Hyundai Kefico Corporation
Company Profile
■URL
https://www.hyundai-kefico.com/en/main/index.do
■Address
Business Overview
-The Company is a manufacturer of engine control units and transmission control units in the Hyundai Motor Group.
-The Company was founded as a joint venture among Hyundai Motor, Robert Bosch and Mitsubishi Electric in 1987. In 2012, the Company became a wholly-owned subsidiary of Hyundai Motor Group and changed its corporate name to Hyundai Kefico Corporation.
-Percentage breakdown of sales by customer.
(In KRW hundred millions)
| Customers | FY ended Dec. 2024 | FY ended Dec. 2023 | FY ended Dec. 2022 | |||
| Net sales | Net sales | Net sales | Net sales | Net sales | Ratio(%) | |
| Hyundai Motor Company | 7,147 | 28 | 6,670 | 27 | 5,524 | 25 |
| Kia Motors Corp | 4,158 | 16 | 3,683 | 15 | 3,261 | 15 |
| Hyundai Glovis | 5,520 | 21 | 5,322 | 22 | 4,488 | 20 |
| KEFICO Automotive Systems (Beijing) Co., Ltd. | 1,716 | 7 | 1,547 | 6 | 1,411 | 6 |
| Other group companies | 7,352 | 28 | 7,361 | 30 | 7,279 | 34 |
| Total | 25,893 | 100 | 24,583 | 100 | 21,963 | 100 |
Shareholders
(As of December 31, 2024)
| Major Shareholder | Interest Ratio (%) |
| Hyundai Motor Company | 100.00 |
| Total | 100.00 |
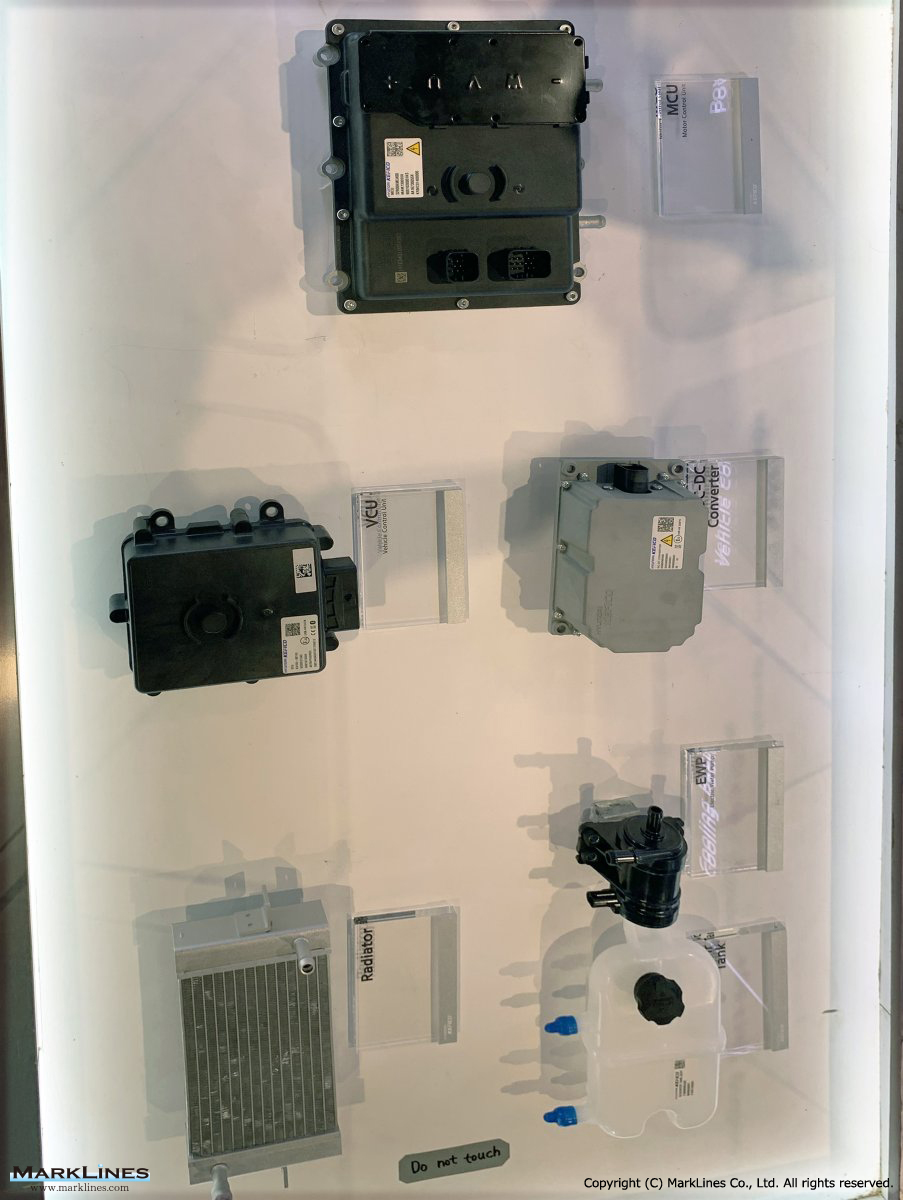
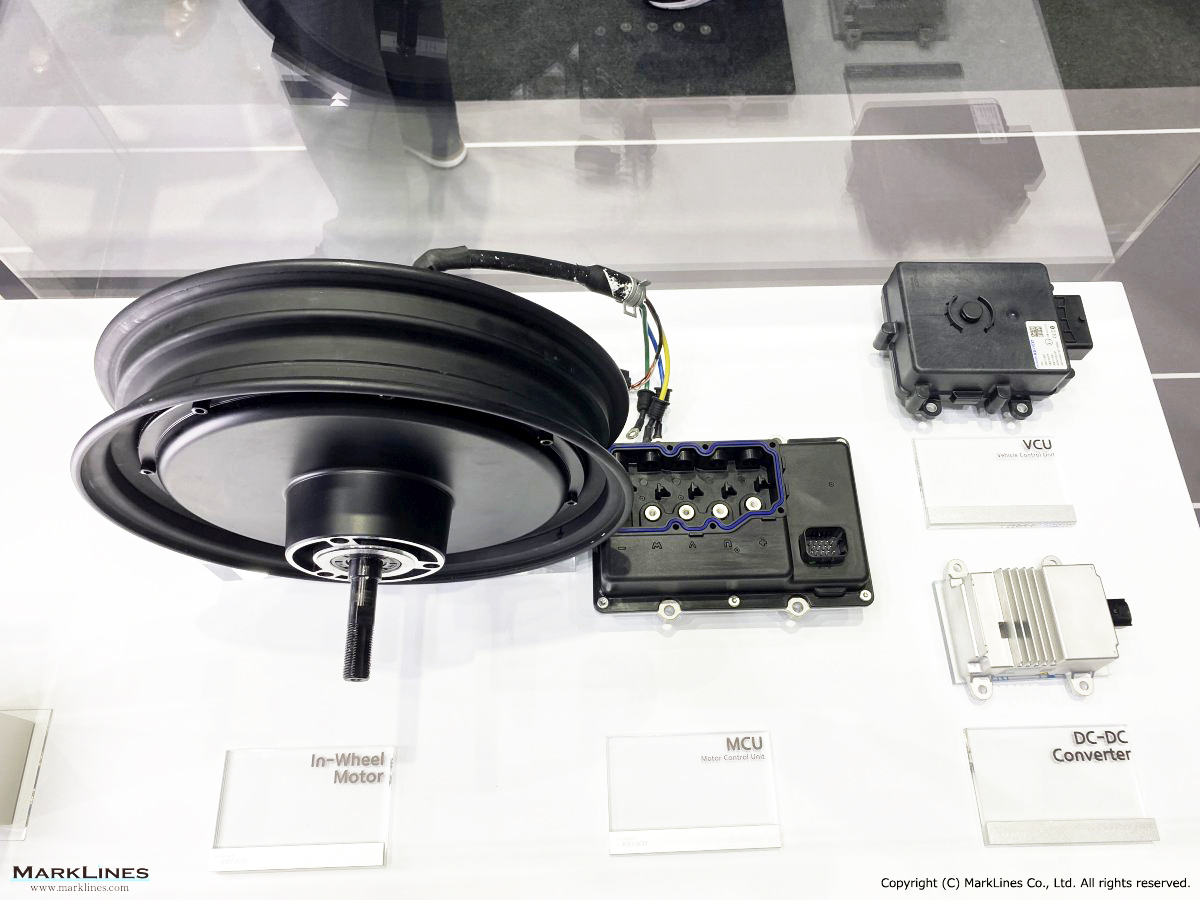
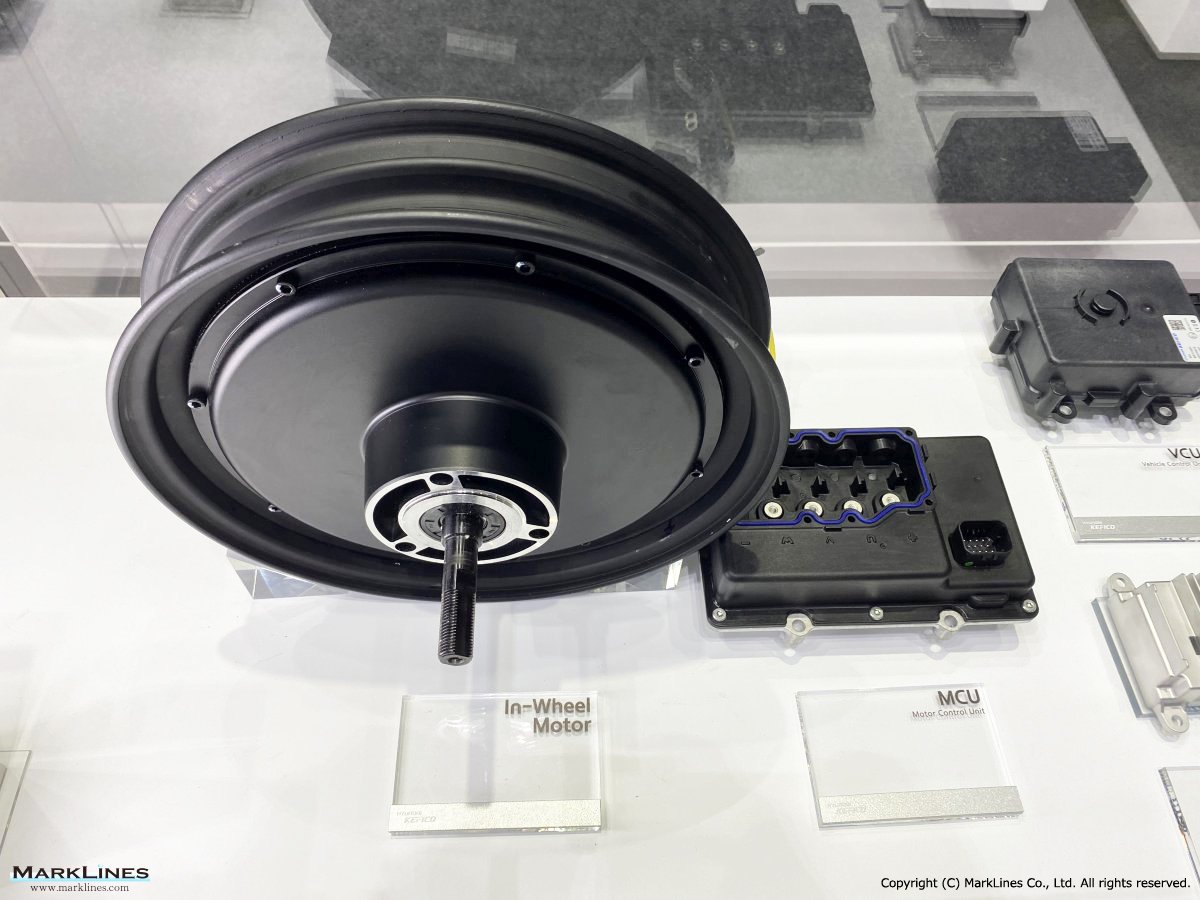
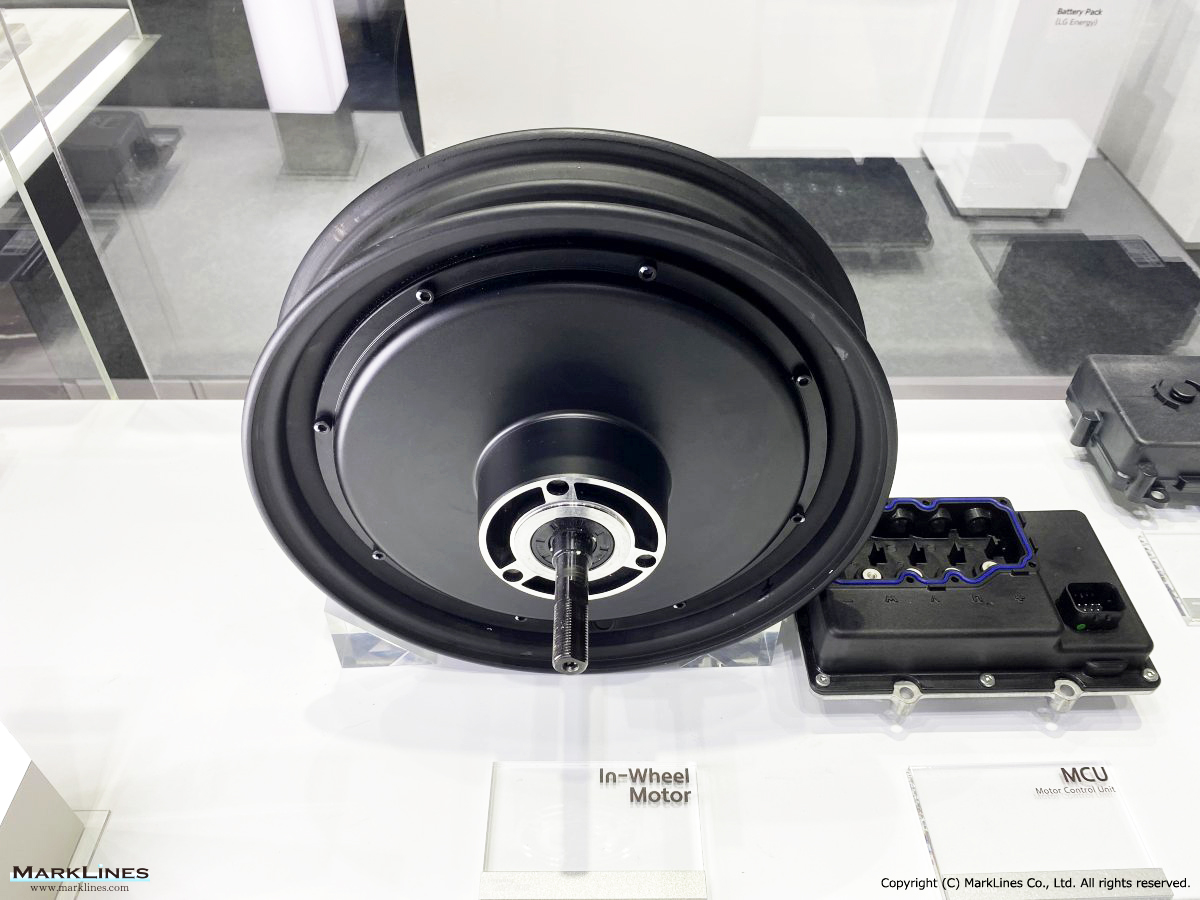
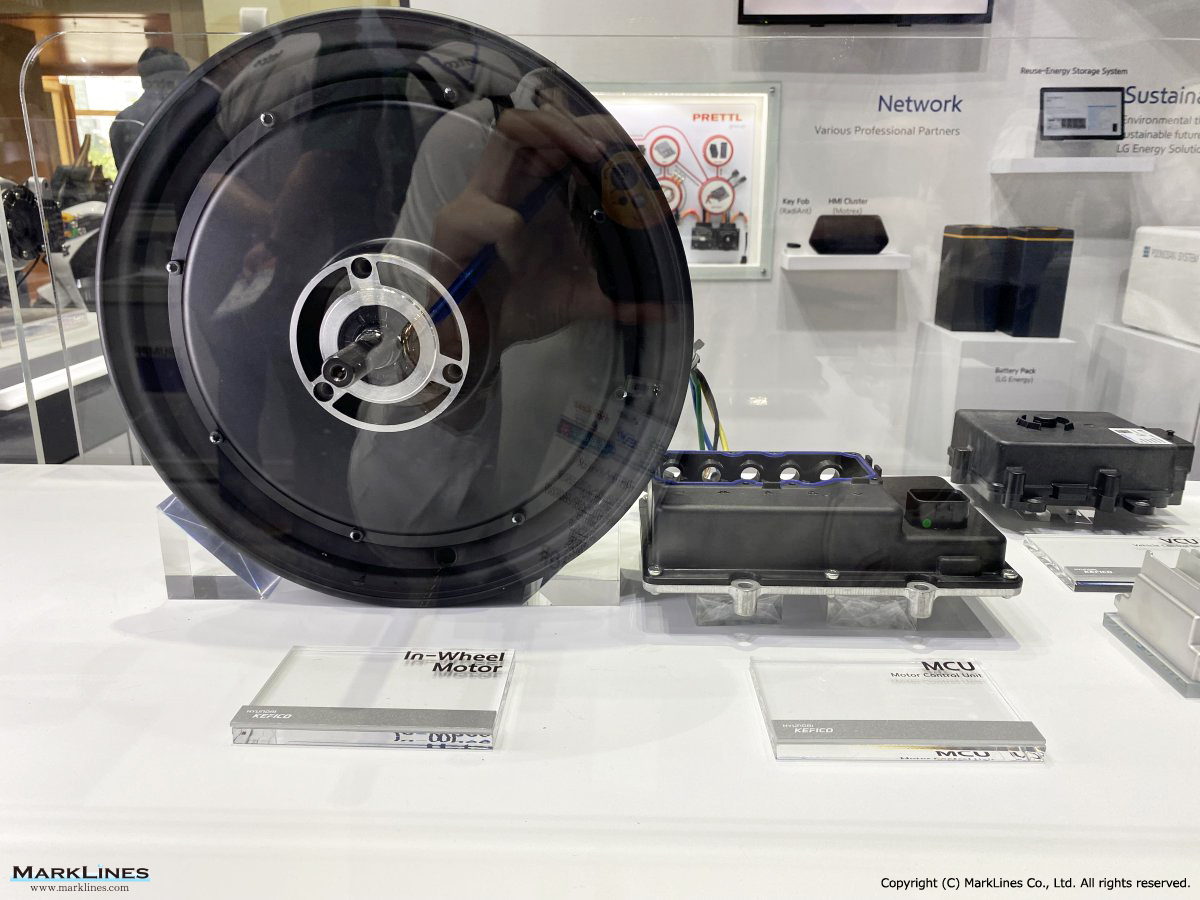
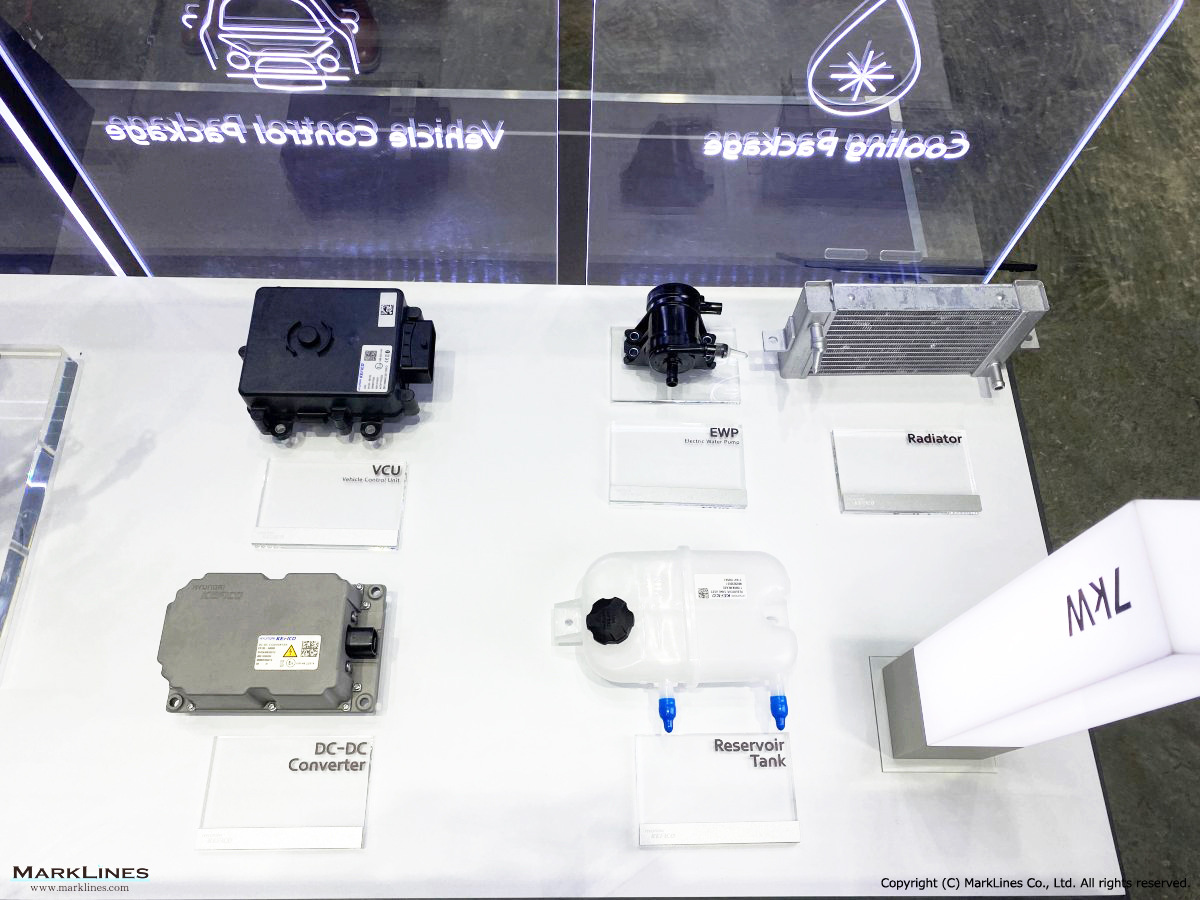
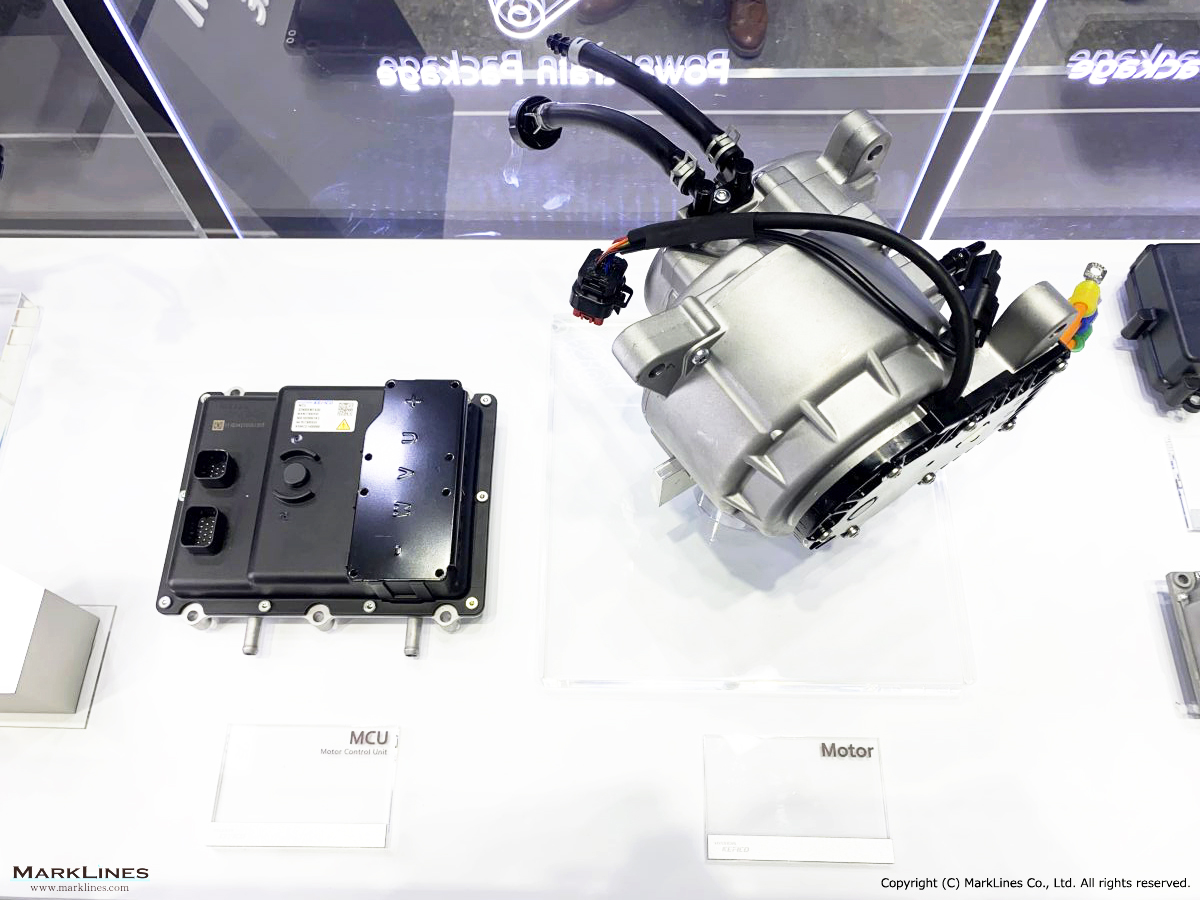
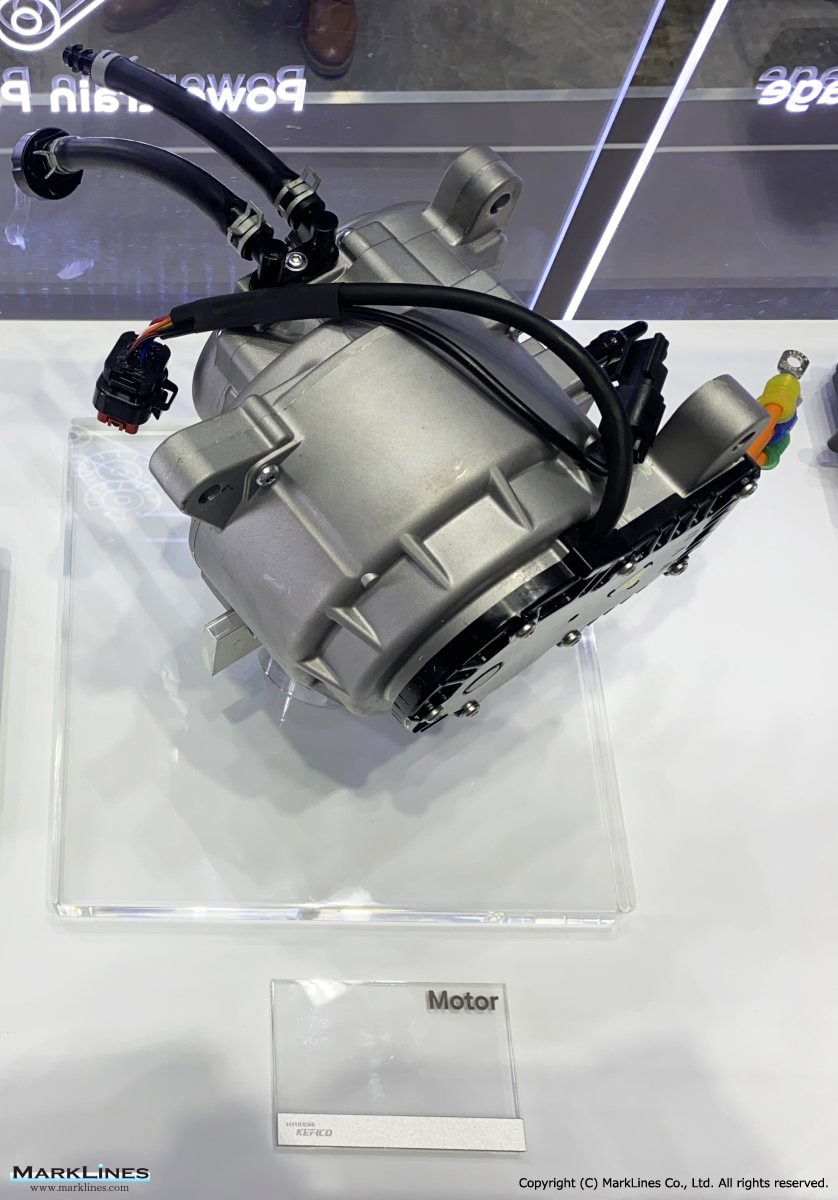
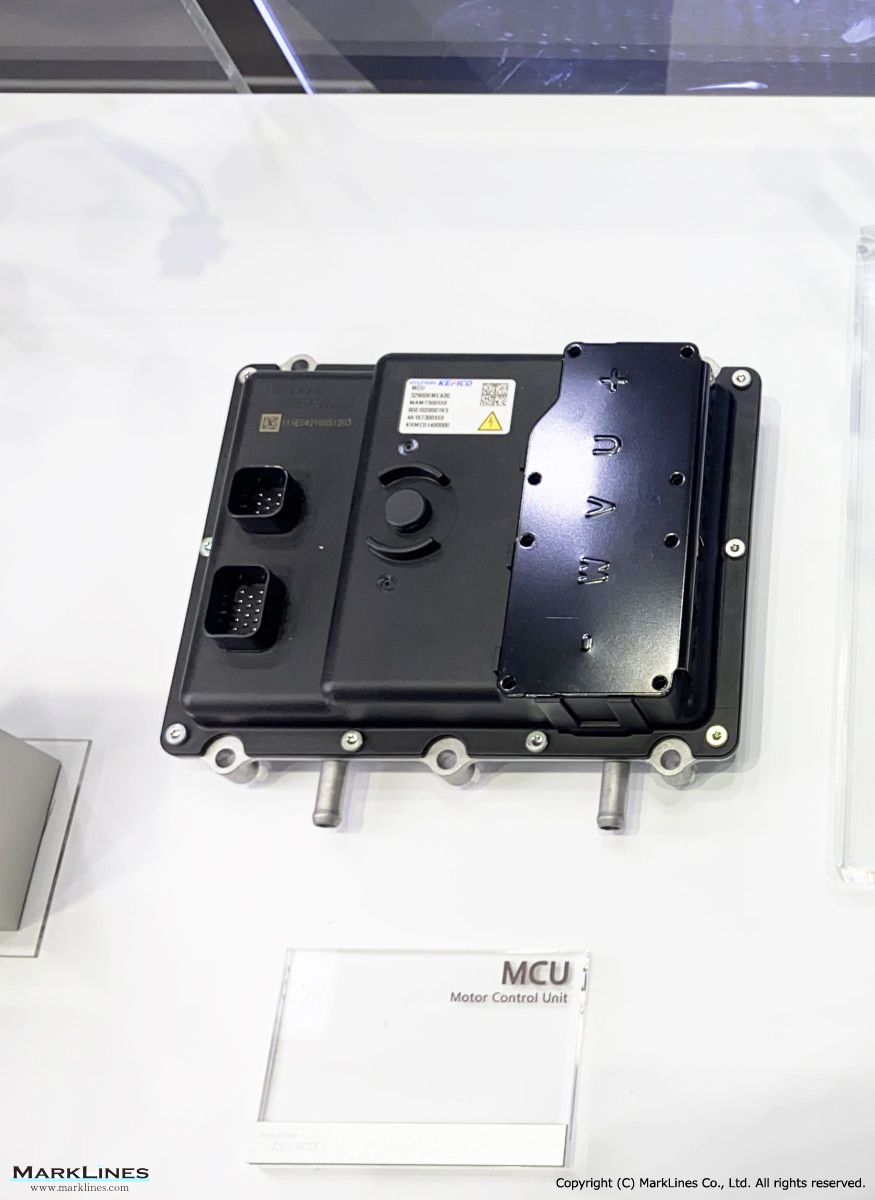
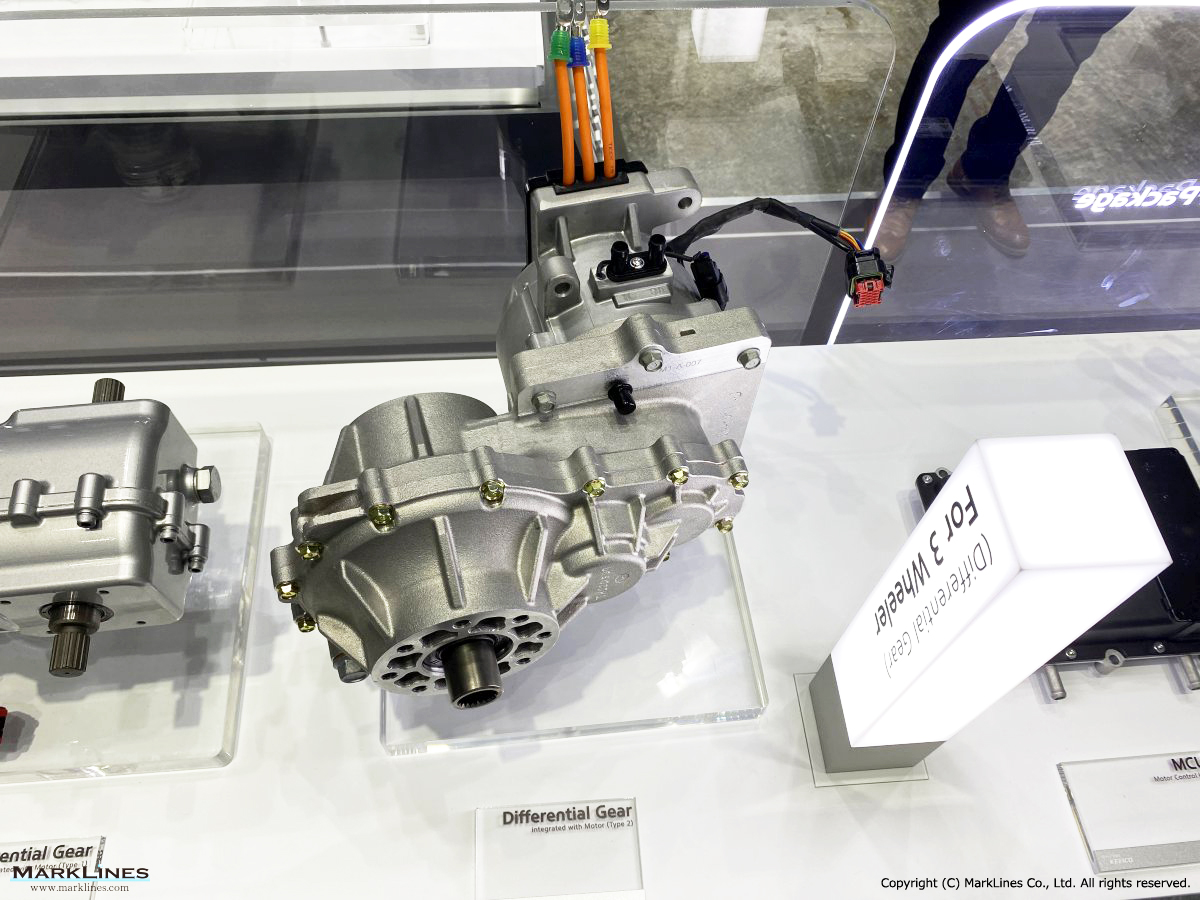
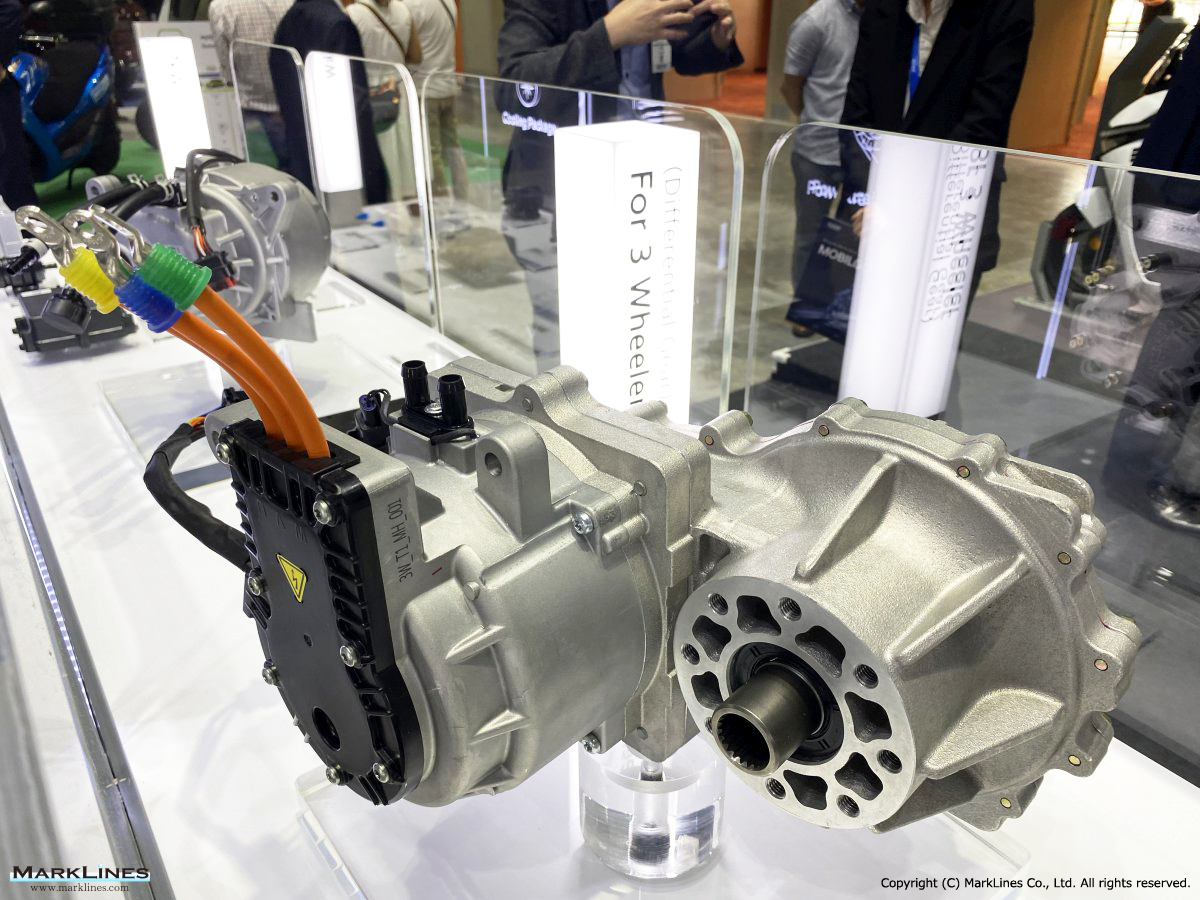
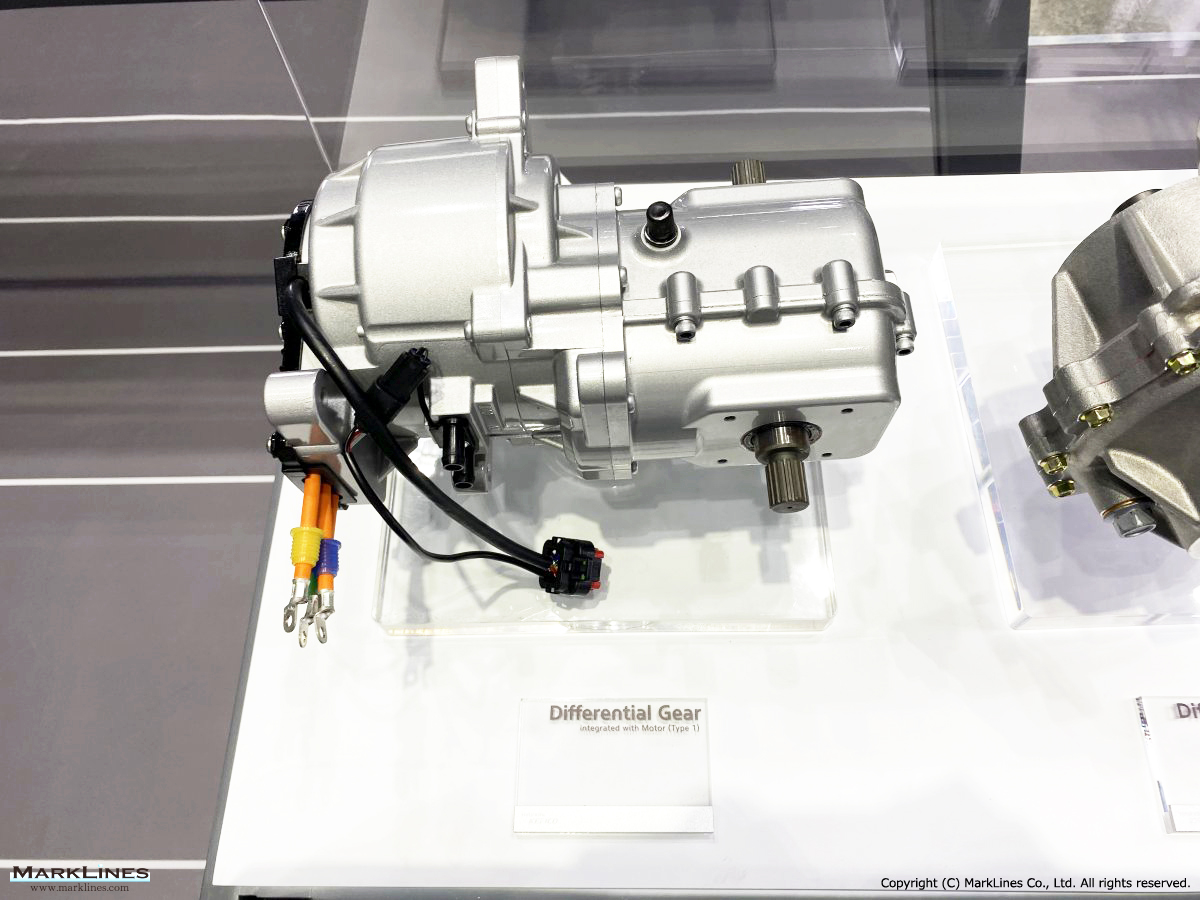
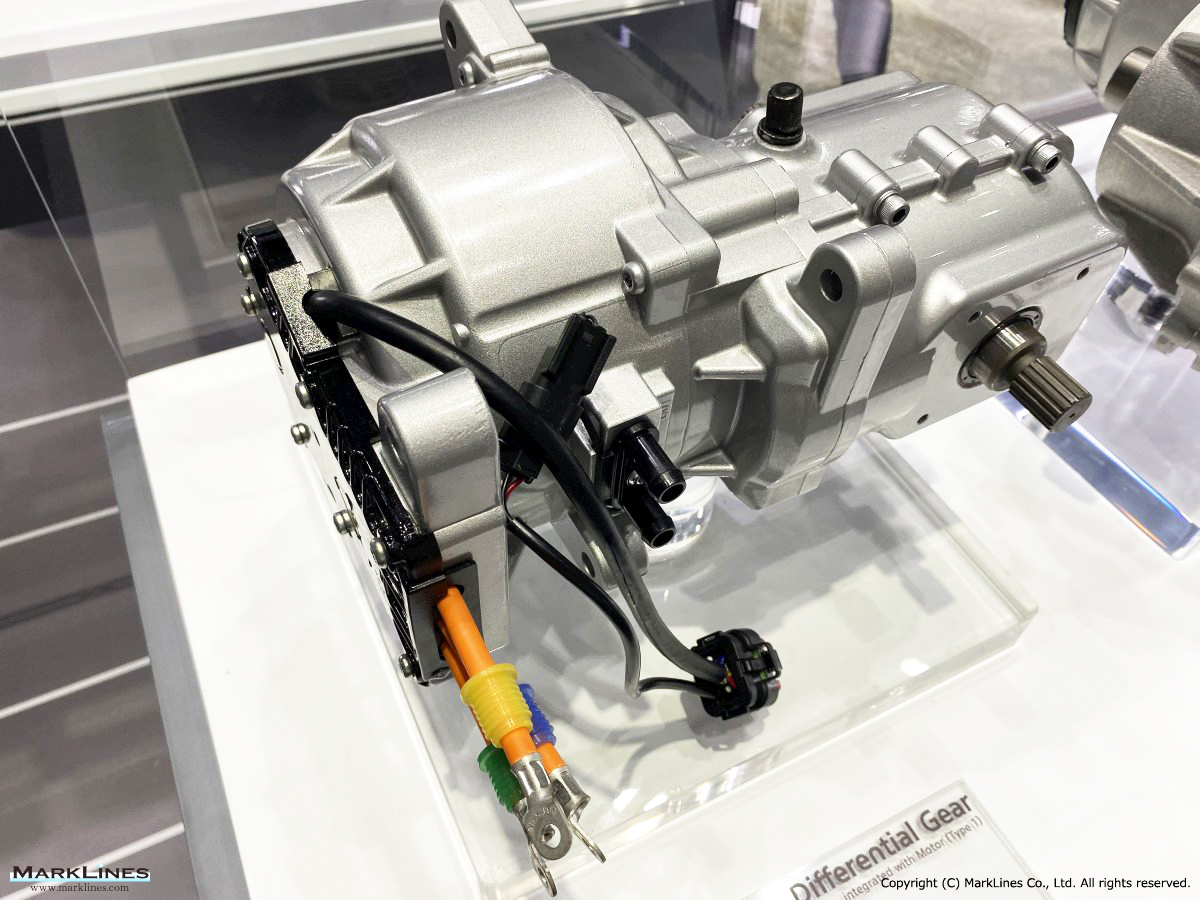
Products
FCEV
Hydrogen supply system module
-Hydrogen storage system management unit
-Hydrogen supply system assembly
-Hydrogen supply / shutoff valve
-Hydrogen pressure sensor
-Hydrogen gas sensor
Air Supply system
-Air Cut-off Valve
-Air Pressure Control Valve
-Fuel cell air compressor control unit
Control system
-Fuel cell control unit
-Fuel cell battery management system
-Fuel cell stack voltage monitor
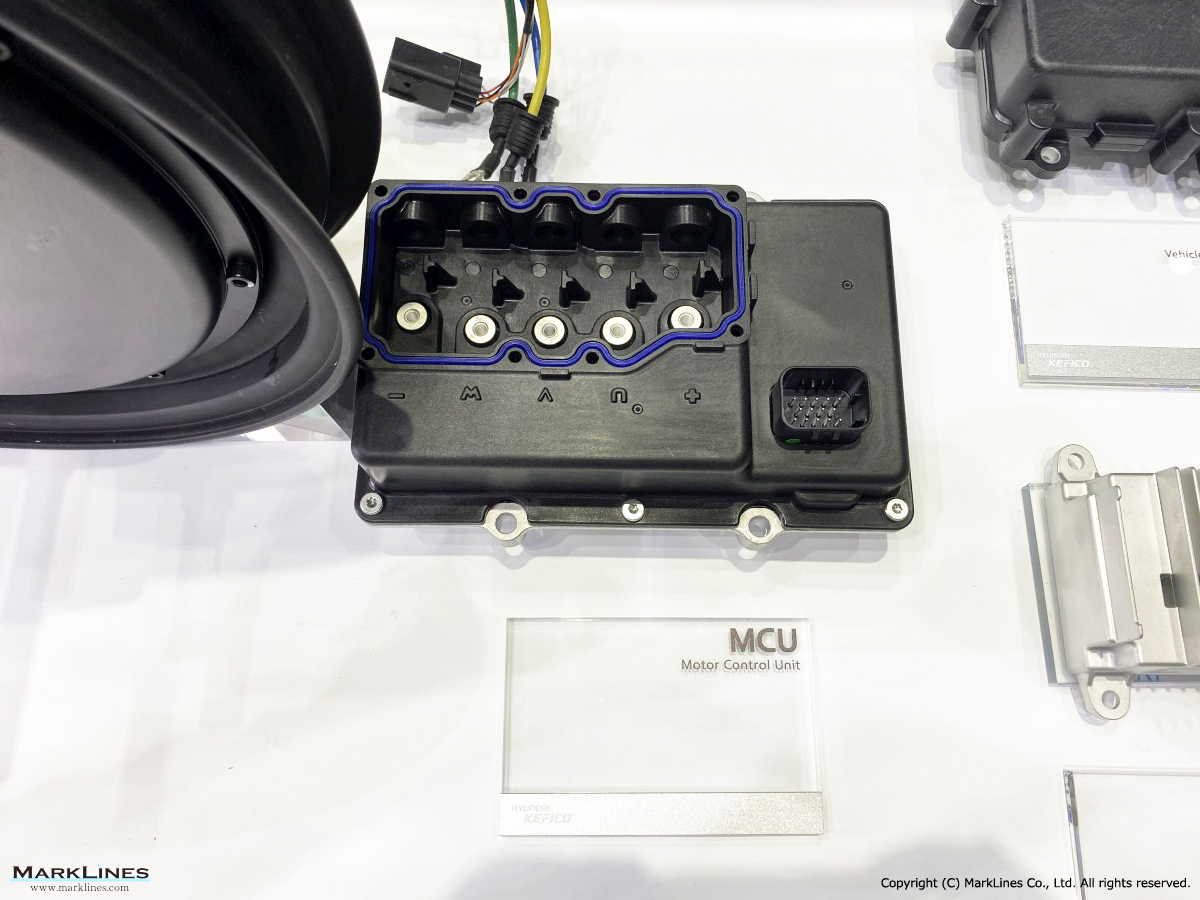
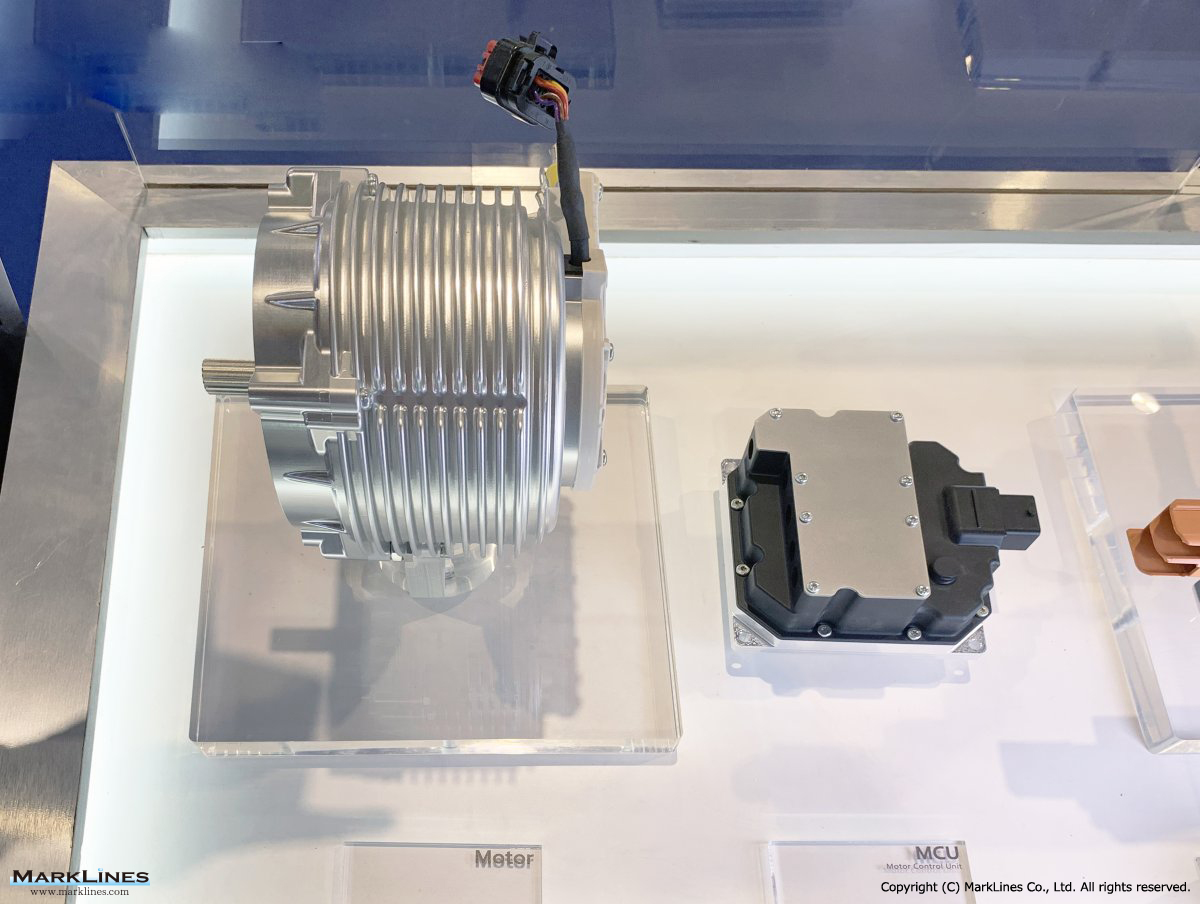
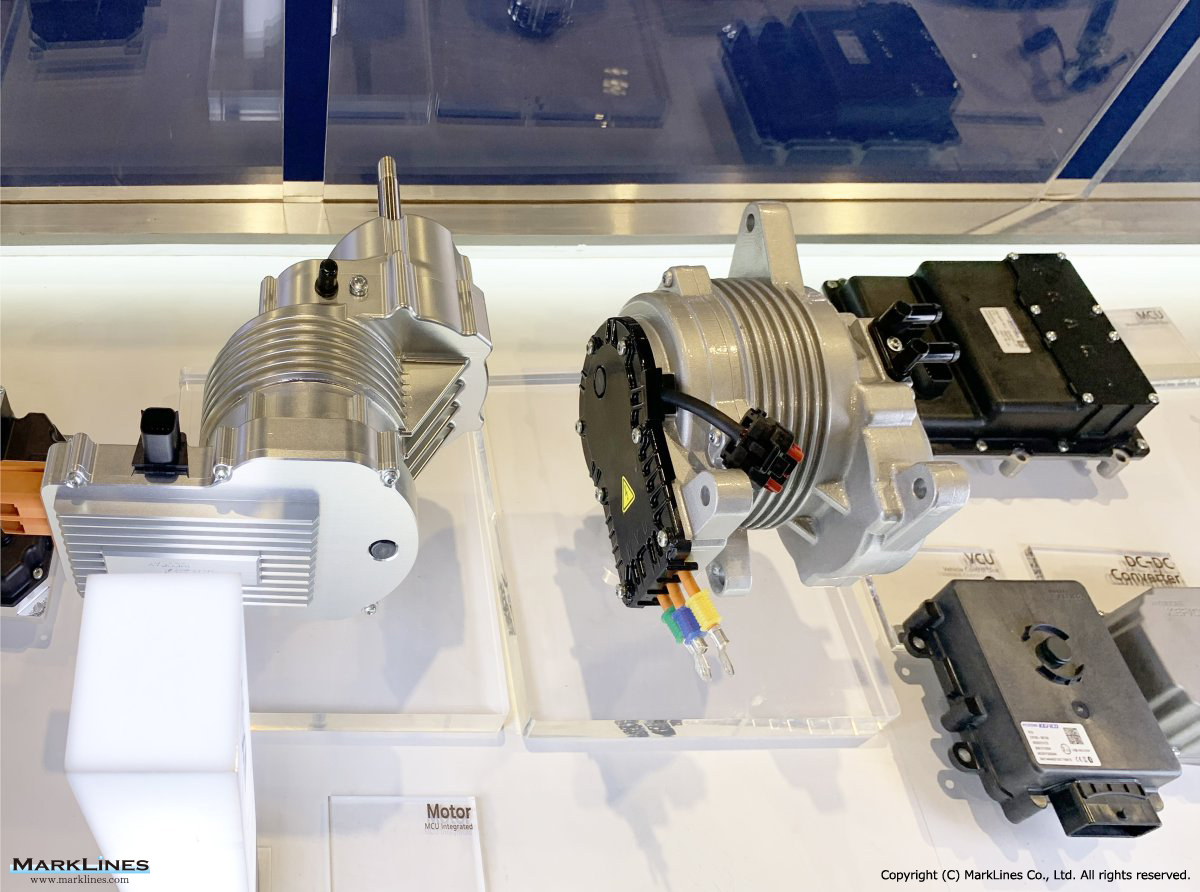
-Motor control unit
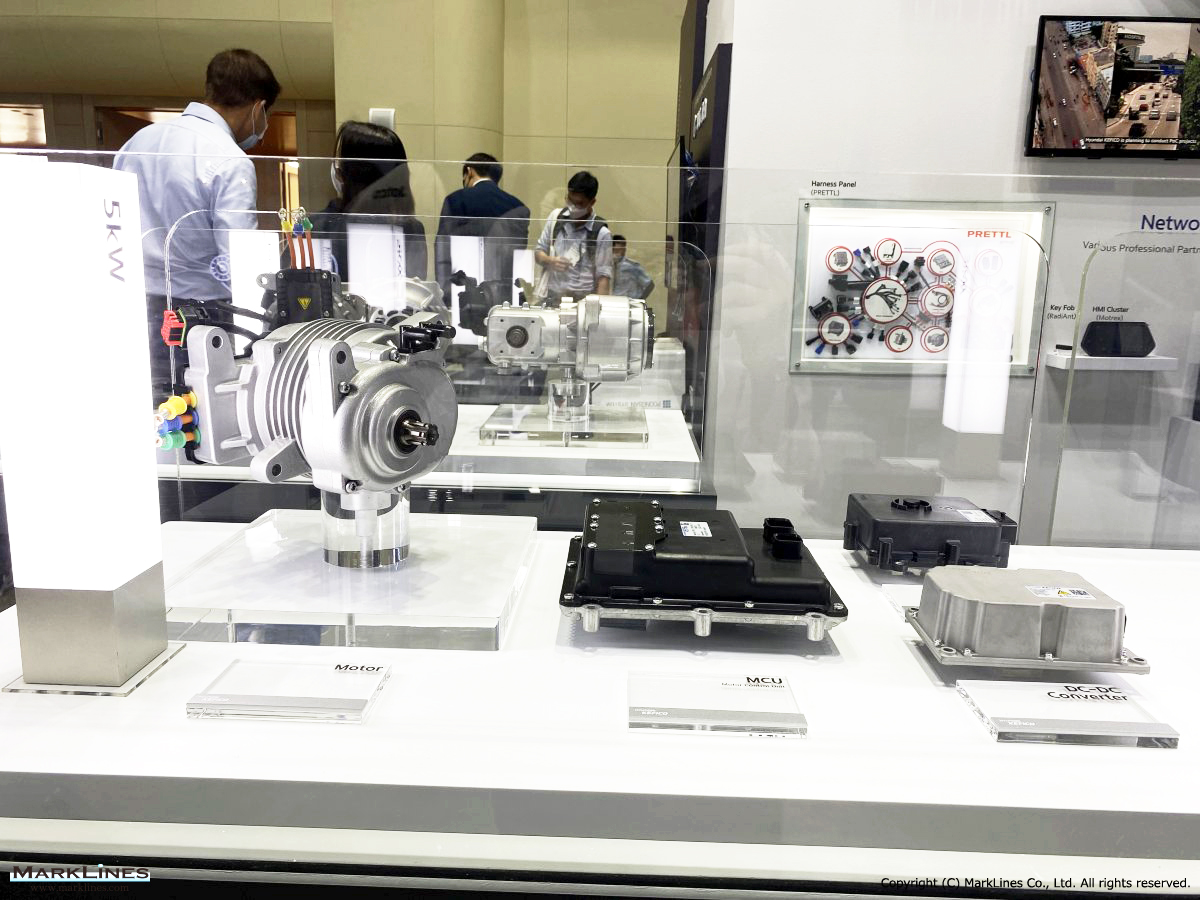
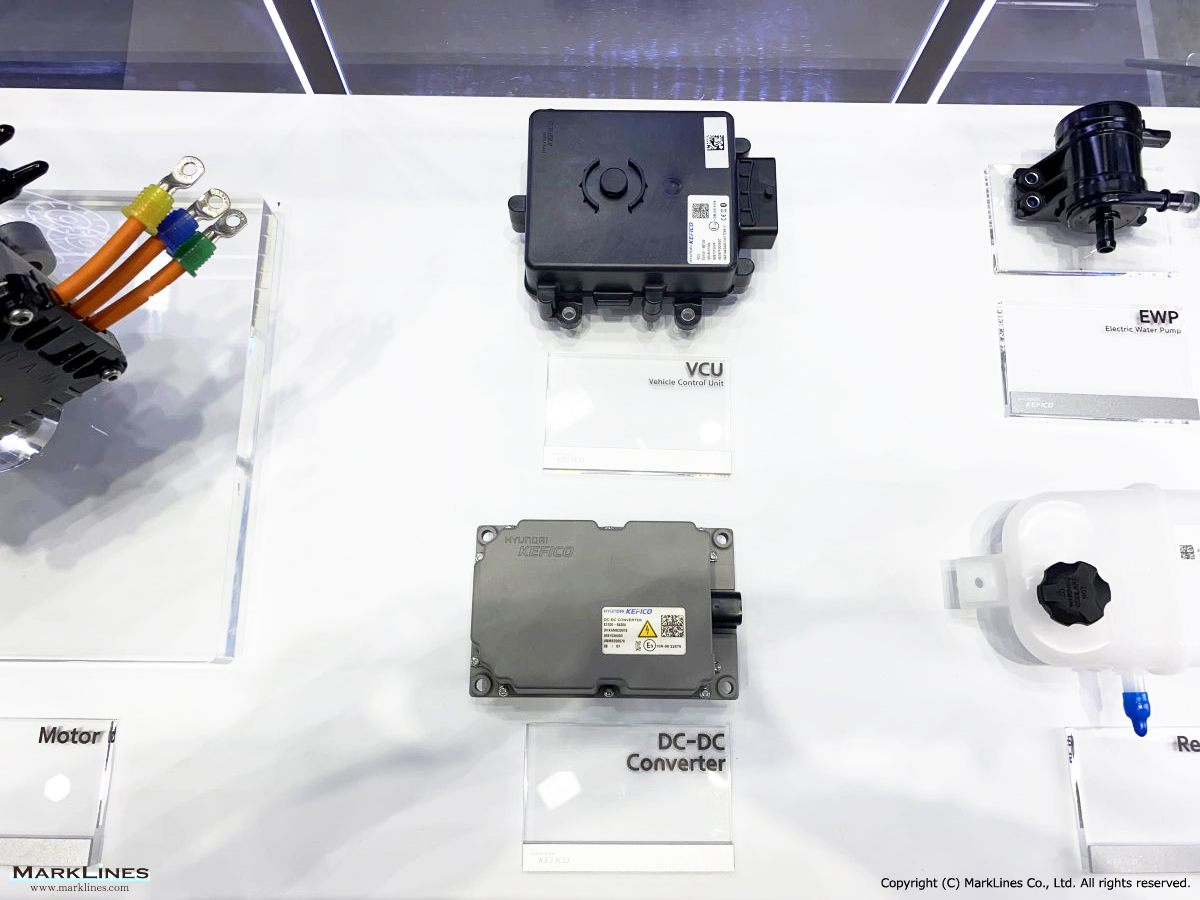
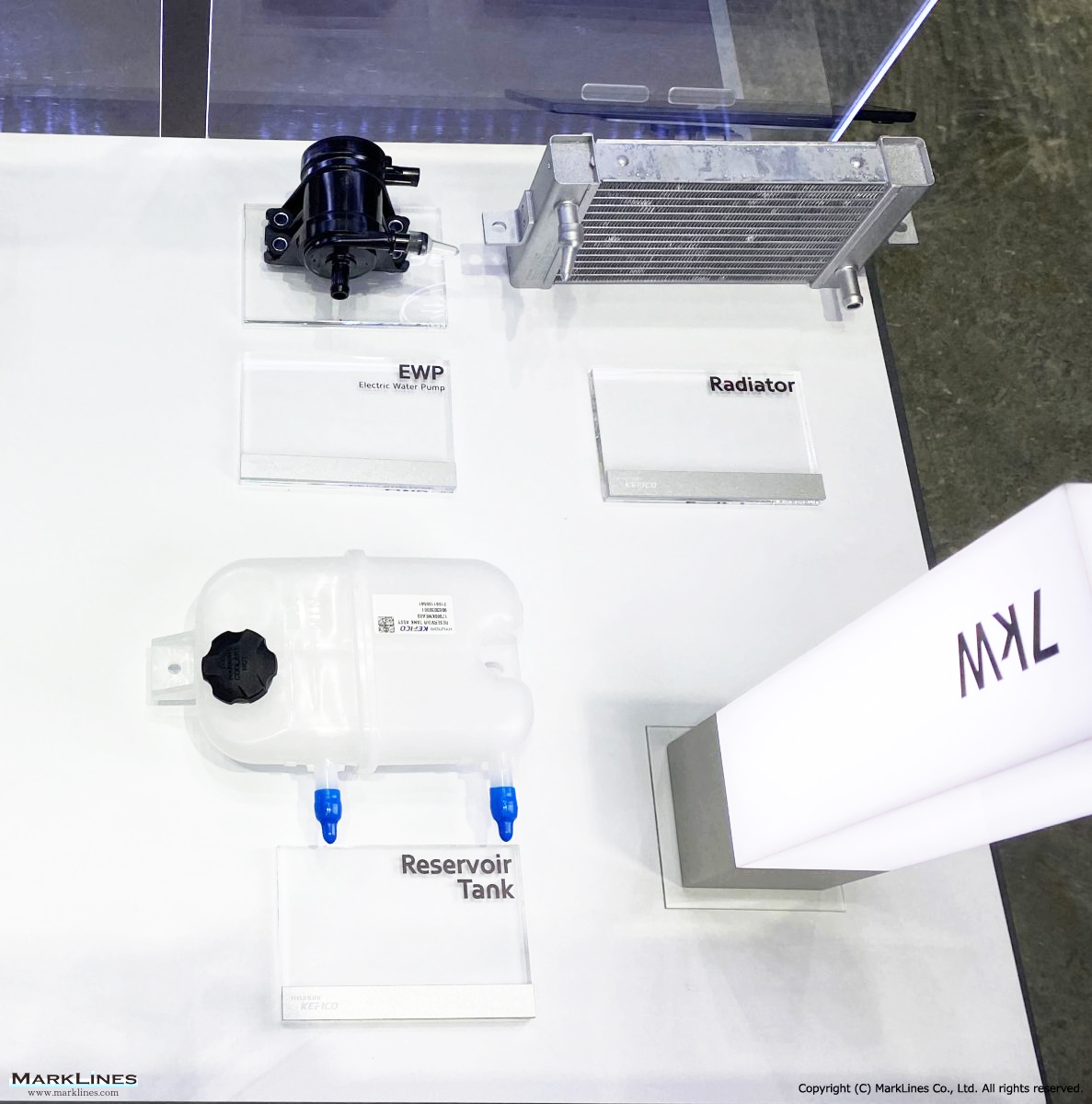
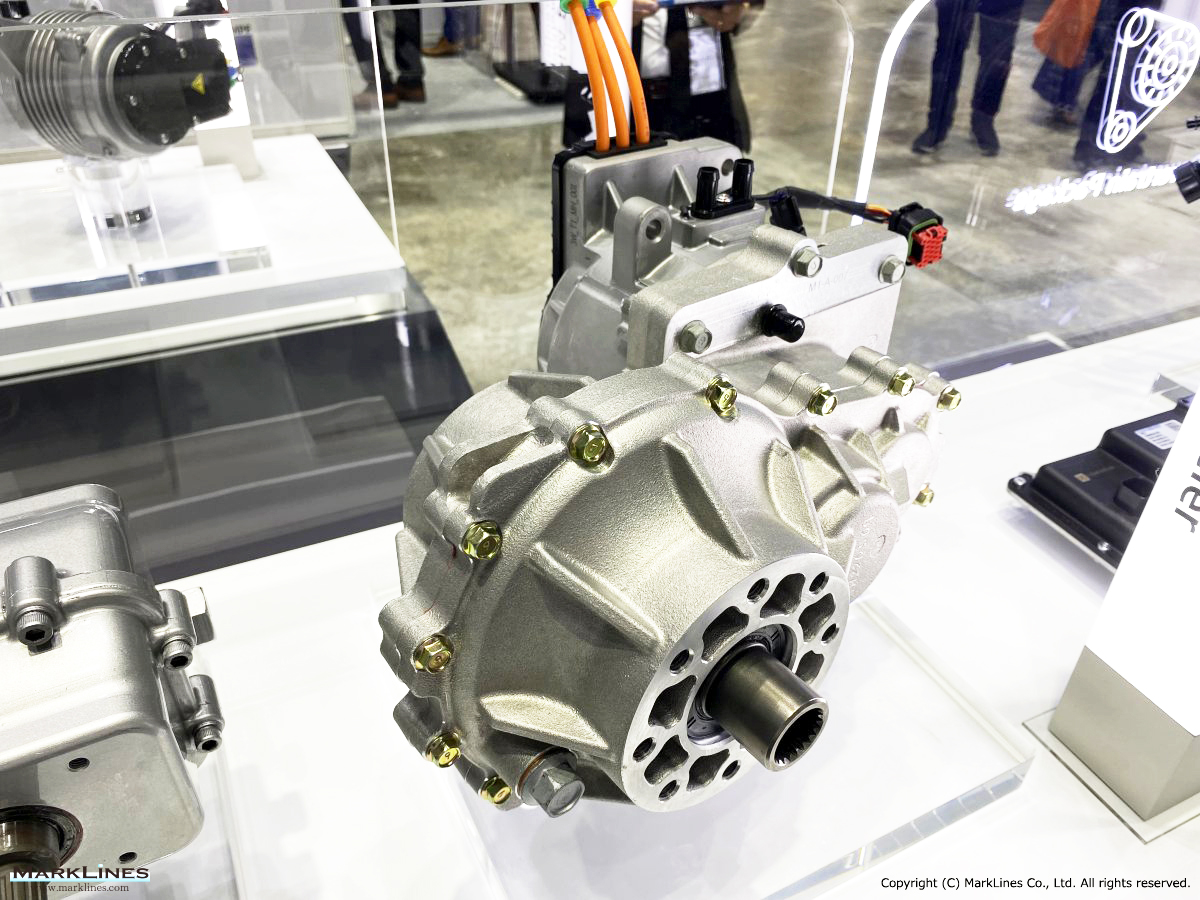
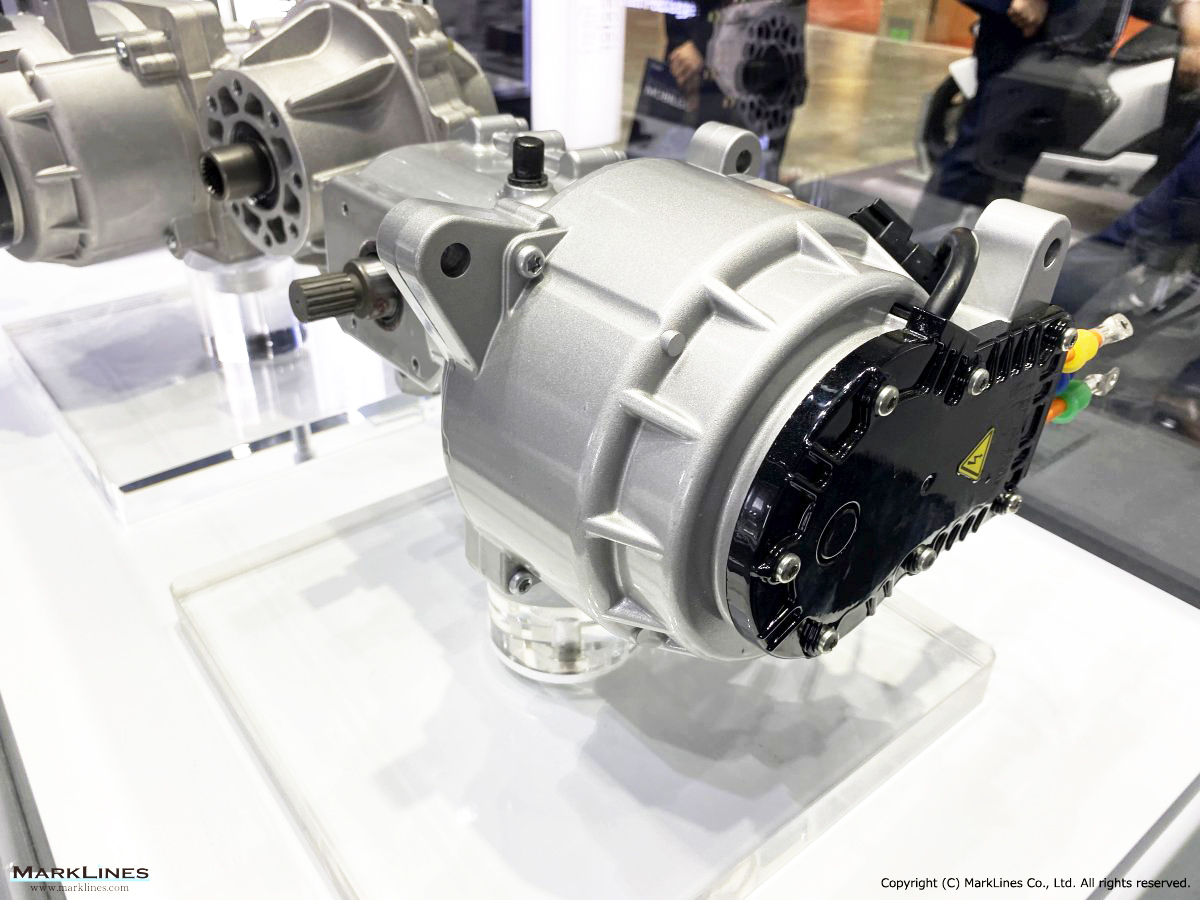
EV/HEV
EV
-EV Motor Control Unit
-Electric Power Control Unit
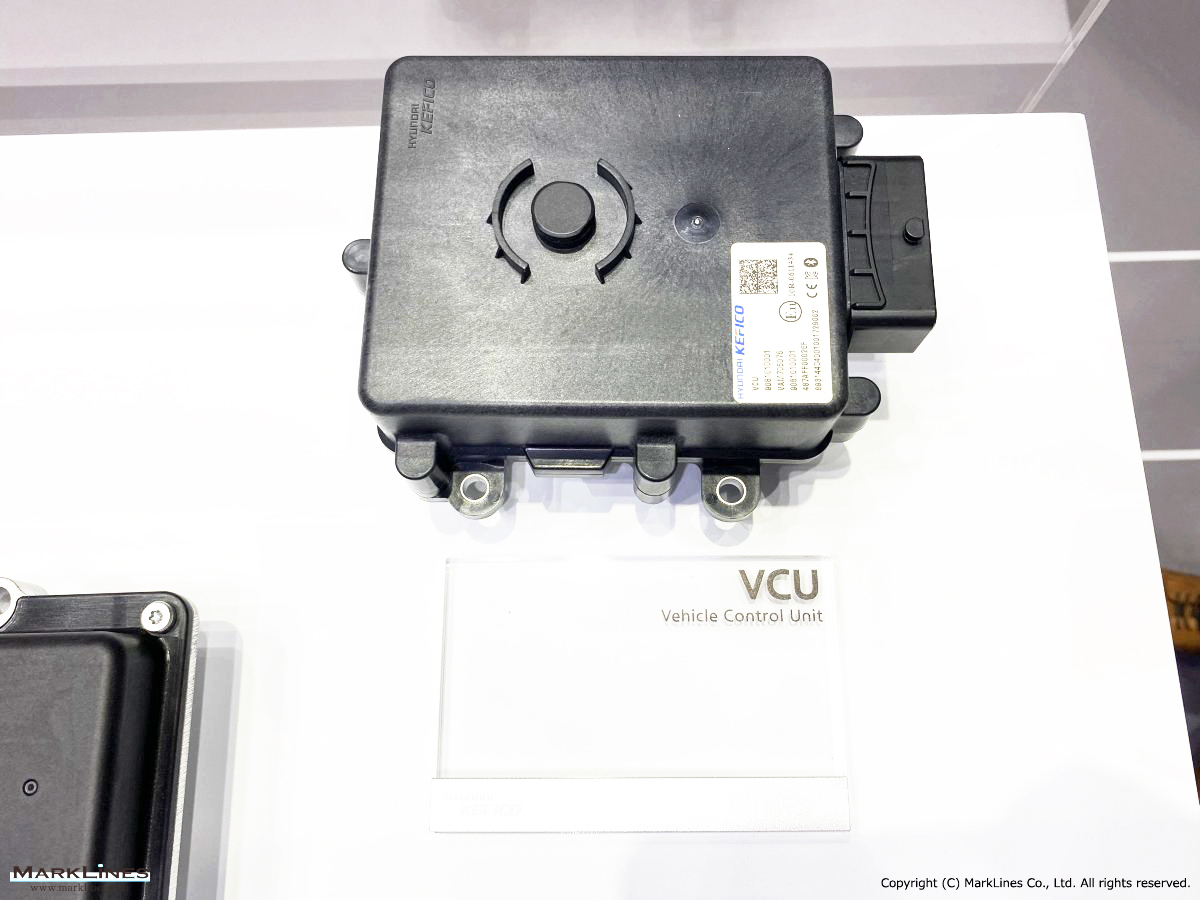
-Vehicle platform controller
-On-Board Charger
-Low Voltage DC-DC Converter
-EV battery management system
-Power relay assembly
-Electronic precharge relay
-Vehicle charging management system
-SBW control unit
-SBW actuator
HEV
-Hybrid control unit
-Hybrid power control unit
-Vehicle domain control unit
-V2L converter
-HEV battery management system
EV Charger
Internal combustion engine
GDI
-GDI engine control unit
-LPDI High pressure injector
-High pressure injector
-High pressure sensor
-High pressure pump
-Fuel rail
-Purge control solenoid valve
-Active purge pressure sensor
-Manifold absolute pressure sensor
-Air flow sensor
-Electronic throttle control valve
-Differential pressure sensor
-Oxygen sensor
-Dual purge ejector
-Air fuel module system
-Camshaft position sensor
-Crankshaft position sensor
-Continuously variable valve duration actuator
-Oil pressure sensor
MPI
-MPI engine control unit
-Low pressure fuel injector (MPI)
-Low pressure fuel injector (LPI)
-Purge control solenoid valve
-Manifold absolute pressure sensor
-Intake pressure sensor
-Air flow sensor
-Oxygen sensor
-Differential pressure sensor
-Electronic throttle control valve
-Air fuel module system
-Camshaft position sensor
-Crankshaft position sensor
-Continuously variable valve duration actuator
-Oil pressure sensor
PDI
-GDI engine control unit
-High pressure injector
-Low pressure injector (MPI)
-Low pressure injector (LPI)
-High pressure pump
-High pressure sensor
-Fuel rail (GDI)
-Purge control solenoid valve
-Manifold absolute pressure sensor
-Air flow sensor
-Oxygen sensor
-Differential pressure sensor
-Electronic throttle control valve
-Dual purge ejector
-Air fuel module system
-Camshaft position sensor
-Crankshaft position sensor
-Continuously variable valve duration actuator
-Oil pressure sensor
Diesel
-Diesel engine control unit
-Diesel fuel injector
-Diesel pump
-Common rail
-Manifold absolute pressure sensor
-Air flow sensor
-Oxygen sensor
-Differential pressure sensor
-Low-pressure exhaust gas recirculation (LP-EGR) valve
-Air fuel module system
-Camshaft position sensor
-Crankshaft position sensor
-Continuously variable valve duration actuator
-Engine oil pressure sensor
Automatic transmission
-Transmission control unit
-SBW control unit
-Speed sensor
-Inhibitor switch
-SBW actuator
-Solenoid valve
-E-module
History
| 1987 | The Company was founded as a joint venture among Hyundai Motor, Robert Bosch and Mitsubishi Electric. |
| 1987 | The Company began commercial production of engine control units. |
| 1989 | The Company began commercial production of fuel injectors, air flow sensors and transmission control units. |
| 1992 | The Company established KETI (Kefico Engineering Technology Institute). |
| 1993 | The Company began commercial production of oxygen sensors. |
| 1994 | The Company began commercial production of auto cruise control systems. |
| 1995 | The Company began commercial production of idle speed actuators. |
| 1996 | The Company began commercial production of throttle position sensors and manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensors. |
| 1996 | The Company acquired ISO9002 certification. |
| 1996 | The Company established the Application Engineering Center. |
| 1997 | The Company began commercial production of fuel tank pressure sensors and A/T solenoid valves. |
| 1998 | The Company began commercial production of powertrain control units. |
| 1998 | The Company acquired QS9000 and ISO9001 certification. |
| 1999 | The Company developed proprietary acceleration sensors. |
| 2003 | The Company acquired ISO14001 certification. |
| 2004 | The Company acquired ISO/TS16949 certification. |
| 2005 | The Company established the Reliability Center. |
| 2005 | Mitsubishi Electric sold all shares in the Company to Robert Bosch. |
| 2006 | The Company began commercial production of purge control solenoid valves. |
| 2007 | The Company was awarded five-star rating for quality from Hyundai/Kia. |
| 2007 | The Company produced its 100 millionth injector. |
| 2007 | The Company started commercial production of intake manifold modules for use in Theta2 engines. |
| 2008 | The Company received five-star ratings from both Hyundai Motor and Kia Motors in recognition of its high levels of technology and delivery performance. |
| 2008 | The Company began mass production of electronic throttle controls and 6-speed transmission control units. |
| 2008 | The Company established KEFICO Automotive Systems (Beijing) Co., Ltd. in China. |
| 2009 | The Company established KEFICO Vietnam Company Limited in Vietnam. |
| 2010 | The Company's Vietnam plant started mass production. |
| 2010 | The Company's Rizhao plant in Shandong Province started mass production. |
| 2012 | the Company became a wholly-owned subsidiary of Hyundai Motor Group. |
| 2012 | Changed its corporate name to Hyundai Kefico Corporation. |
| 2015 | The Company established KEFICO Automotive Systems (Chongqing) Co., Ltd. in China. |
| 2016 | The Company established HYUNDAI KEFICO MEXICO, S. DE R.L. DE C.V. in Mexico. |
| 2019 | Completed the second production plant in Vietnam |
| 2020 | Acquired Hyundai Autron PT electrification control business |
| 2024 | Established Hyundai Kefico India Private Limited in India |
Supplemental Information 1
The Hyundai Motor Group's Ratio of Shareholding in Automotive Companies |
(As of Dec. 31, 2024) |
|
Name of group company
Company in which the company holds shares |
Hyundai Motor |
Kia Corporation |
Hyundai Mobis |
Hyundai WIA |
Hyundai Transys |
Hyundai Kefico |
| Hyundai Motor | - | 34.53% | - | 25.35% | 41.13% | 100.00% |
| Kia Corporation | - | - | 17.66% | 13.44% | 40.43% | - |
| Hyundai Steel | - | - | 5.92% | - | - | - |
| Hyundai Mobis | 21.86% | - | - | - | 15.74% | - |
| Hyundai GLOVIS | - | - | 0.71% | - | - | - |
| Hyundai WIA | - | - | - | - | 1.88% | - |
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 2013
>>>Business Report FY ended Dec. 2014
>>>Business Report FY ended Dec. 2015
>>>Business Report FY ended Dec. 2016
>>>Business Report FY ended Dec. 2017
>>>Business Report FY ended Dec. 2018
>>>Business Report FY ended Dec. 2019
>>>Business Report FY ended Dec. 2020
>>>Business Report FY ended Dec. 2021
>>>Business Report FY ended Dec. 2022
>>>Business Report FY ended Dec. 2023
Note: A figure in brackets ( ) indicates a loss

 AI Navigator
AI Navigator

































































 Japan
Japan USA
USA Mexico
Mexico Germany
Germany China (Shanghai)
China (Shanghai) Thailand
Thailand India
India