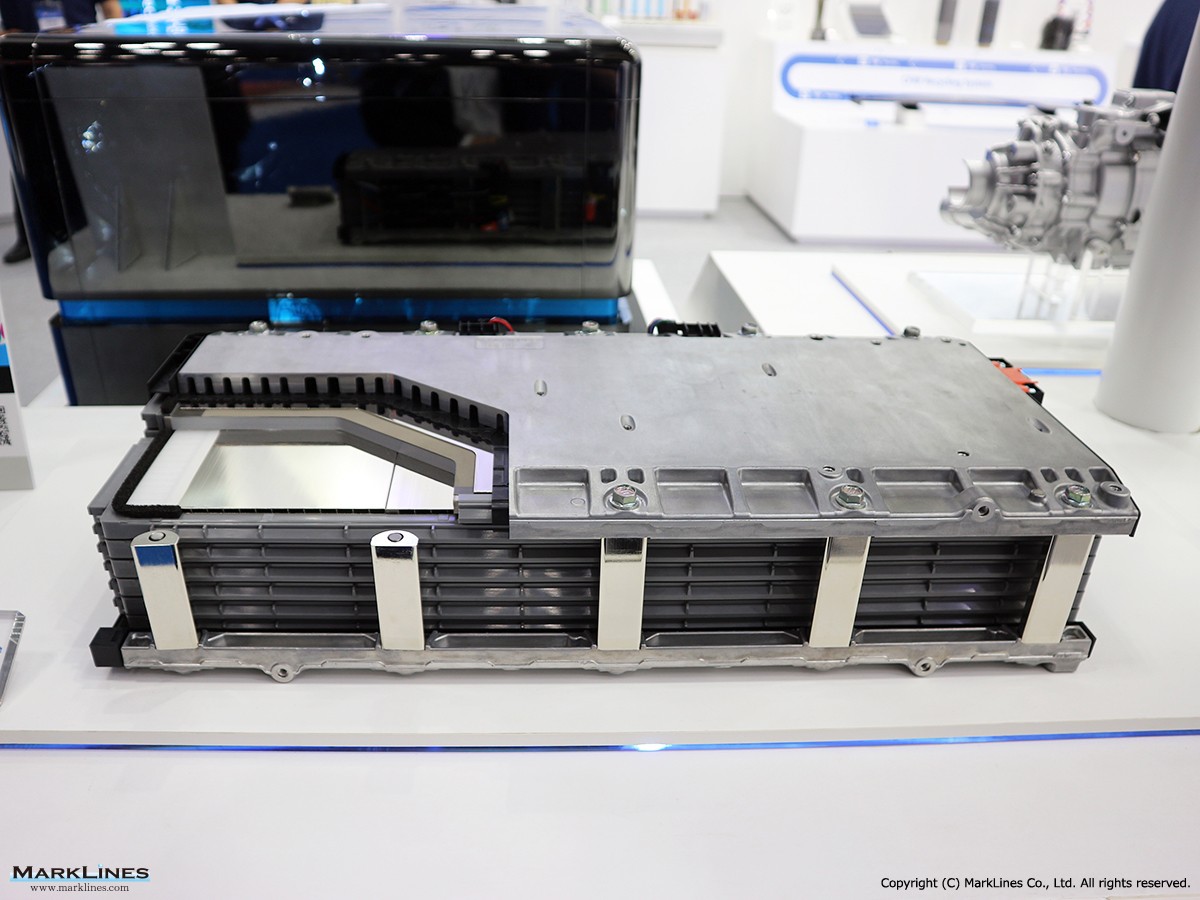
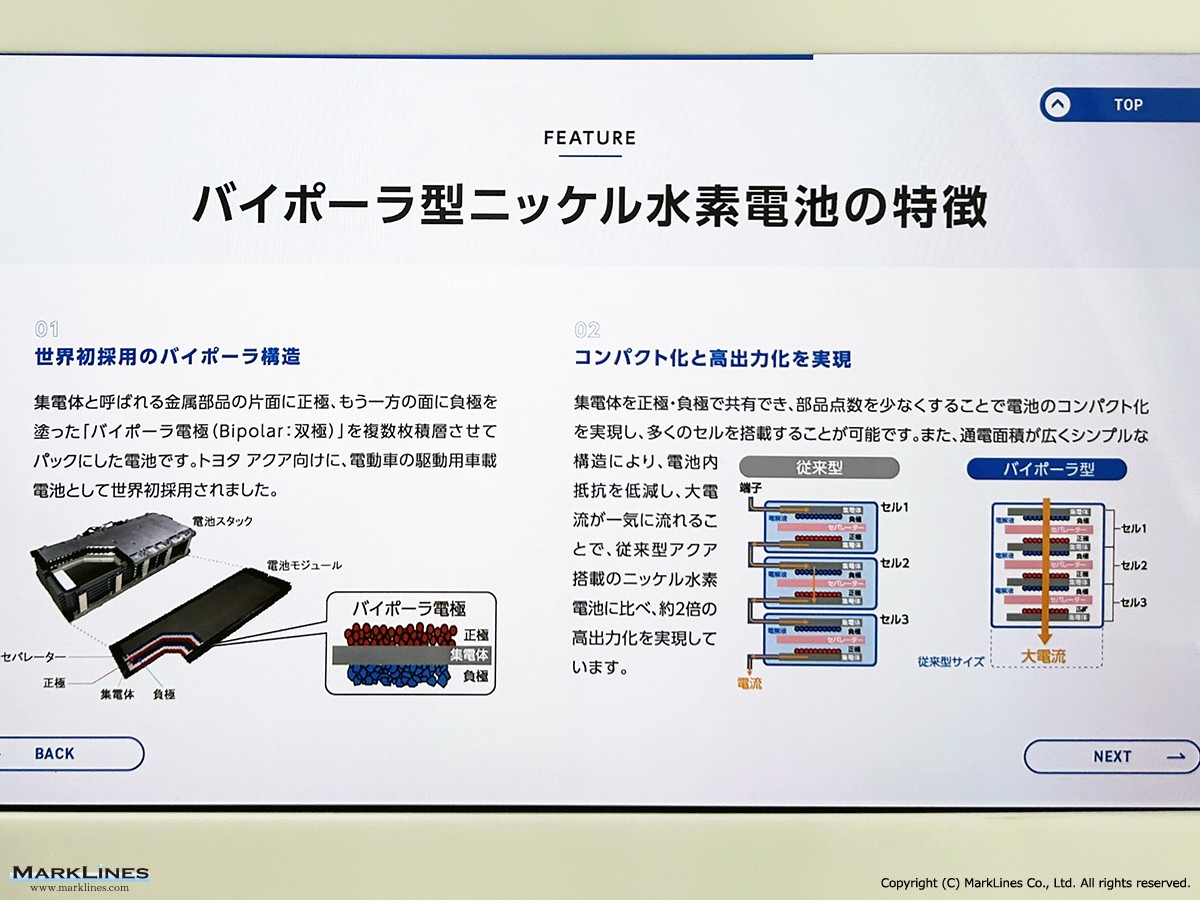
Bipolar nickel-hydrogen batteries for hybrid vehicles
History
| Nov. 1926 | Toyota Industries Corporation was established. |
| Sep. 1933 | Automobile Division was organized. |
| May, 1935 | Completed the prototype of the Model A1 passenger car. |
| Aug. 1937 | Spun off the Automobile Division as Toyota Motor Co., Ltd. (Now Toyota Motor Corporation.) |
| Mar. 1940 | Spun off the steel Production Division as Toyota Steel Works, Ltd. (Now Aichi Steel Works, Ltd.) |
| Oct. 1944 | Obu Plant began operations. |
| May, 1949 | Listed on the Tokyo, Nagoya and Osaka Stock Exchanges. |
| Dec. 1952 | Began manufacturing automotive engines. |
| Aug. 1953 | Kyowa Plant started operations (automobile engines, automobile assembly). |
| Jan. 1960 | Began production of car air-conditioning compressors. |
| Oct. 1997 | Established ST LCD Co., Ltd. jointly with Sony to manufacture liquid crystal equipment. |
| Sep. 1998 | Established TD Deutsche Klimakompressor Ltd. in Germany jointly with Denso to manufacture car air-conditioning compressors. |
| Oct. 1998 | Established TIBC jointly with Ibiden Co. Ltd. to manufacture IC chip plastic package circuits. |
| Aug. 2000 | Changed the name of the company from Toyota Industries Works Corporation to Toyota Industries Corporation. |
| Jun. 2001 | Integrated Technical Development Research Center and semiconductor/electronic equipment operations into Technical Development Center to strengthen electronics business. |
| Aug. 2001 | Completely transferred production of car air conditioning compressors from Denso to Toyota Industries for improved business management efficiency and international competitiveness. |
| Aug. 2001 | Changed name of company to "Toyota Industries Corporation." |
| Oct. 2001 | Higashi chita plant began operation |
| July, 2002 | Higashiura plant began operations. |
| Oct. 2002 | Established a joint venture, Toyota Motor Industries Poland LLP., in Poland with Toyota Motor Corp. to manufacture diesel engines. |
| July, 2004 | Established TD Automotive Compressor Georgia, LLC jointly with Denso to manufacture automobile air-conditioner compressors in the USA. |
| June, 2005 | Established TD Automotive Compressor Kunshan, Co., Ltd. jointly with Denso and two other Toyota Group companies to manufacture automobile air-conditioner compressors in China. |
| Aug. 2007 | Anjo Plant began operations. |
| Feb. 2012 | Established P.T. TD Automotive Compressor Indonesia to manufacture air-conditioner compressors. |
| Jan. 2013 | TIBC Co., Ltd., joint venture with Ibiden Co., Ltd., has been dissolved. |
| Oct. 2016 | Sold off all the shareholdings held in Toyota Motor Industries Poland Sp.zo.o. |
| Oct. 2022 | Ishihama Plant began operations. |
Supplemental Information 1
>>>Business Report FY2007
>>>Business Report FY2008
>>>Business Report FY2009
>>>Business Report FY2010
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2013
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2014
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2015
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2016
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2017
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2018
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2019
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2020
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2021
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2022
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2023
>>>Business Report FY ended Mar. 2024
>>>Archives of Past Exhibits
Note: A figure in brackets ( ) indicates a loss
















































































































 Japan
Japan USA
USA Mexico
Mexico Germany
Germany China (Shanghai)
China (Shanghai) Thailand
Thailand India
India