Hyundai WIA Corporation (Formerly WIA Corporation)
Company Profile
■URL
http://en.hyundai-wia.com/main/main.asp
■Address
Business Overview
-An auto parts manufacturer in the Hyundai/Kia Automotive Group. It is the only Korean auto parts manufacturer that produces engines.
-The company's business is divided into the following two categories
| Business Segment | Products | Sales % (2024) | Sales % (2023) | |
| Automotive parts | Modules | - Modules and module parts | 88.7% | 34.2% |
| Modules parts | - 4WD parts - Constant velocity joints - Engines |
56.0% | ||
| Mobility solutions Machinery |
- Equipment to automate factory operations - Machine tools |
7.3% | 7.2% | |
| Special/Customized products | - Protective equipment | 4.0% | 2.6% | |
-In the fiscal year that ended in Dec. 2024, the automotive-parts business accounted for 92% of company-wide sales.
Shareholders
(As of Dec. 31, 2024)
| Major Shareholders | Interest Ratio (%) |
| Hyundai Motor Company | 25.35 |
| Kia Motors Corporation | 13.44 |
| National Pension Service | 7.63 |
| Total | 46.42 |
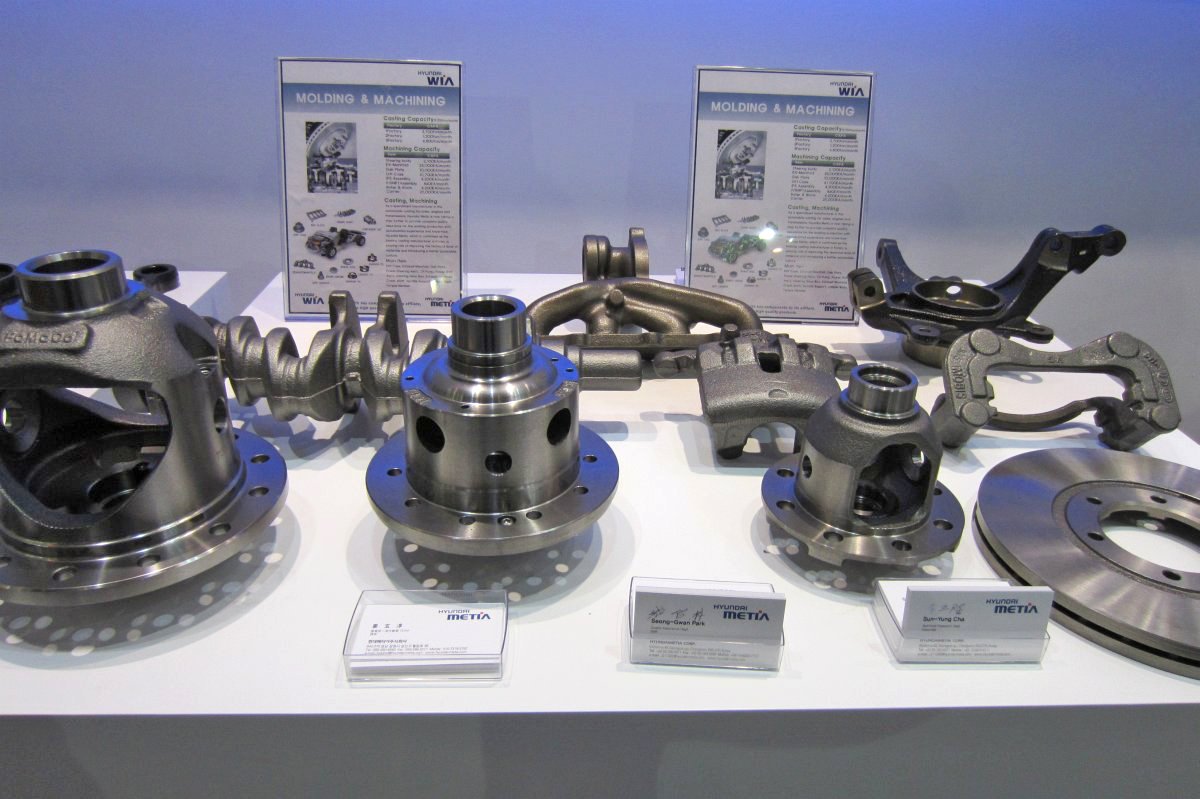
Products
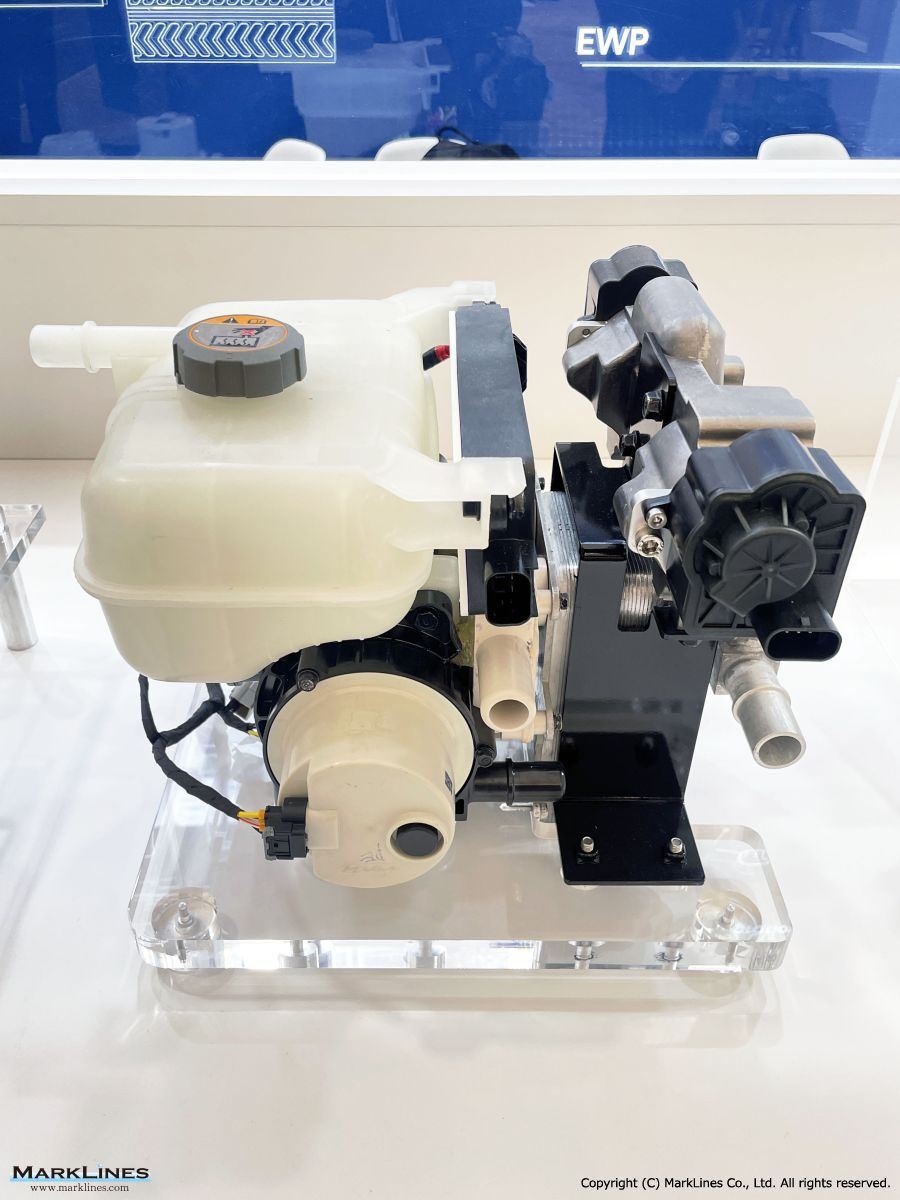
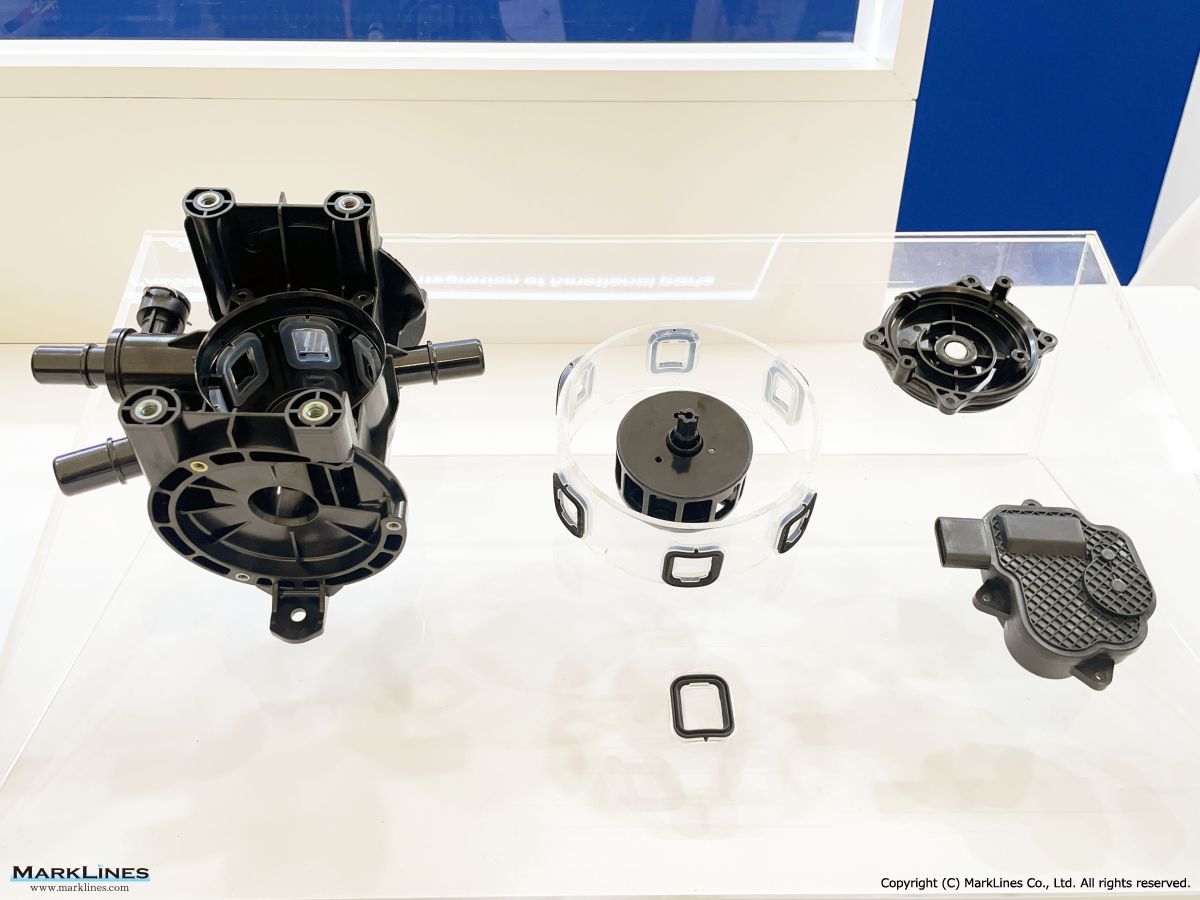
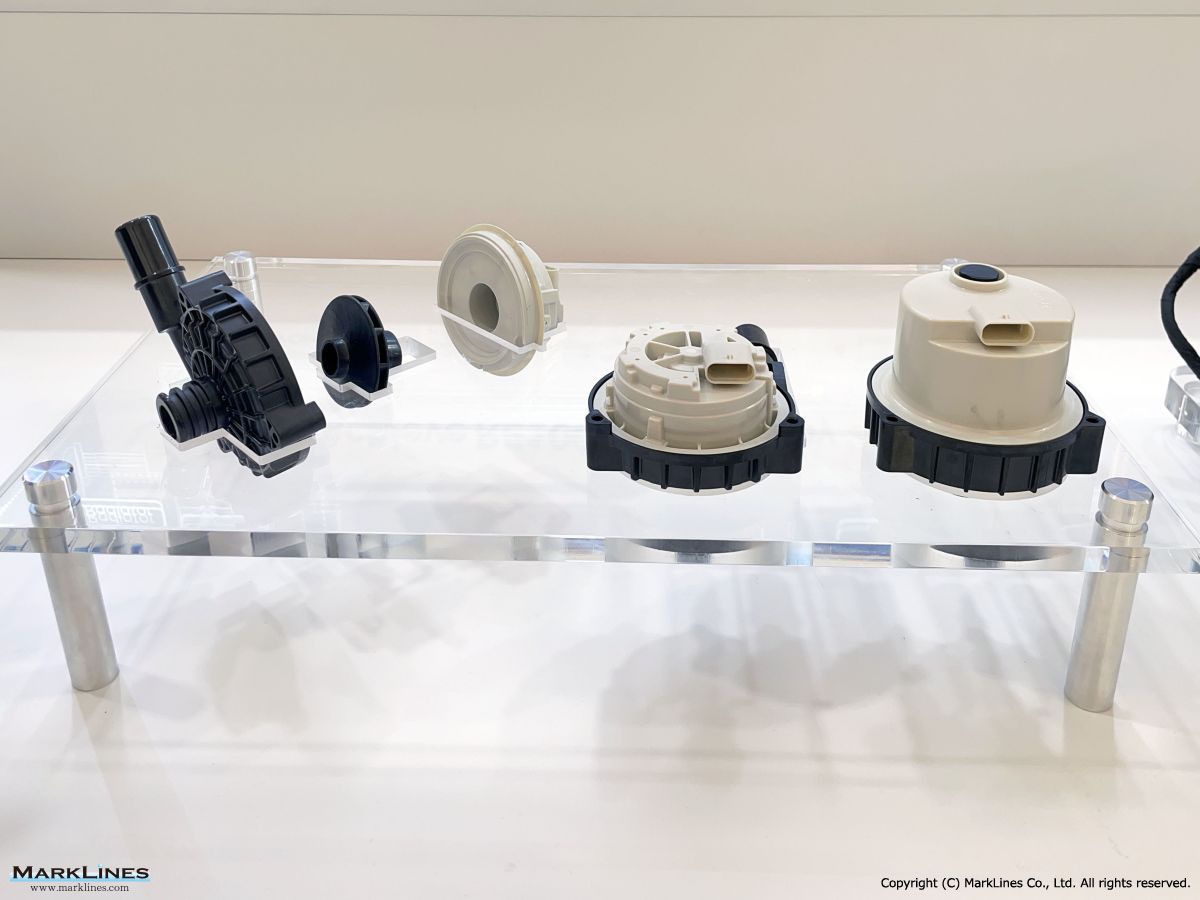
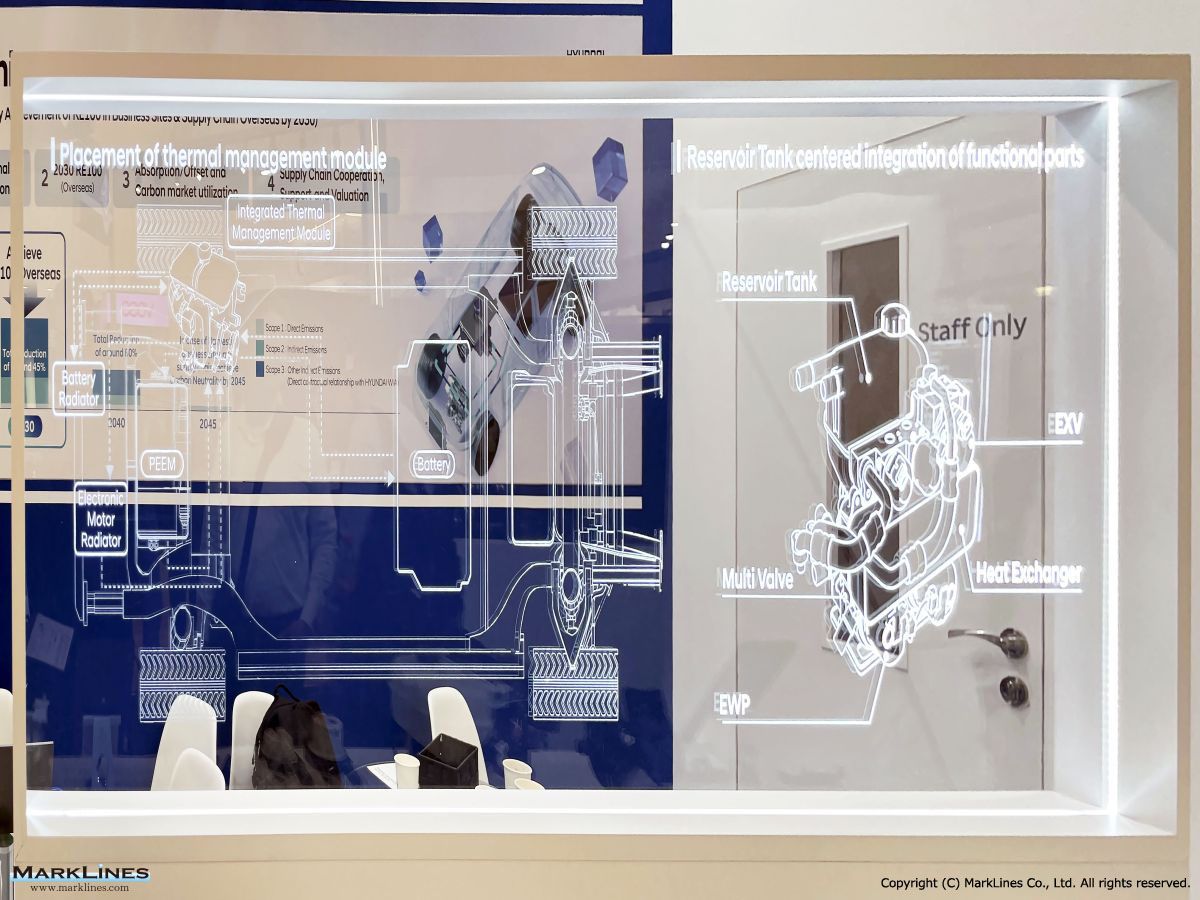
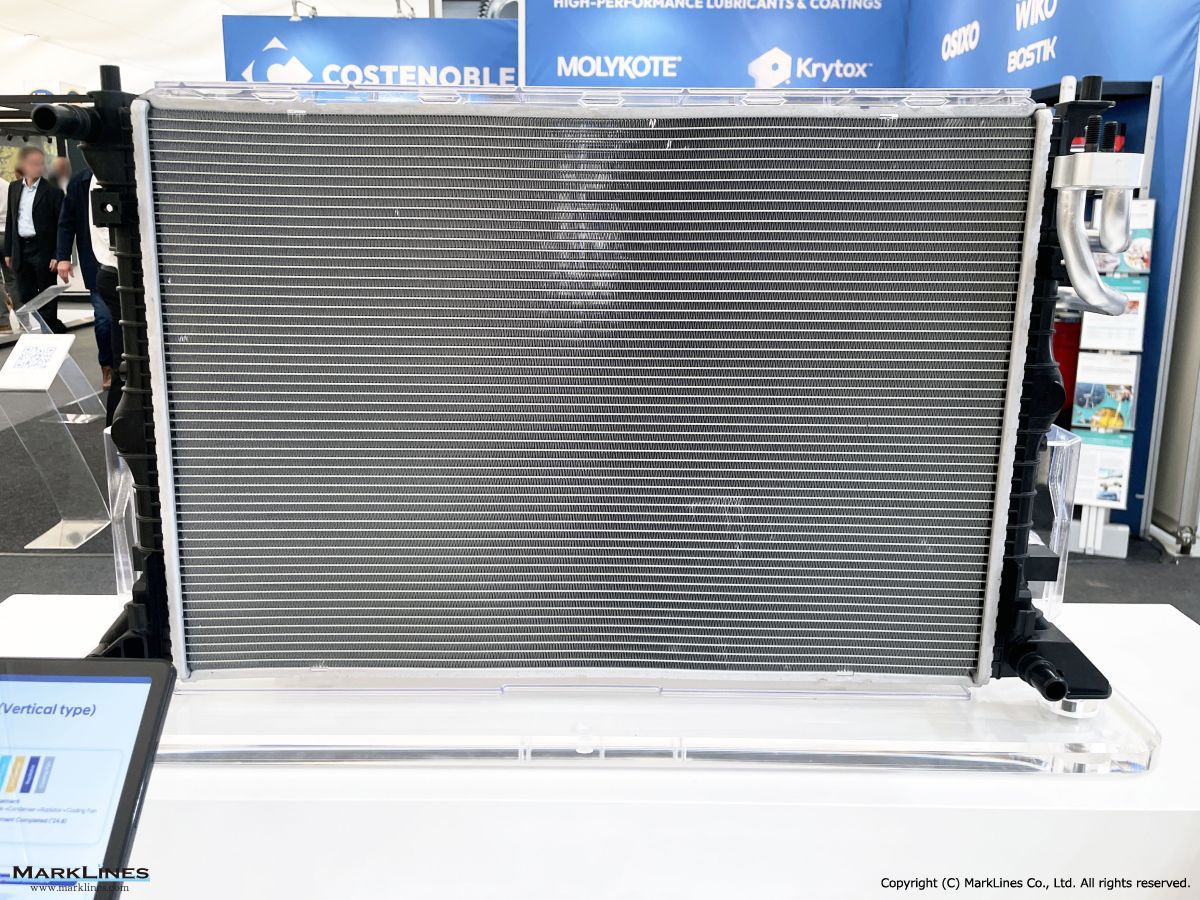
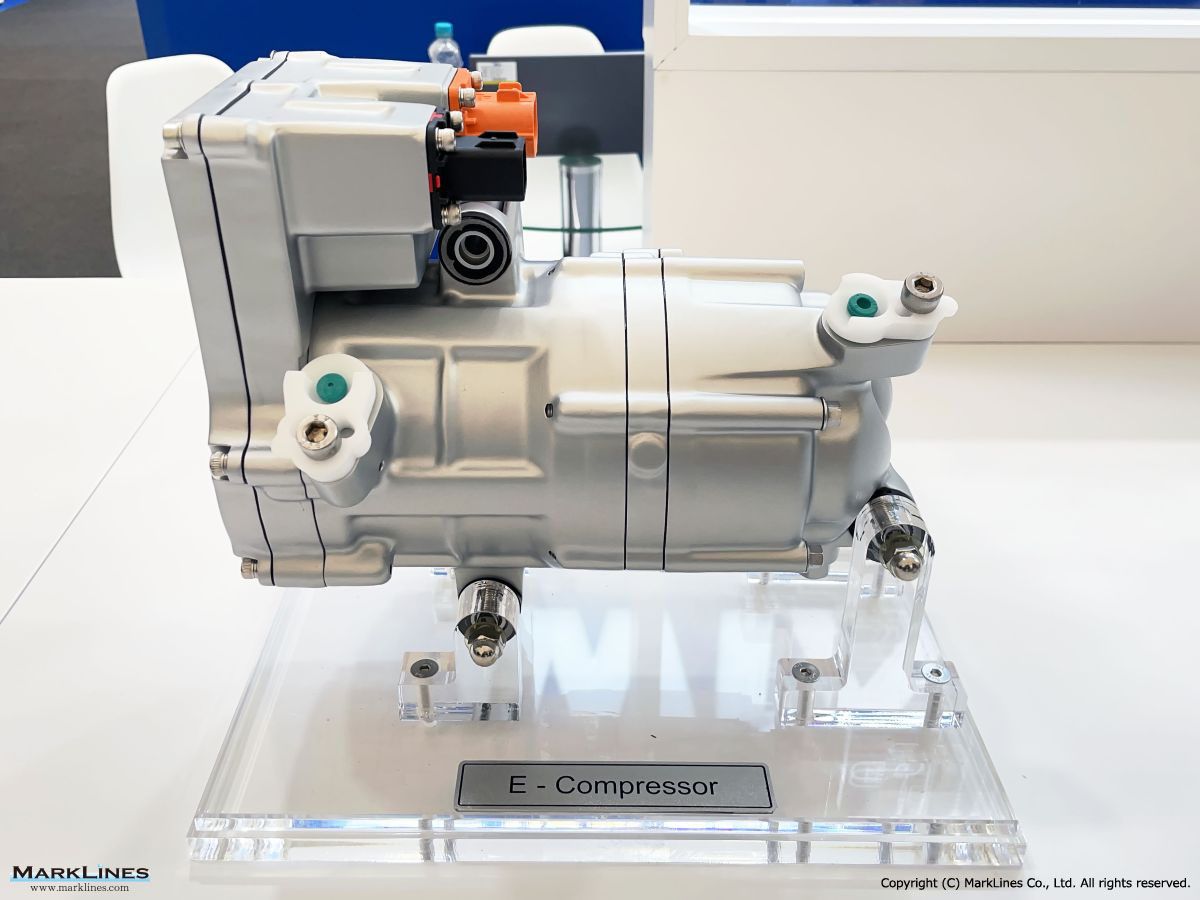
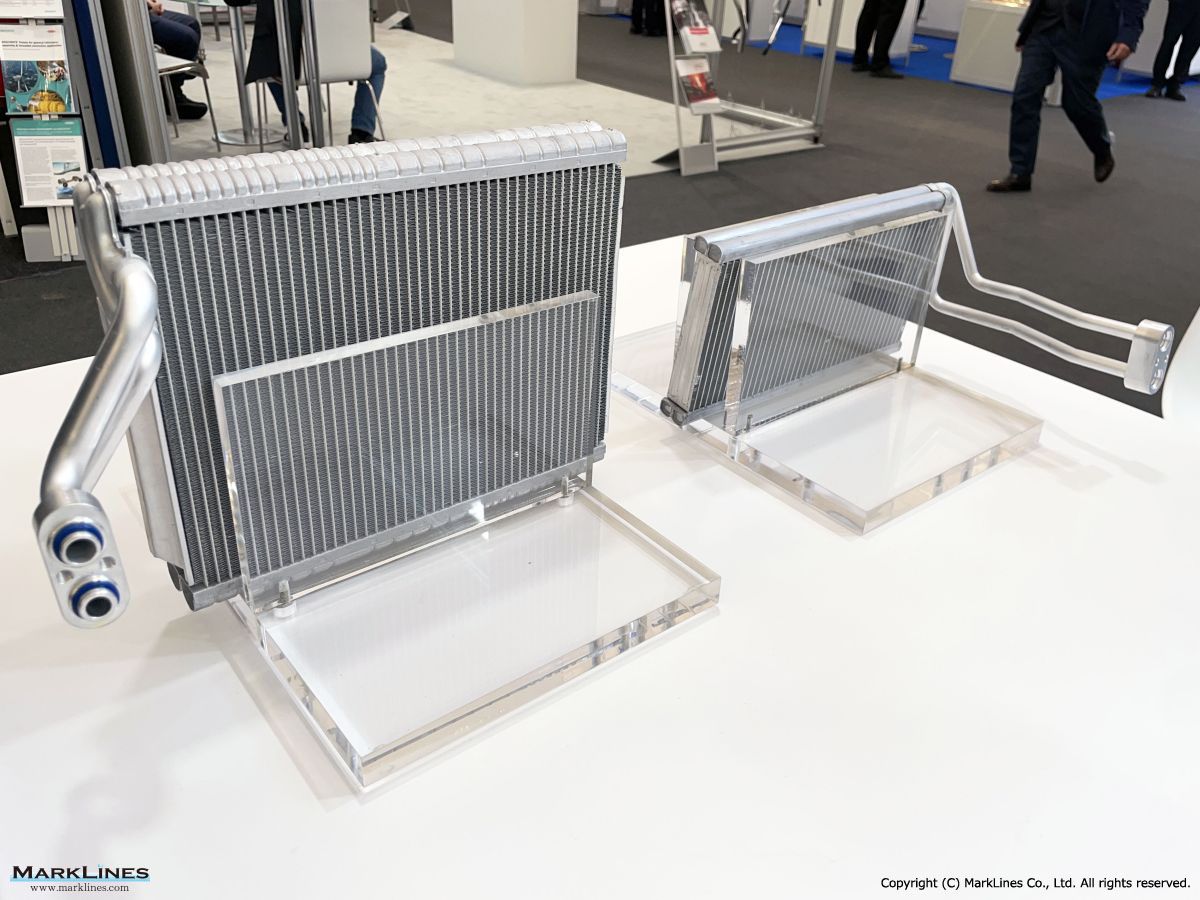
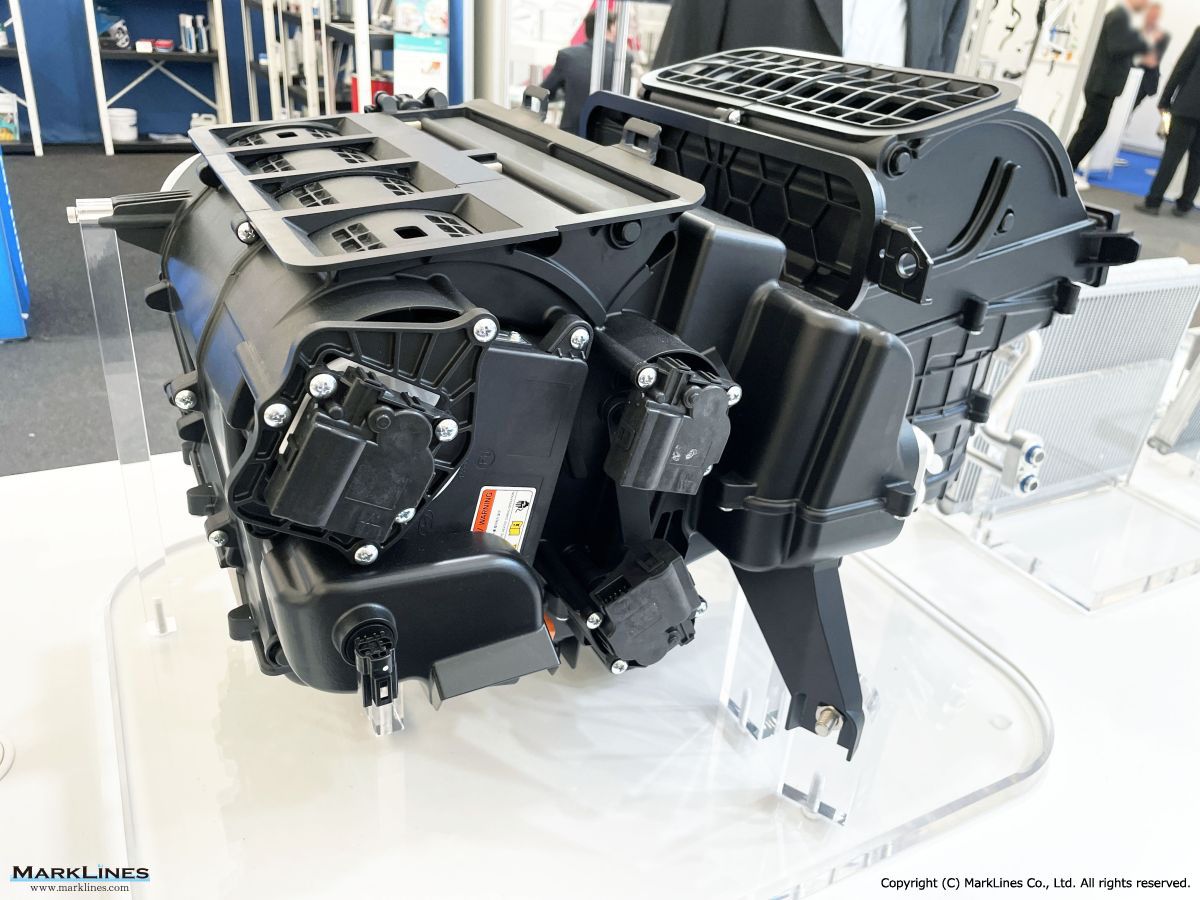
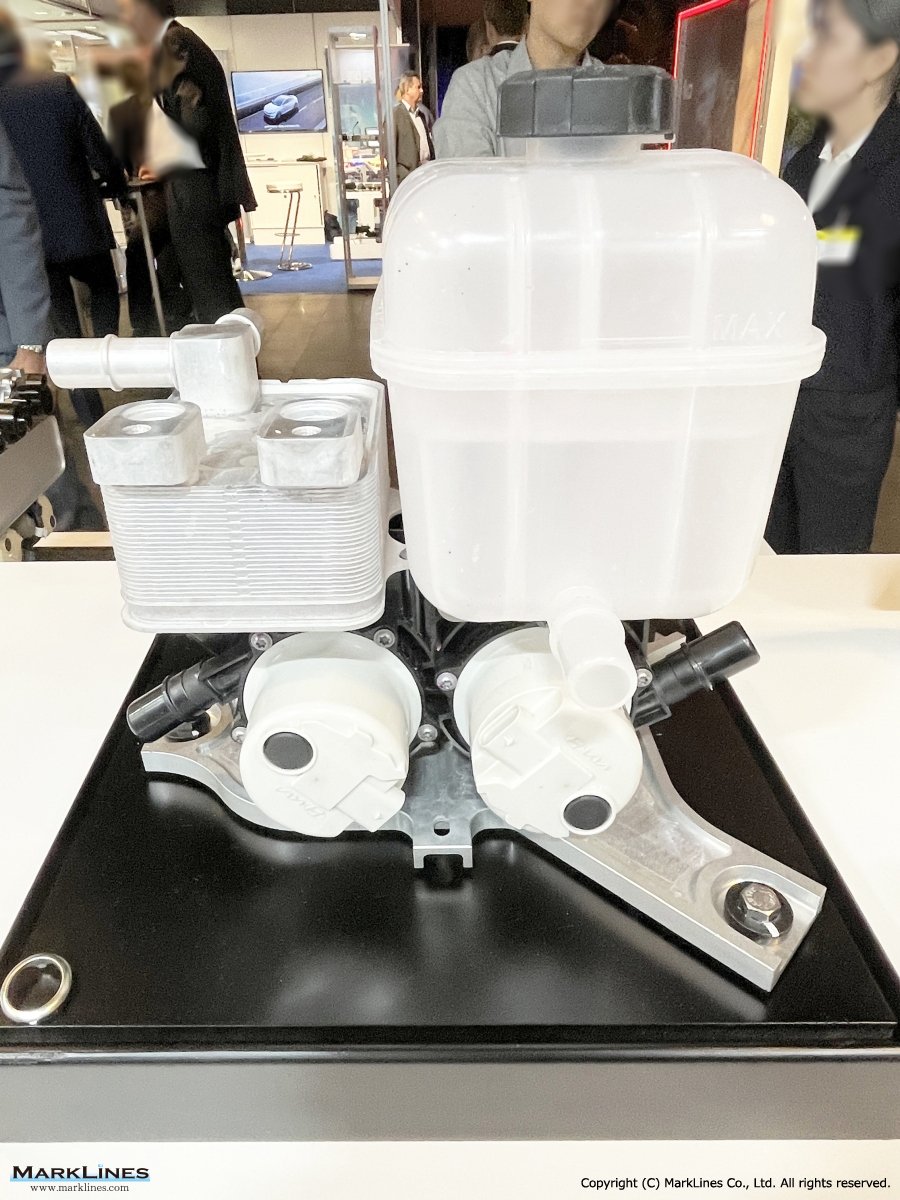
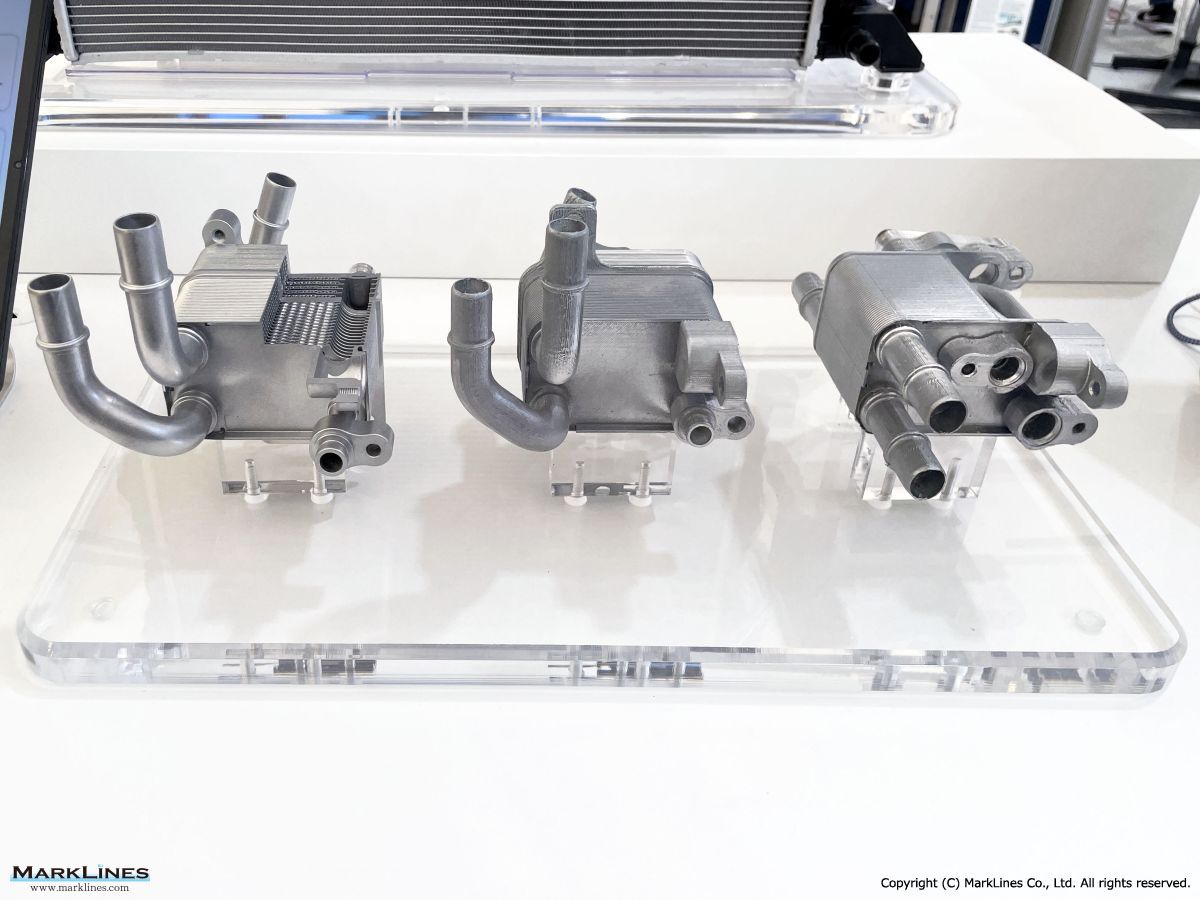
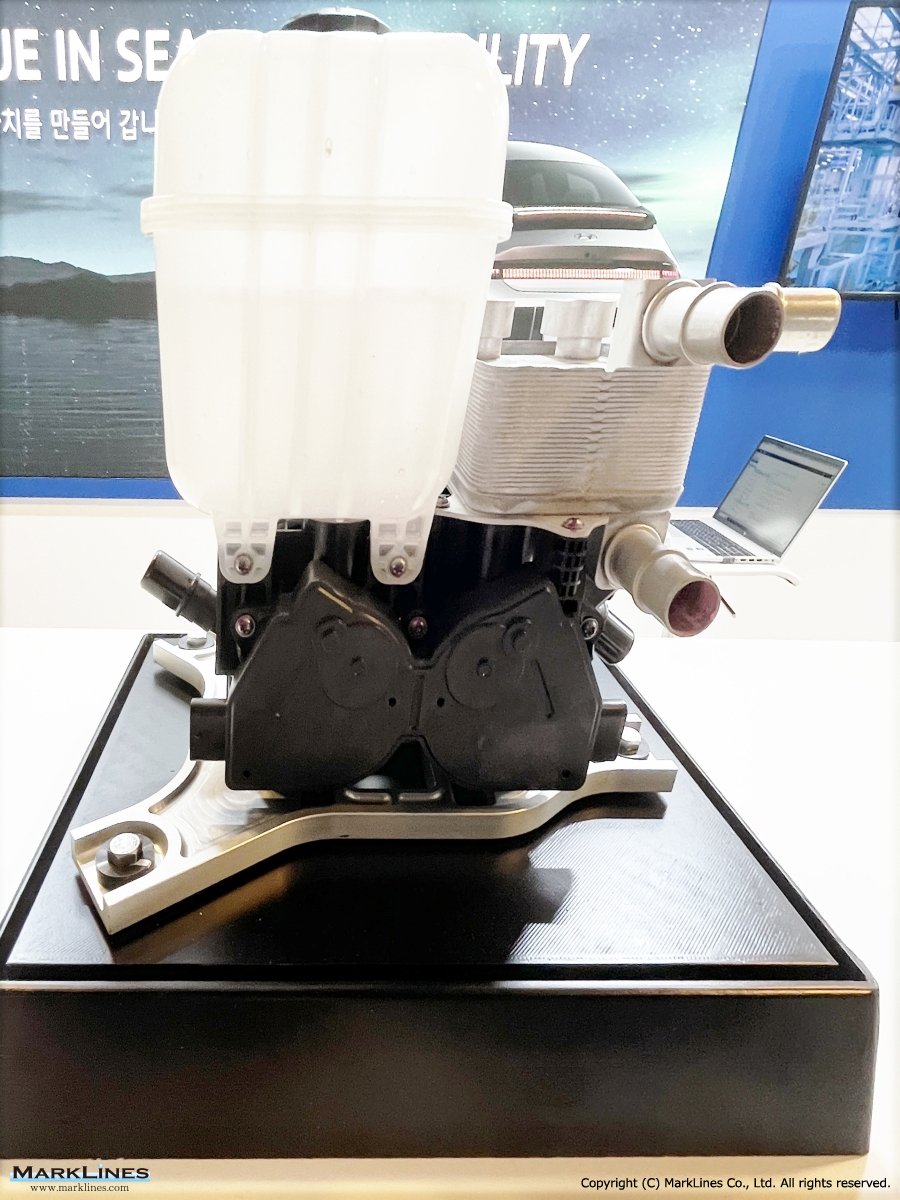
Thermal management
-Integrated thermal management systems
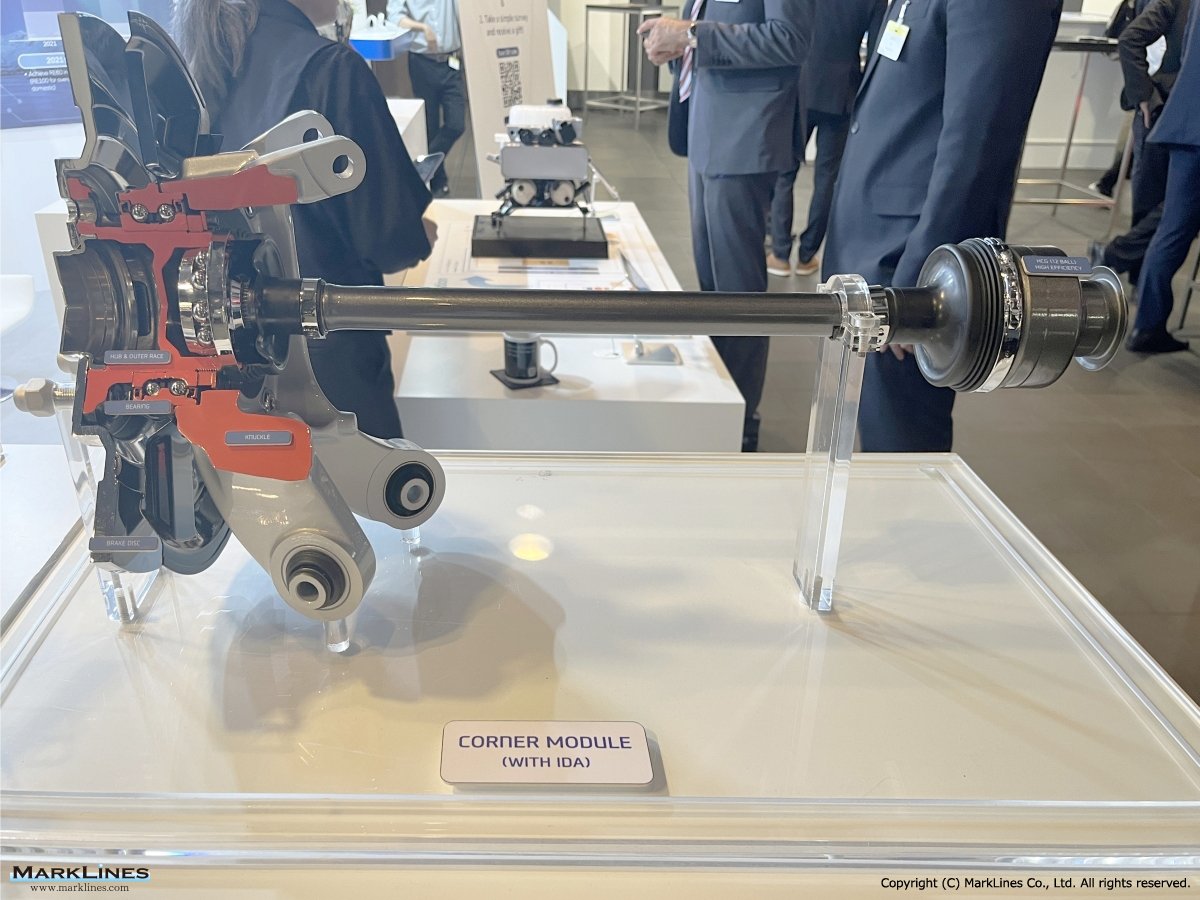
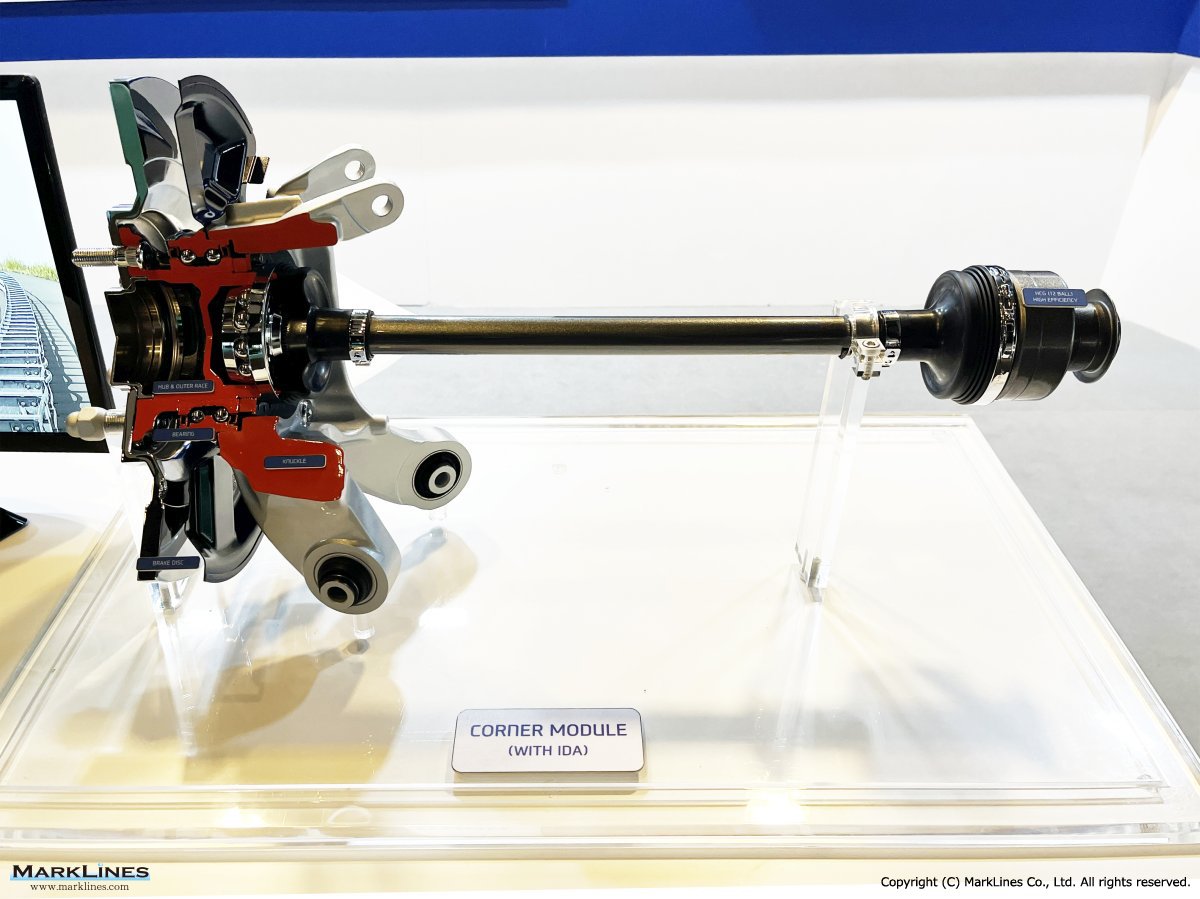
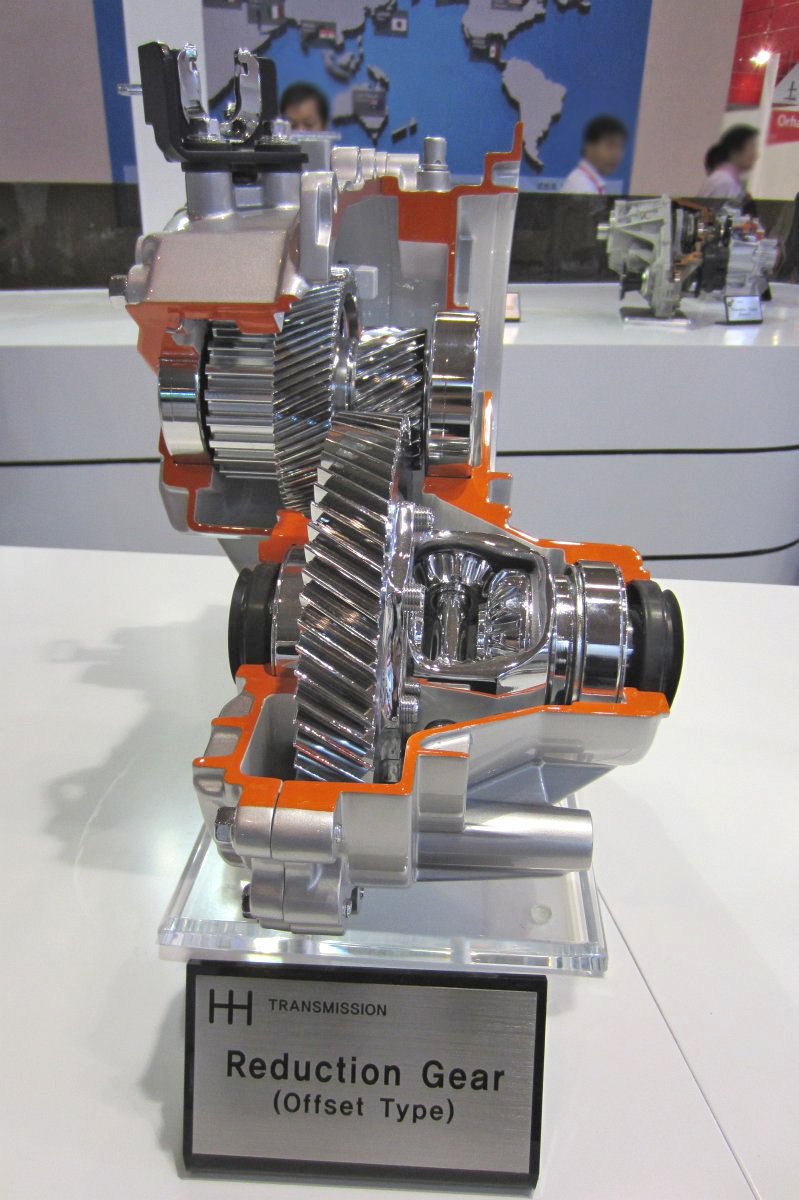
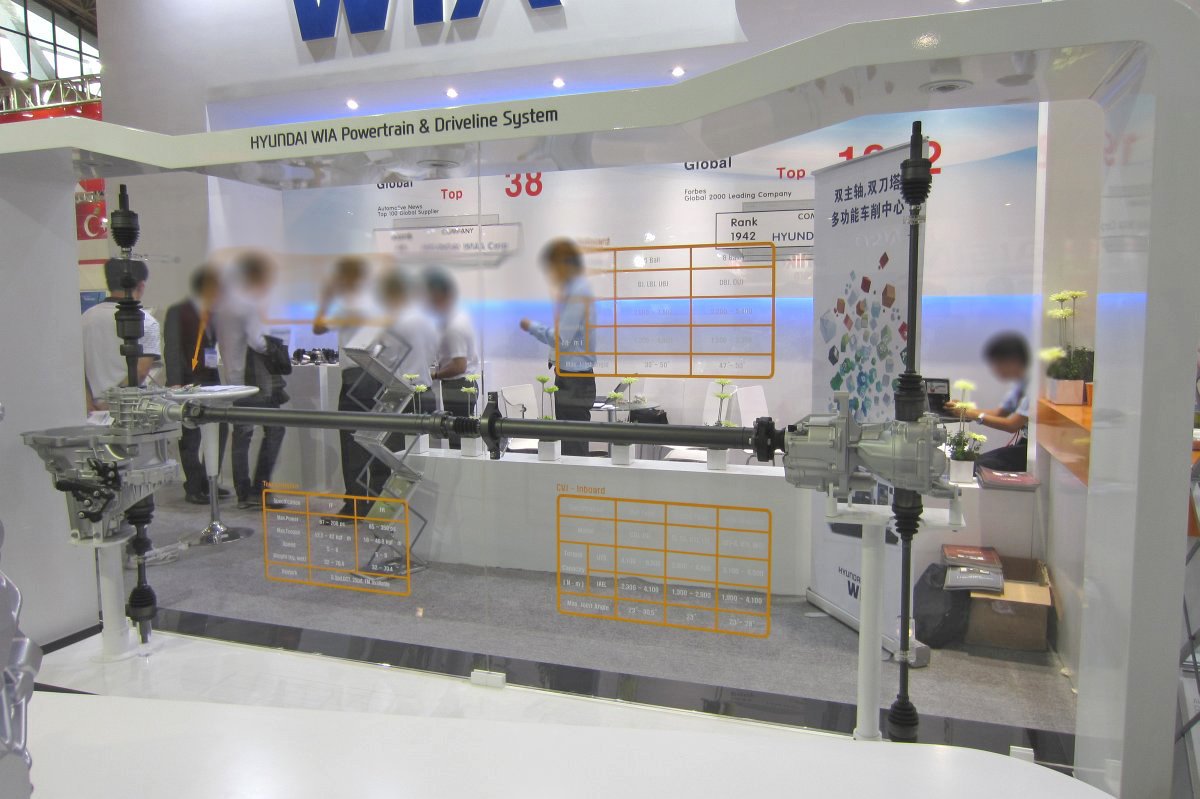
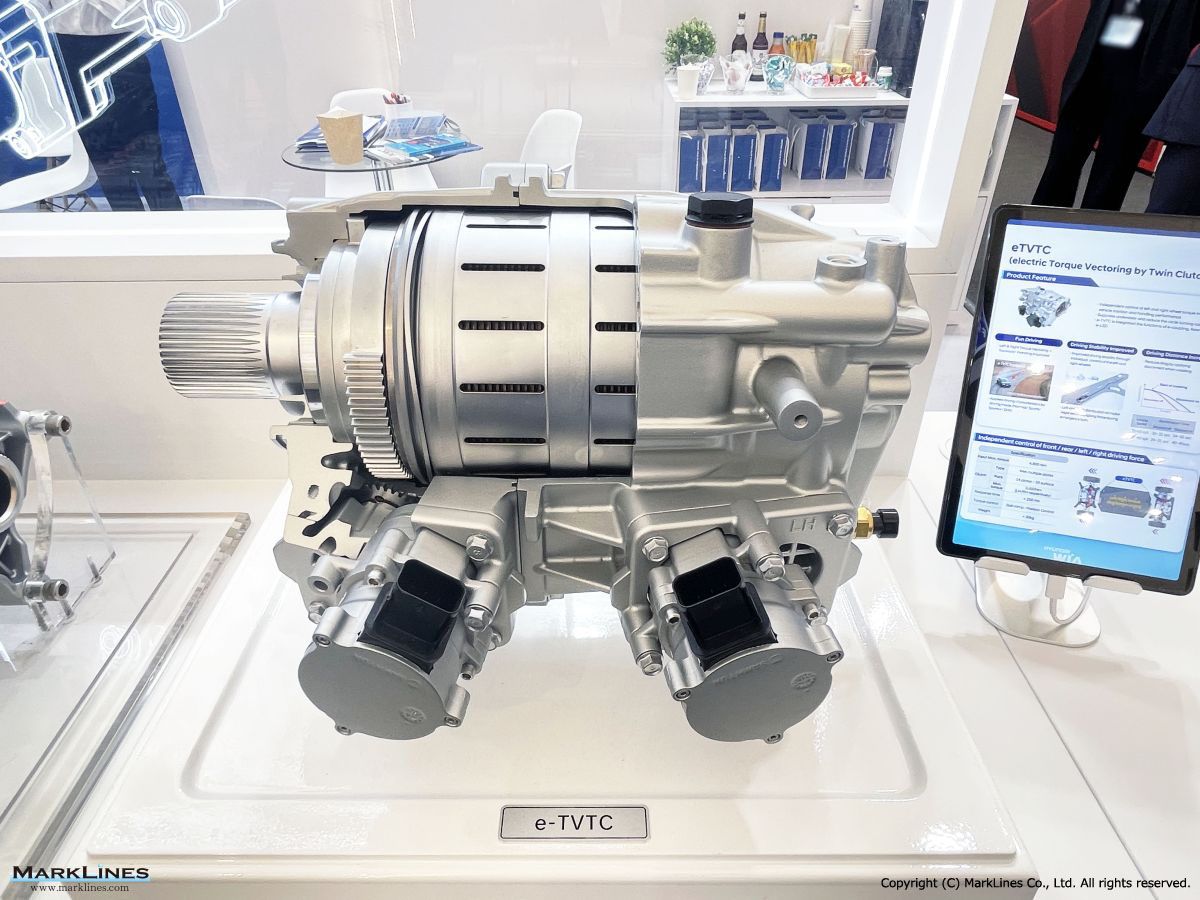
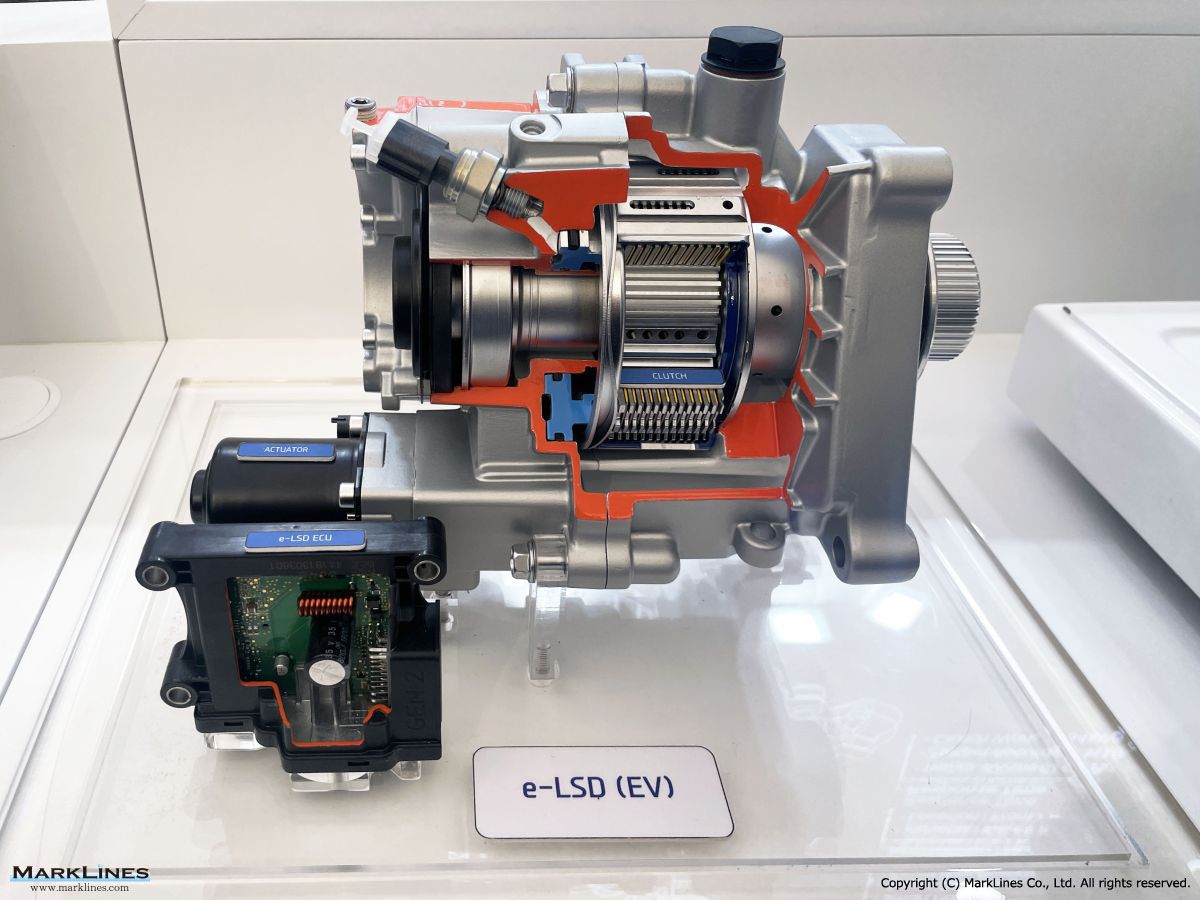
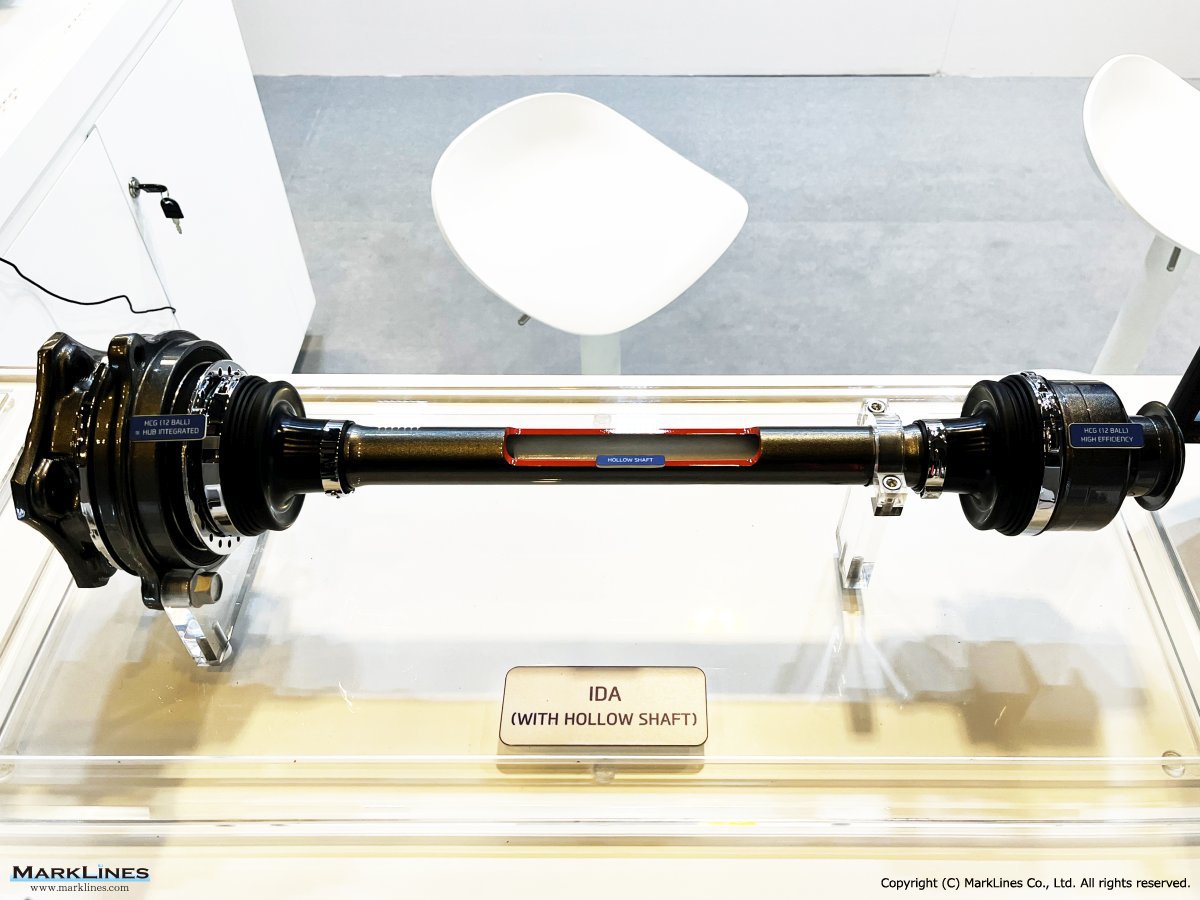
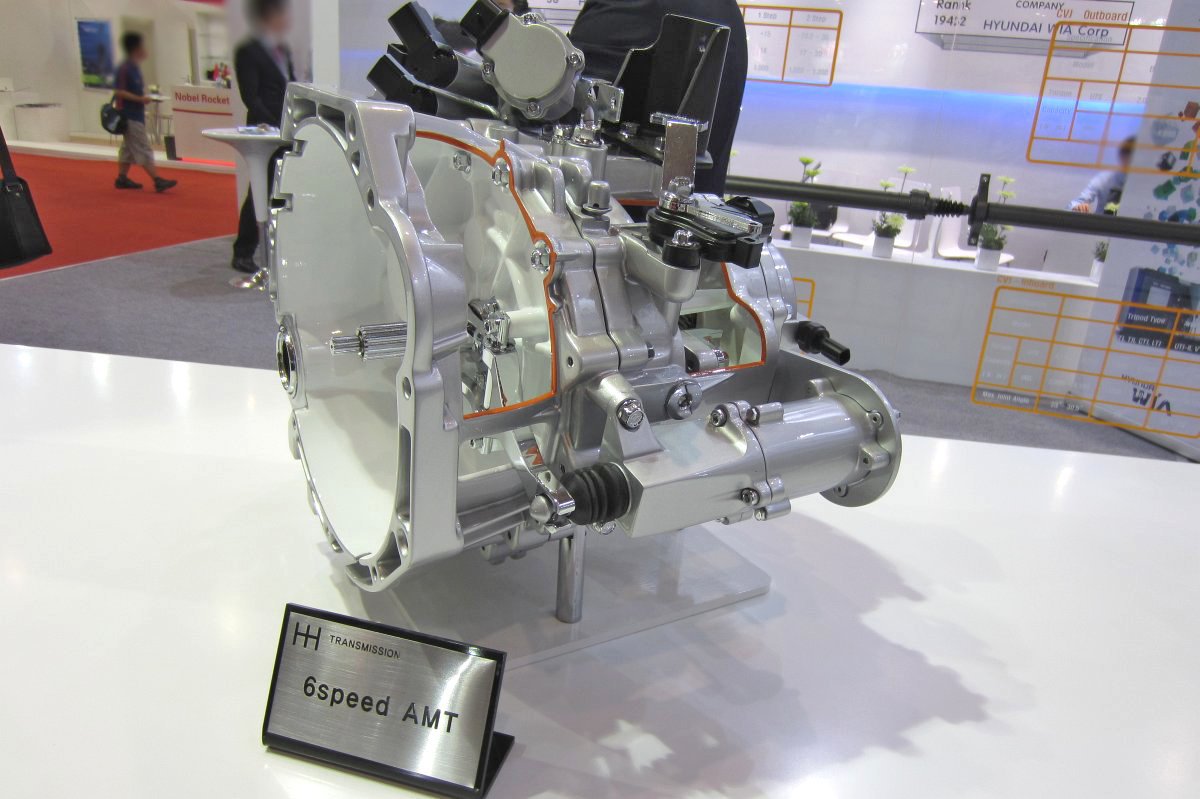
Driveline system
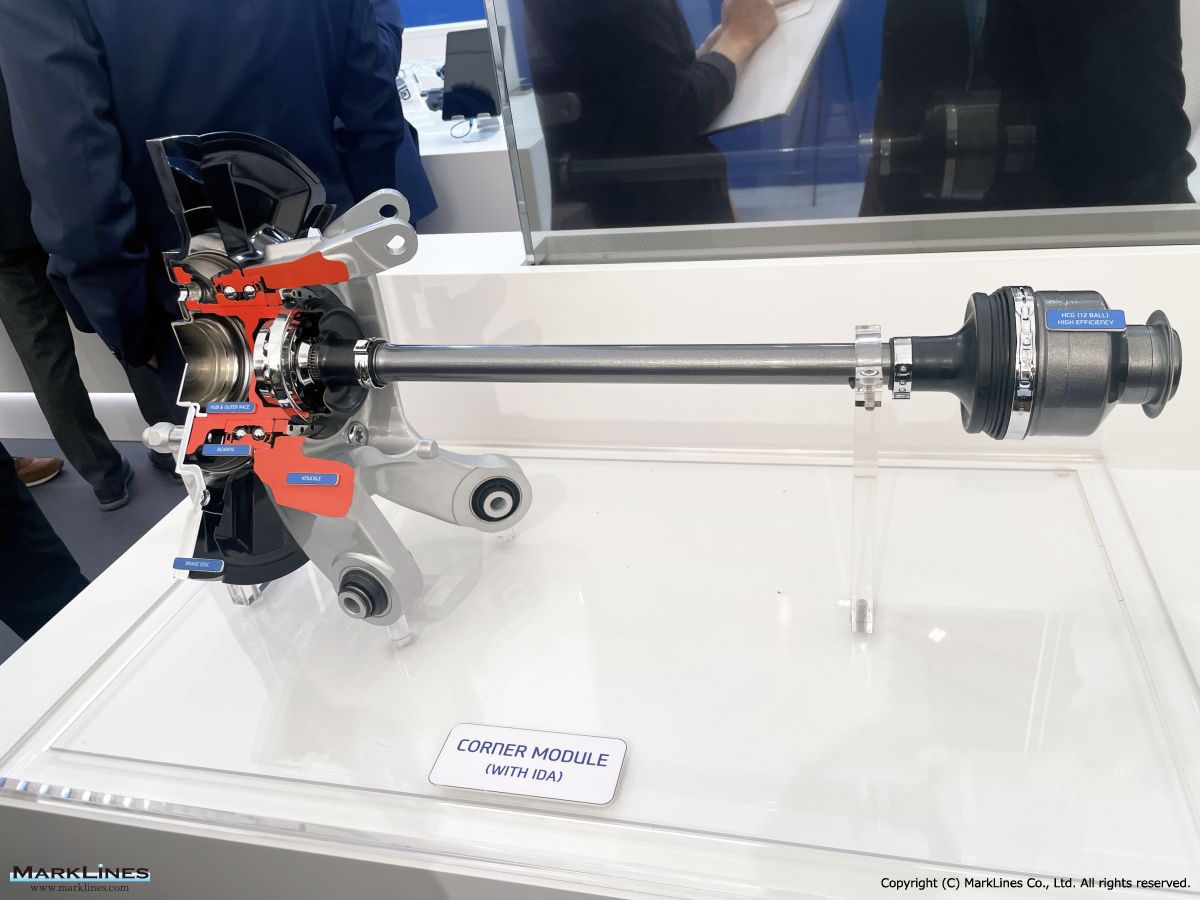
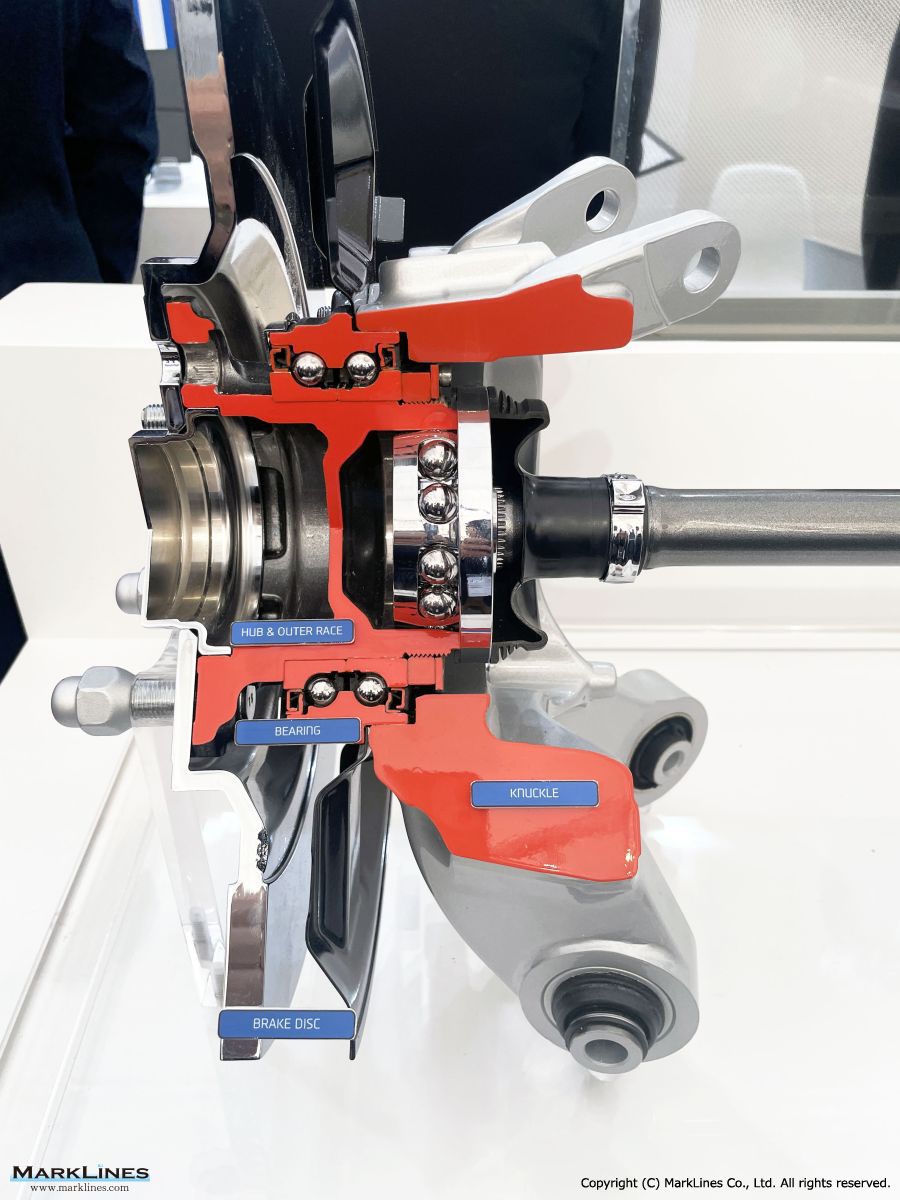
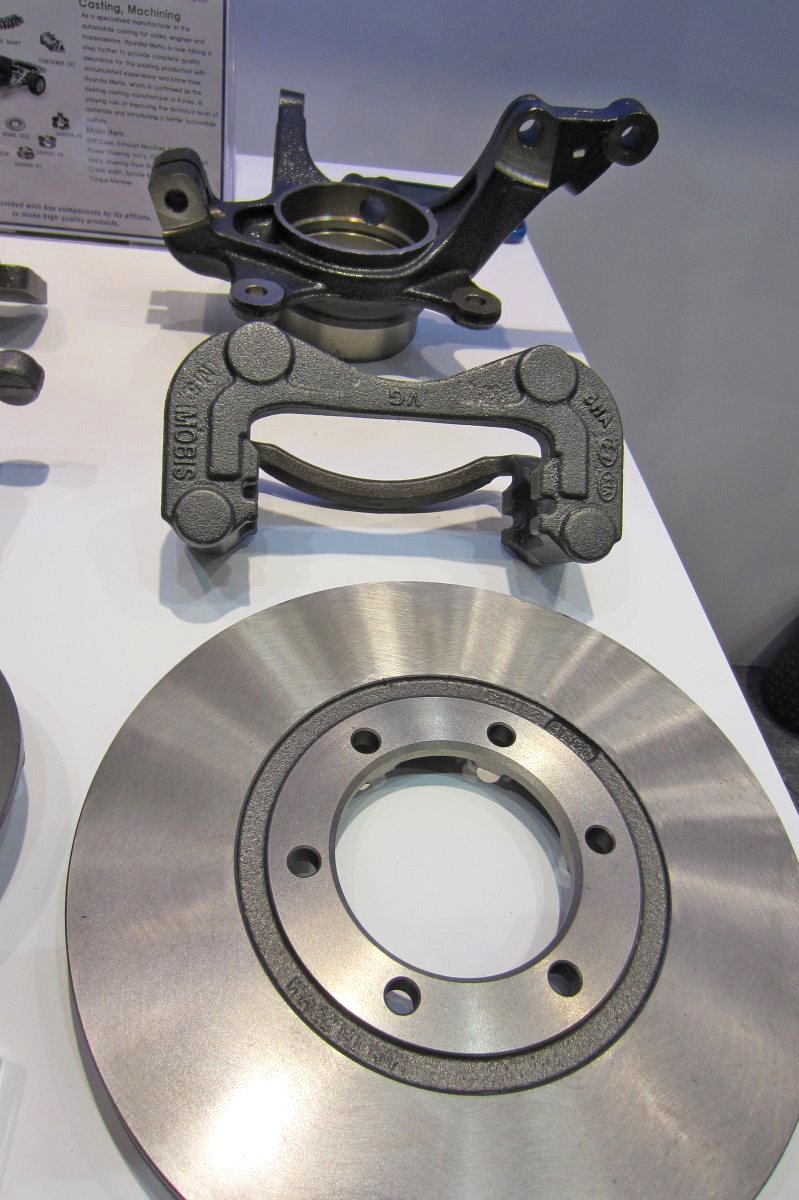
AXLE
- FR Axle/ FRONT (FR Axle/ FRONT)
- FR Axle / REAR (FR Axle/ REAR)
- FF Axle
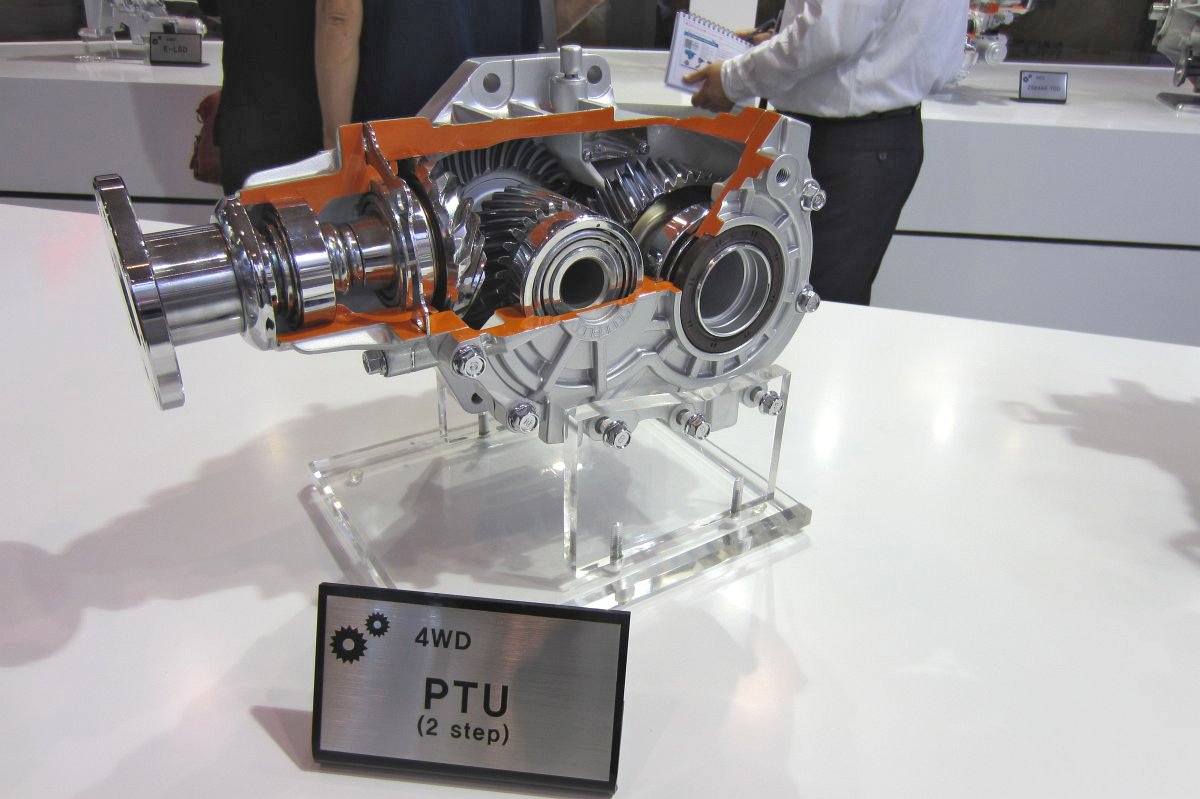
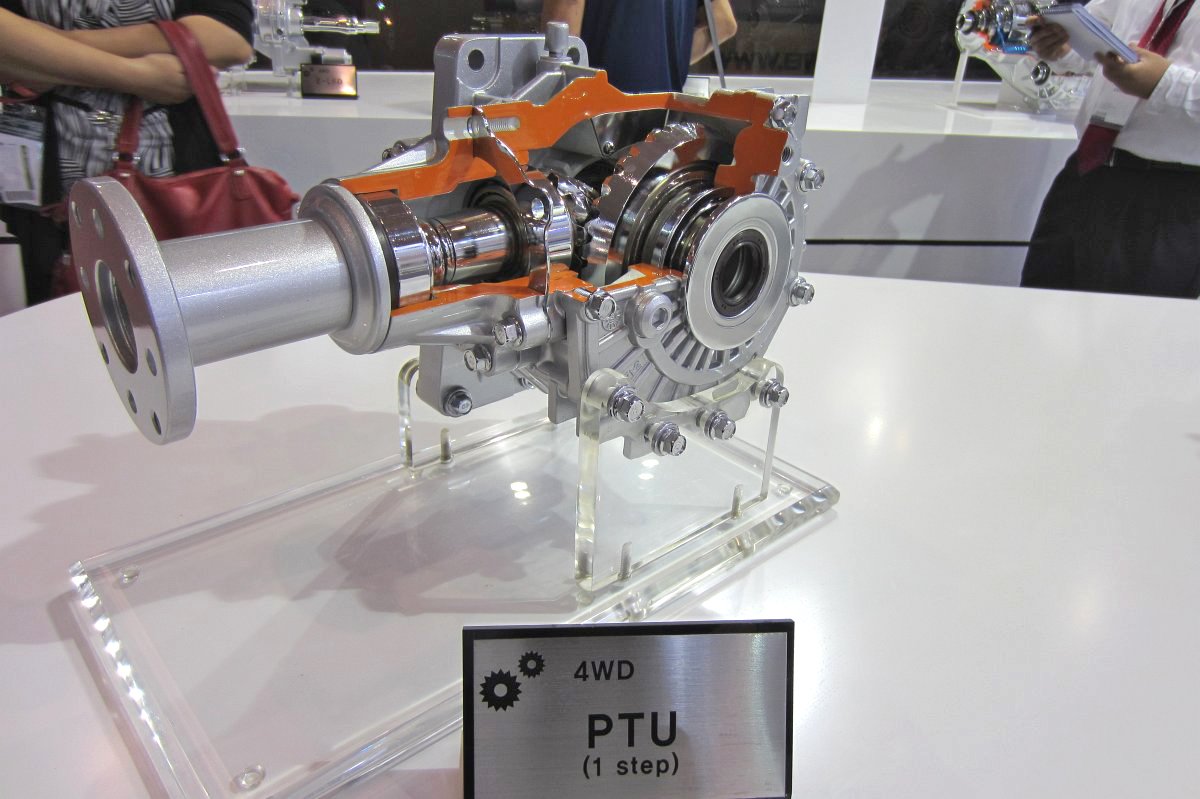
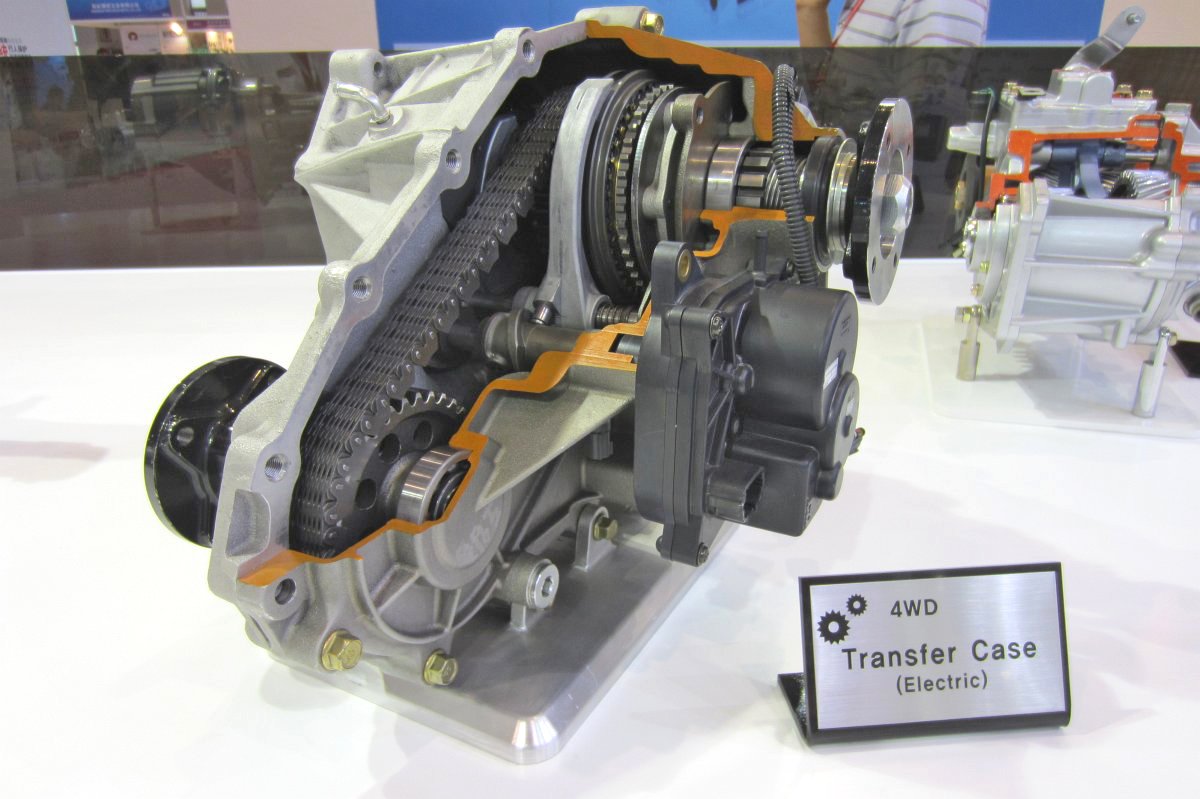
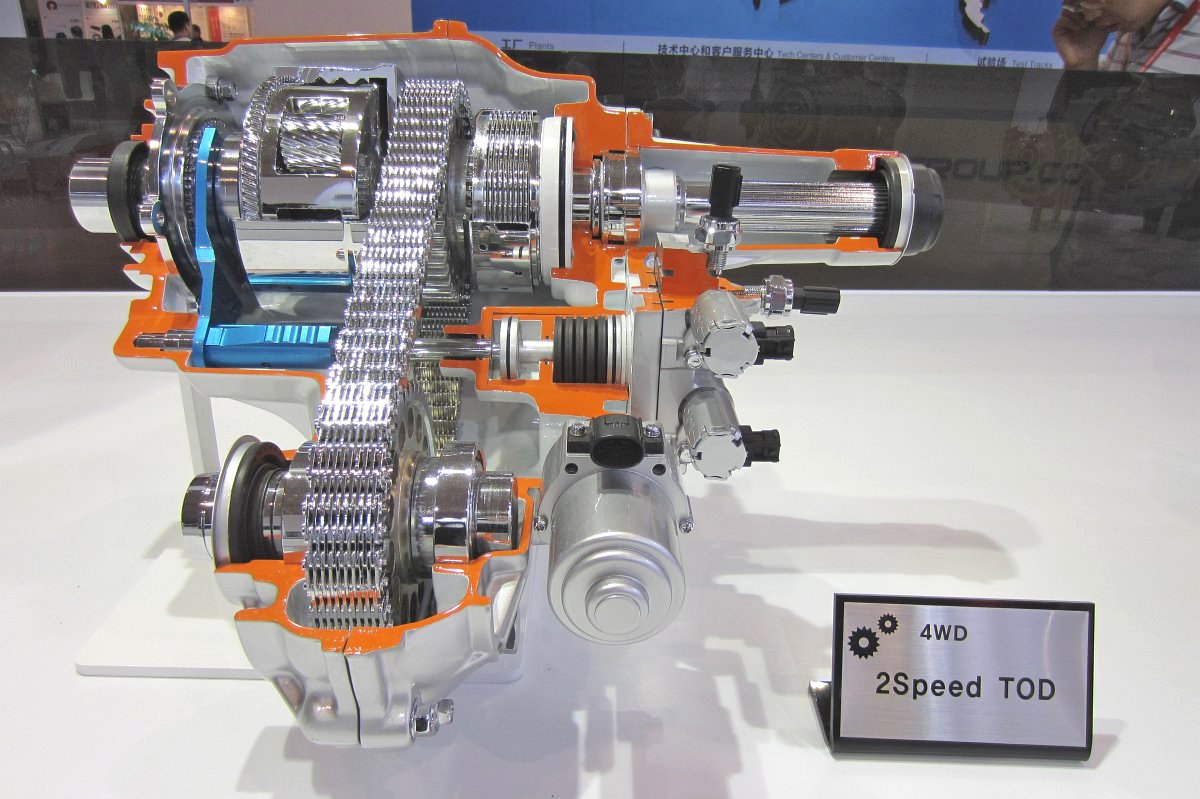
PTU (Power Transfer Unit)
-1-axis PTU
-2-axis PTU
- Offset PTU
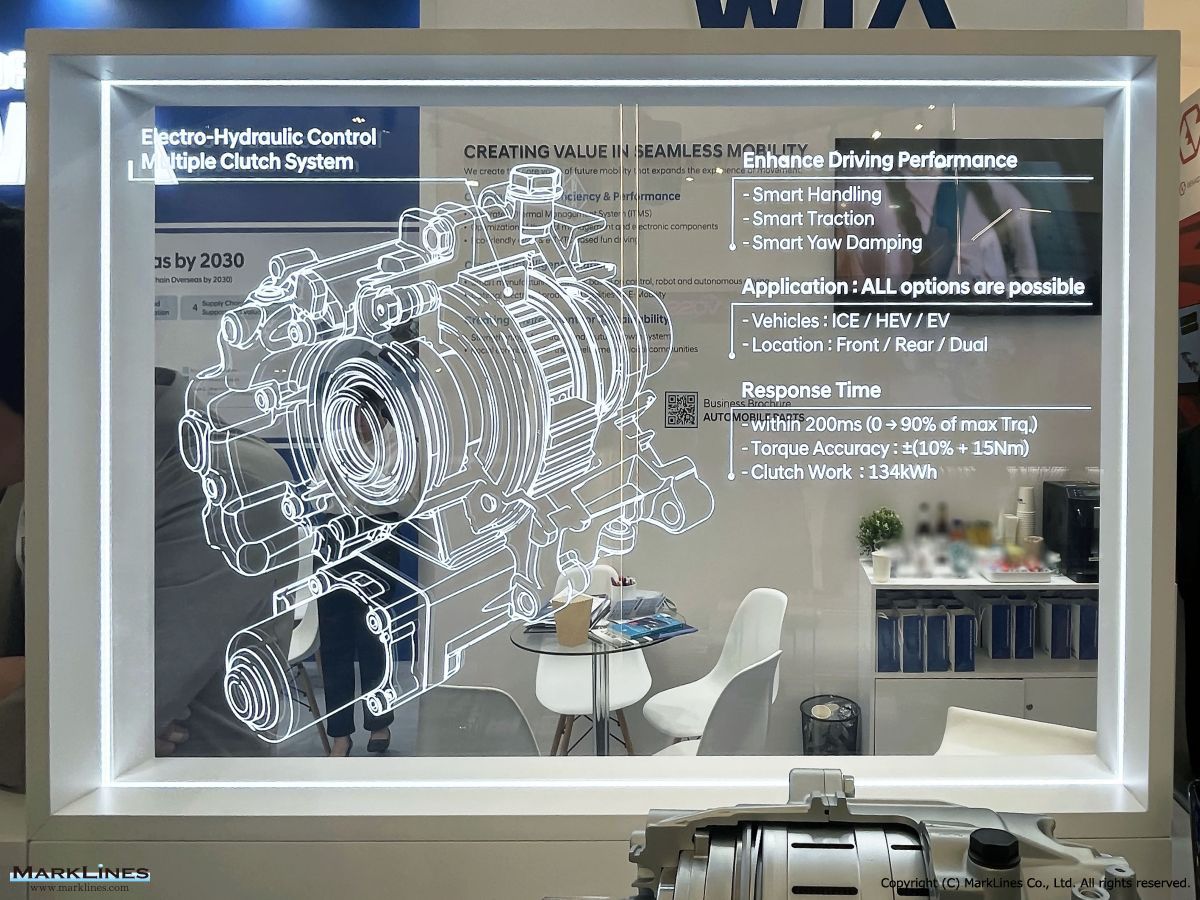
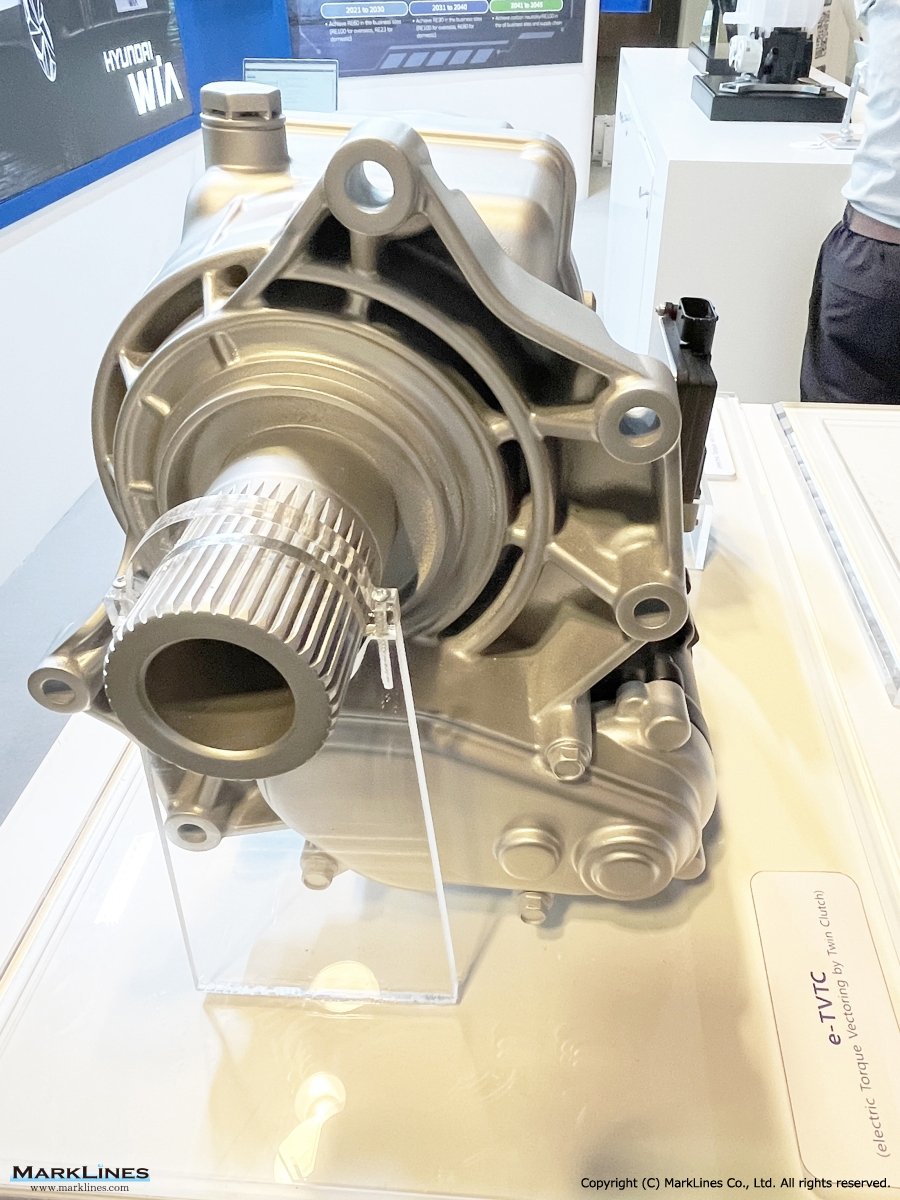
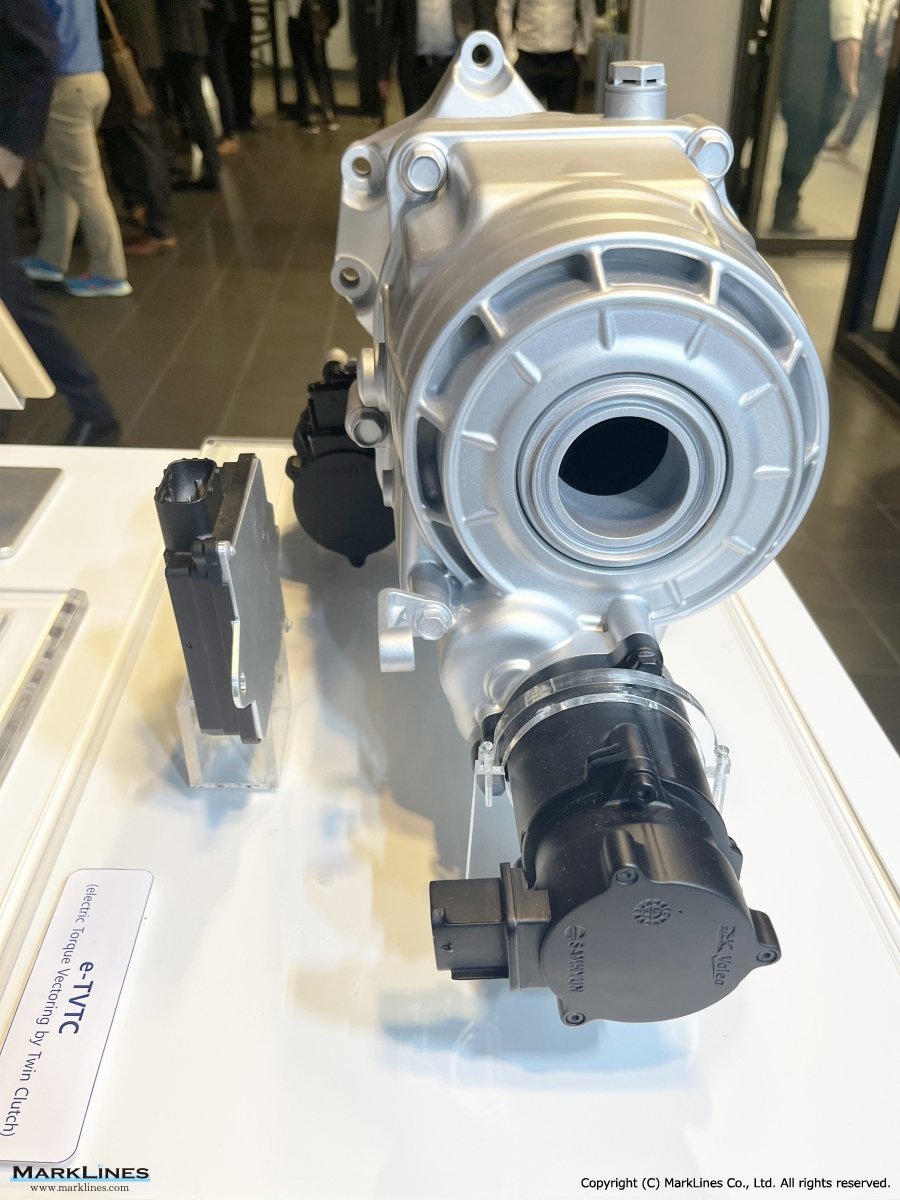
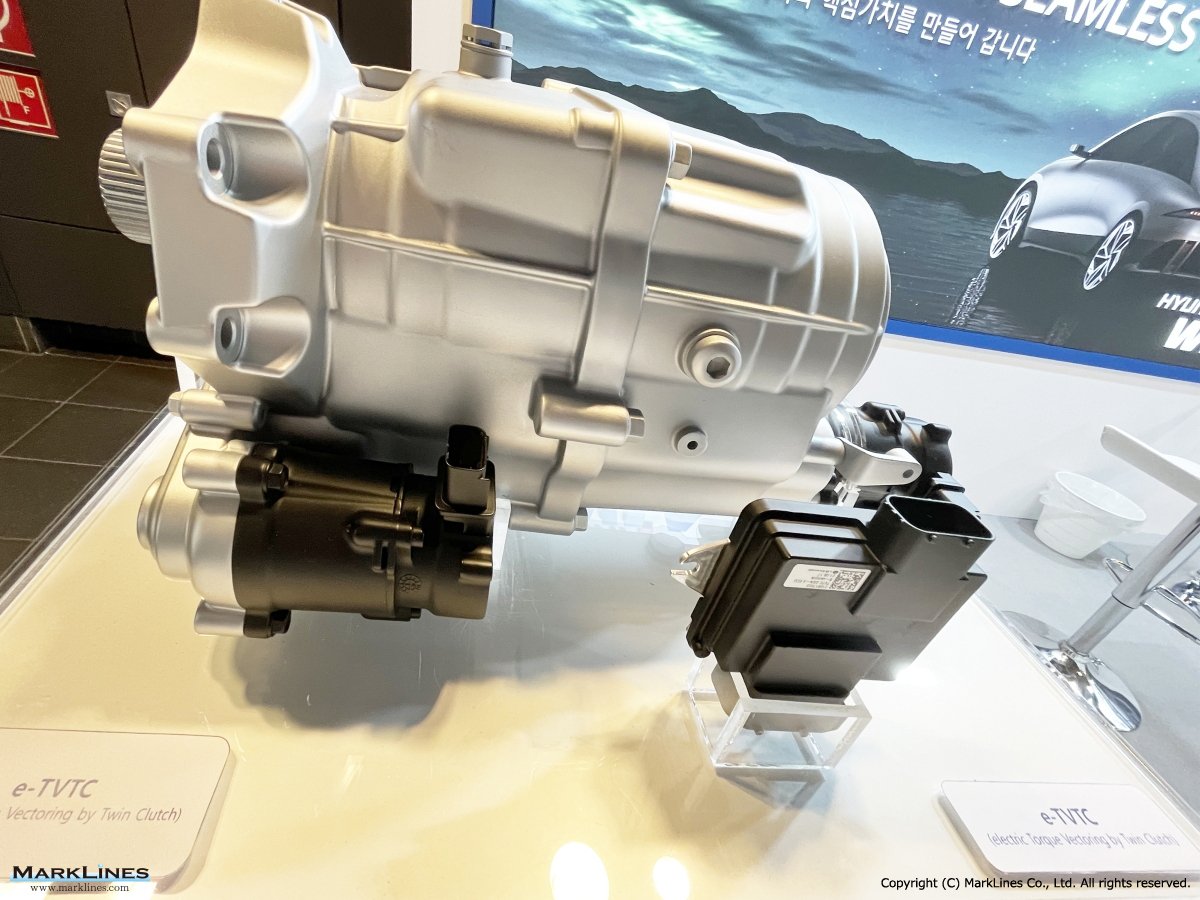
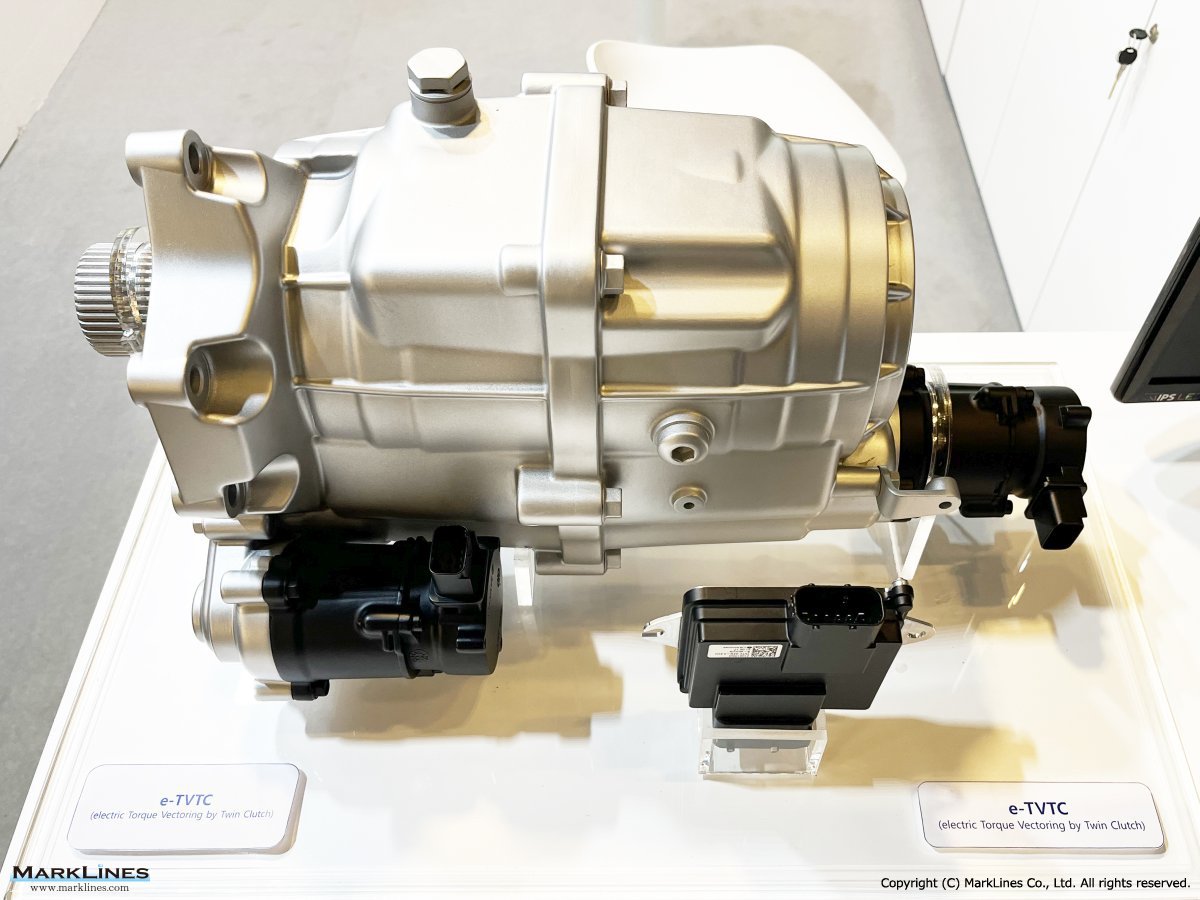
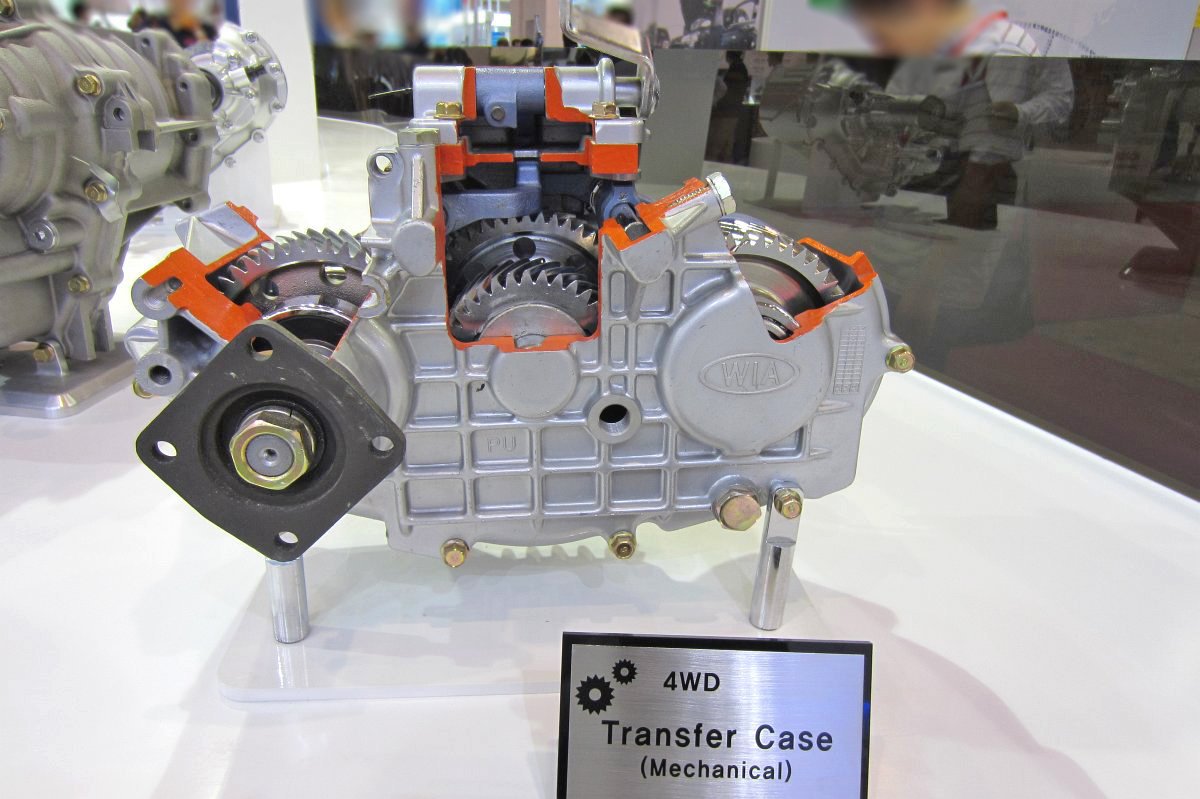
ATC (Active Transfer Case)
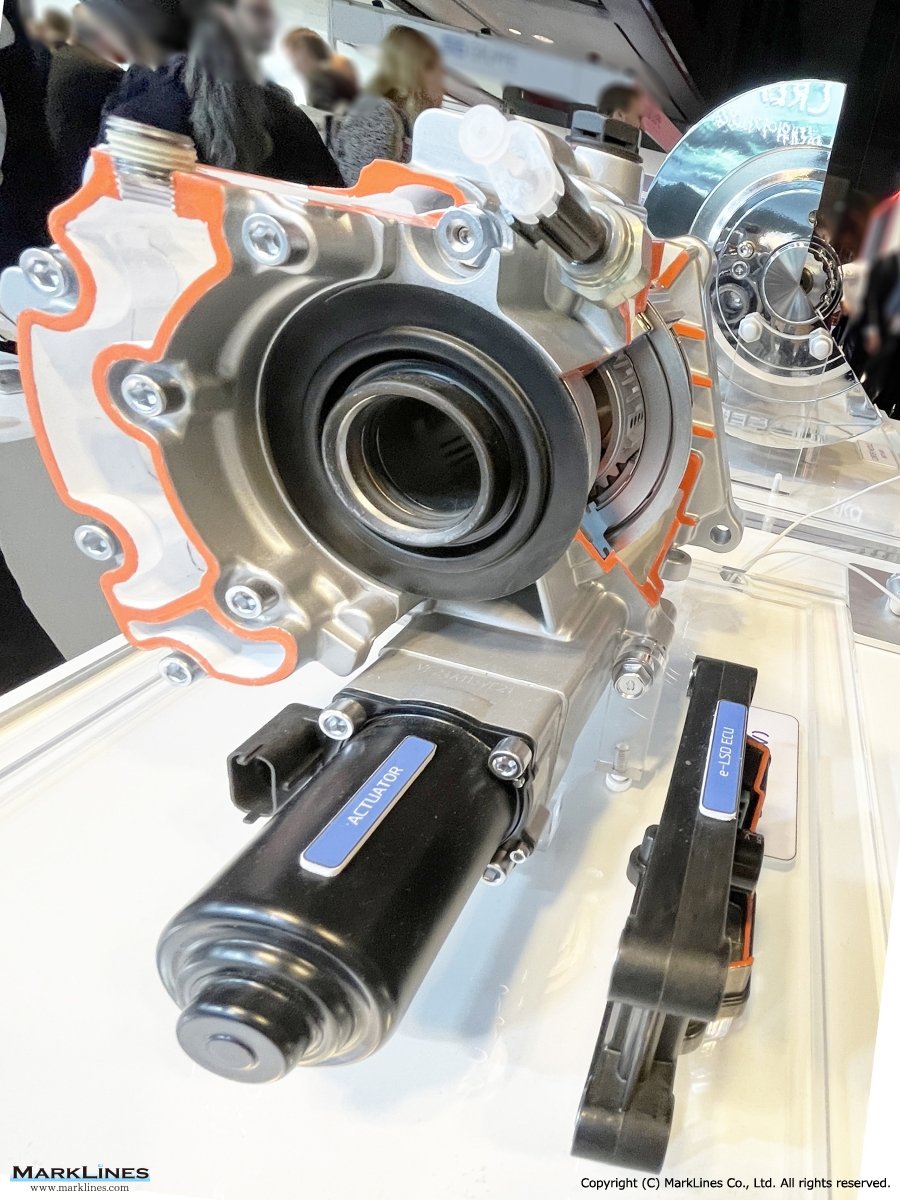
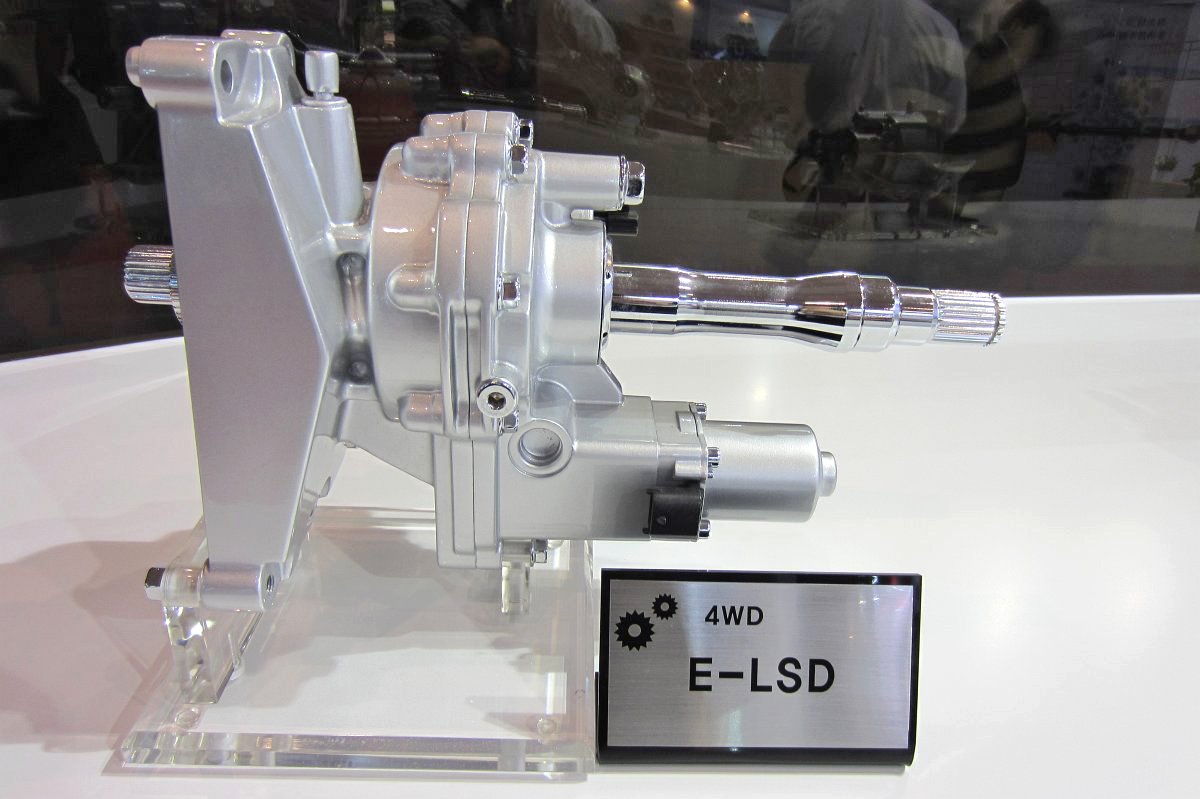
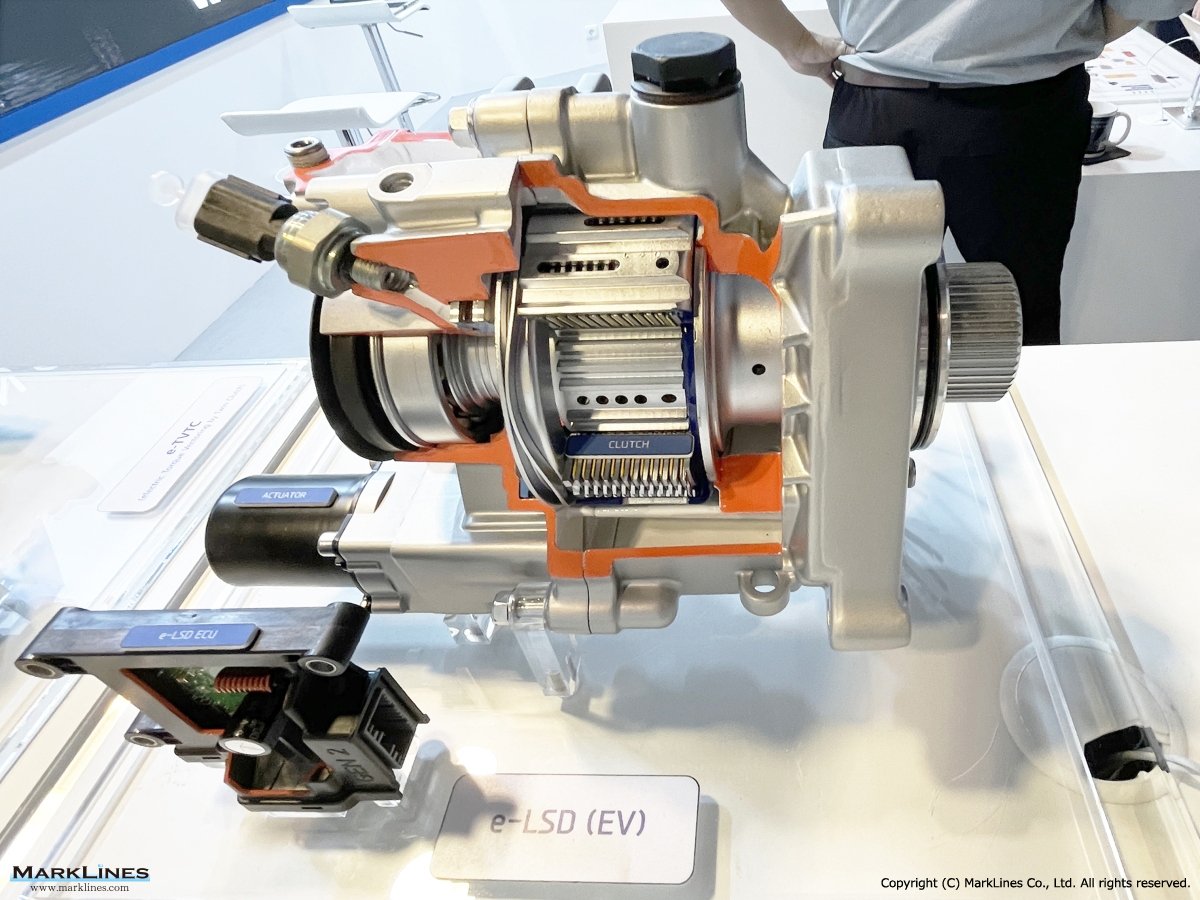
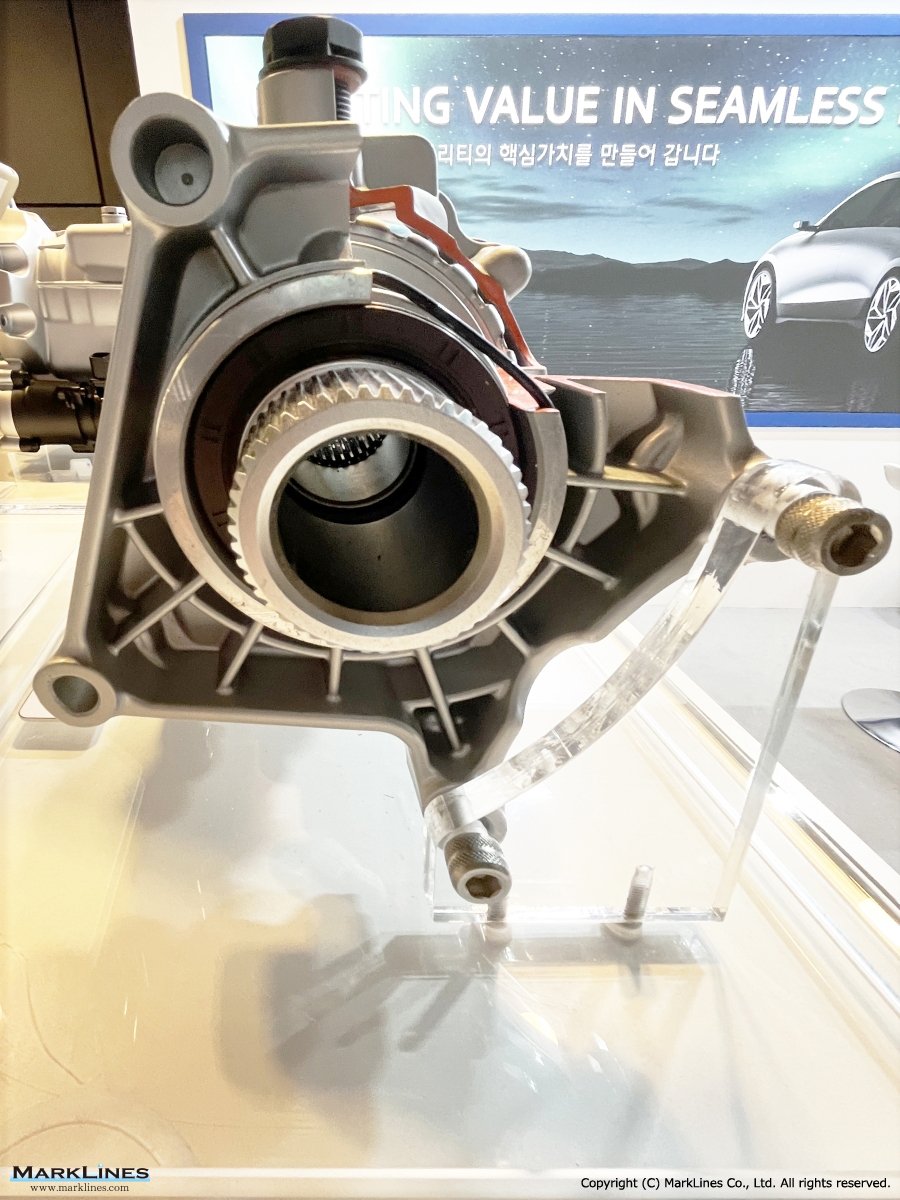
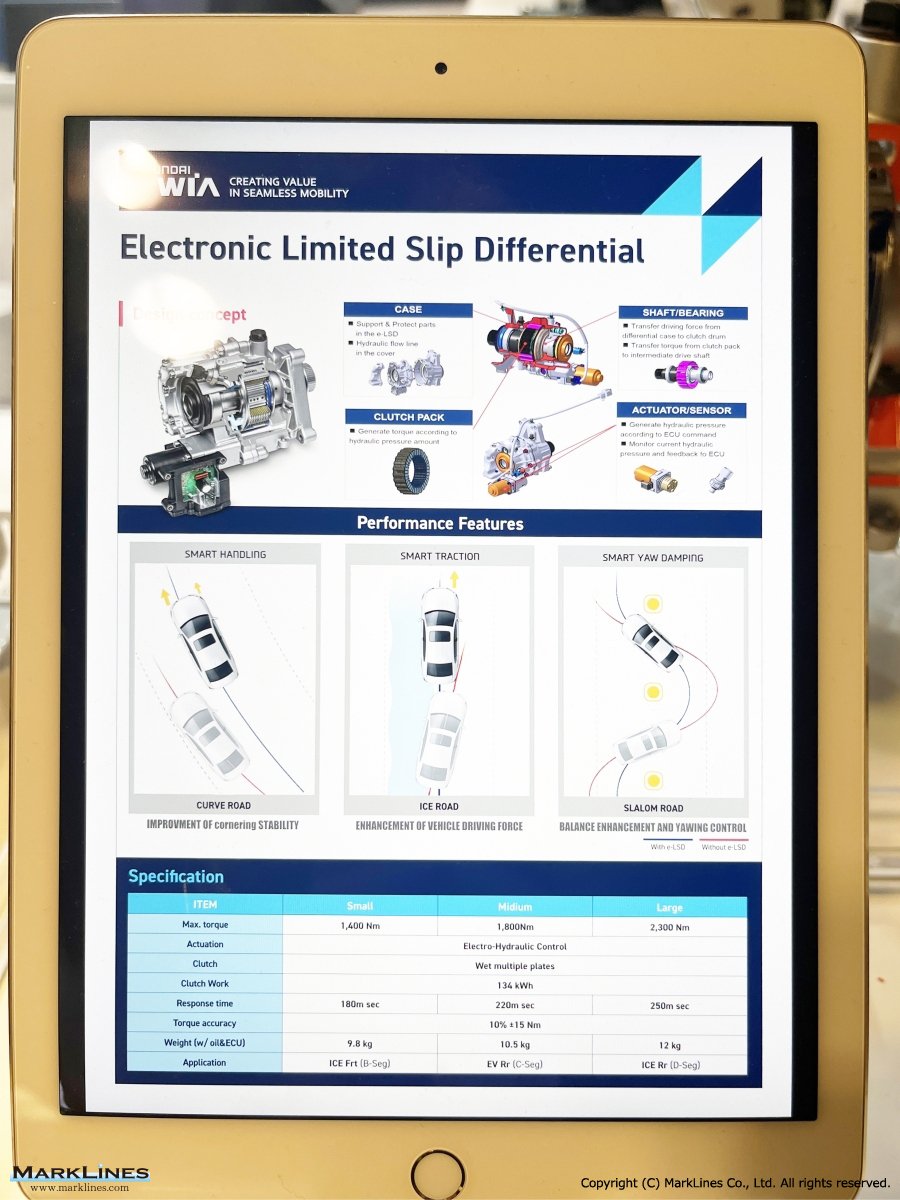
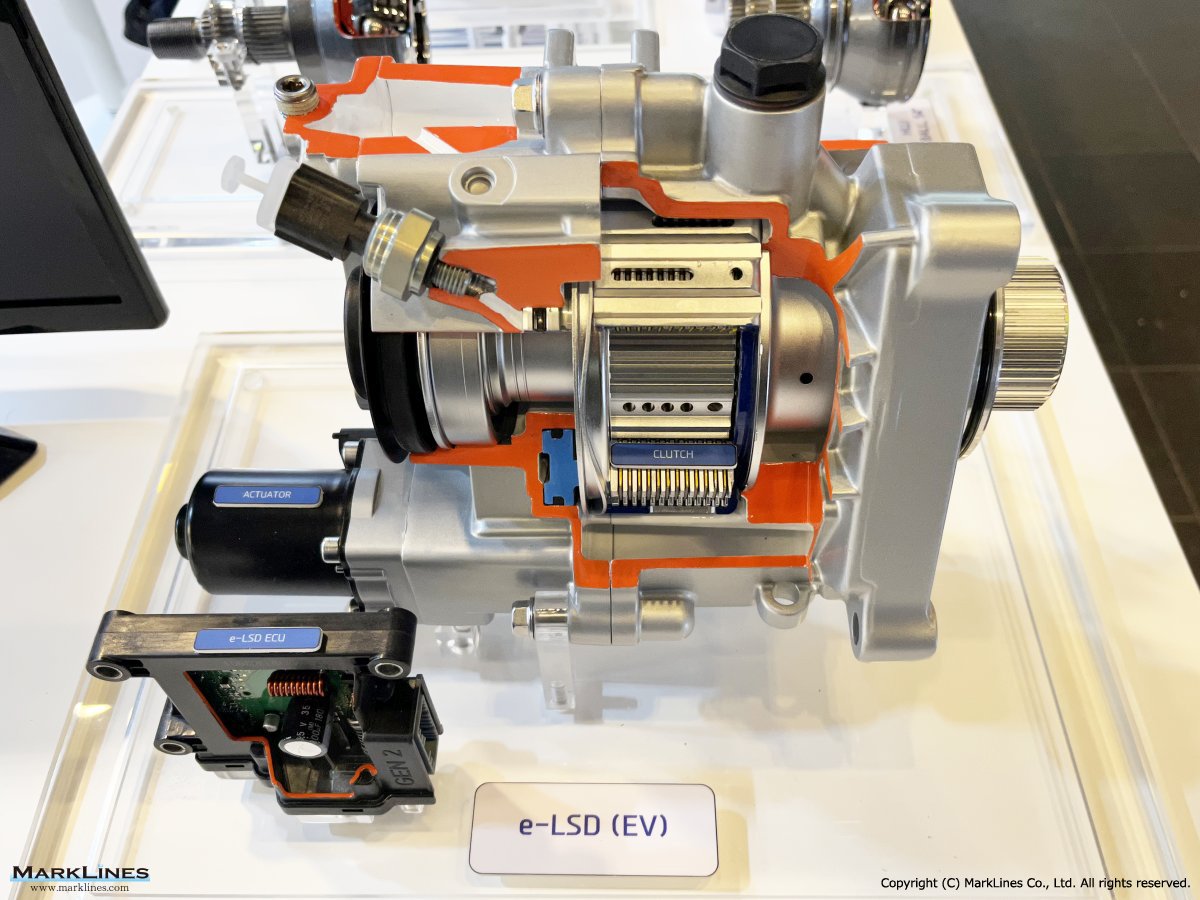
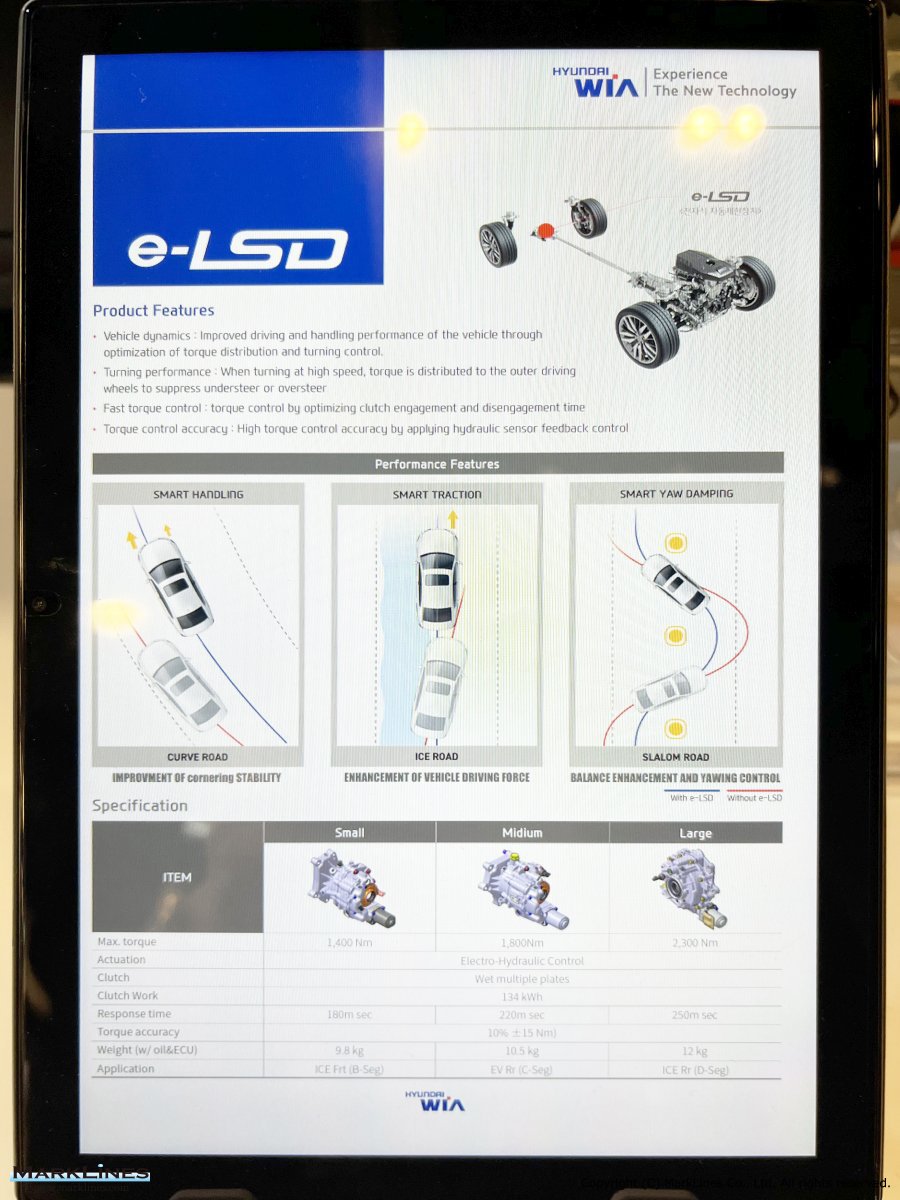
e-LSD (Electronic Limited Slip Differential)
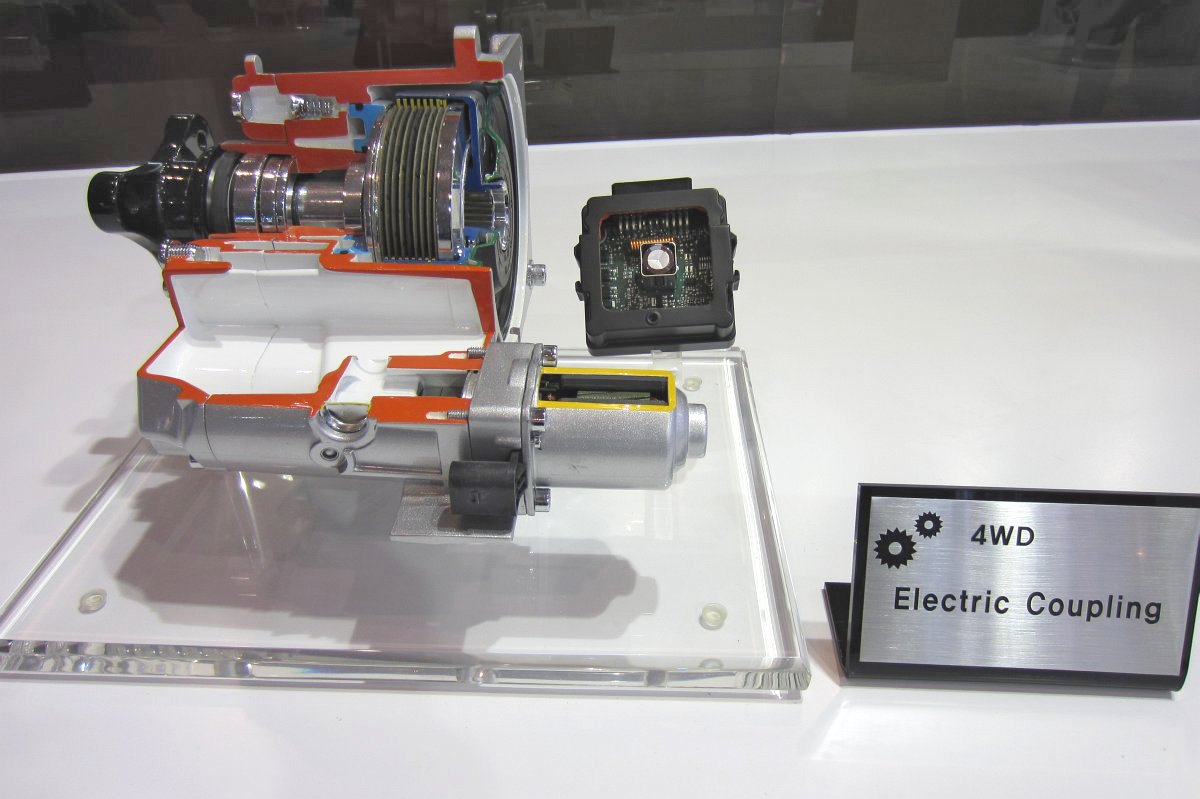
Coupling
Electrified Axle
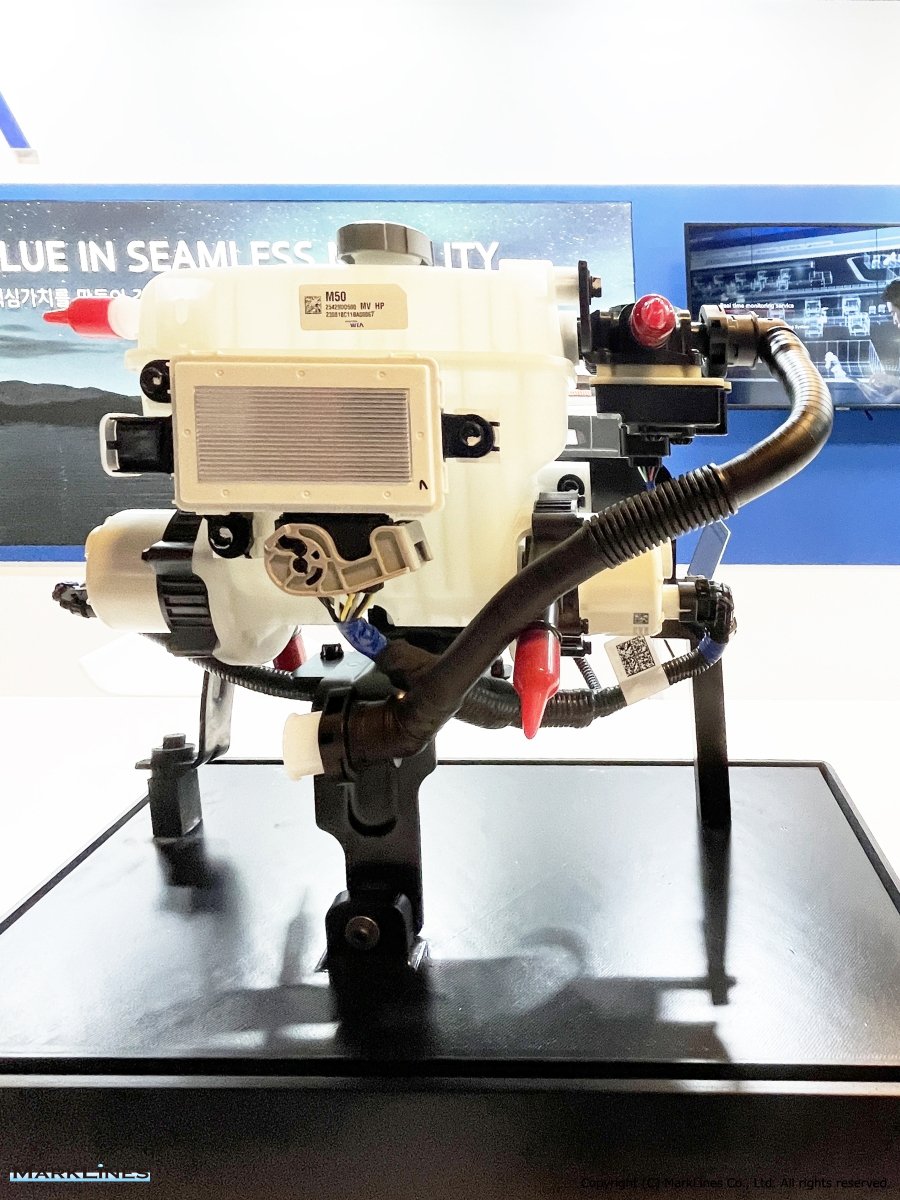
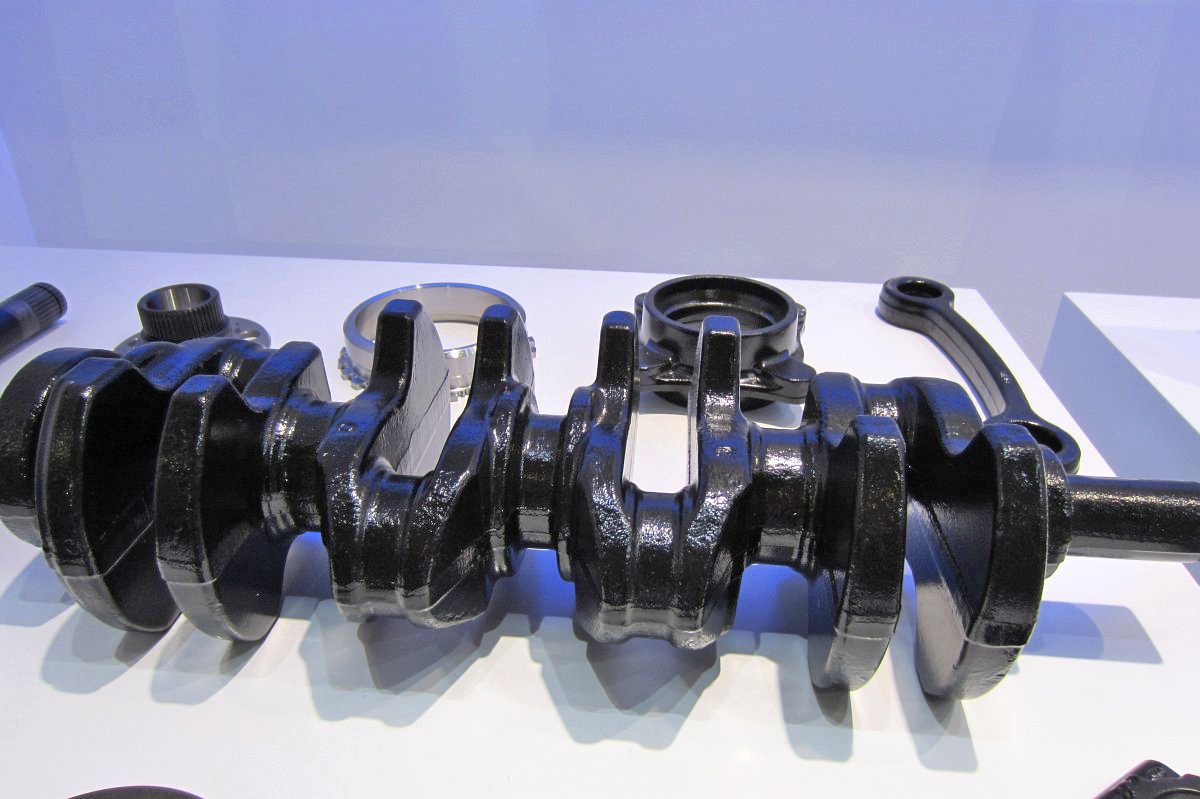
Engines
Gasoline Engine
Diesel Engine
Module
Chassis Module
- Platform Module
- Front Chassis Module
- Rear Chassis Module
Axle Module
- Truck Front Module
- Truck Rear Module
Tire Module
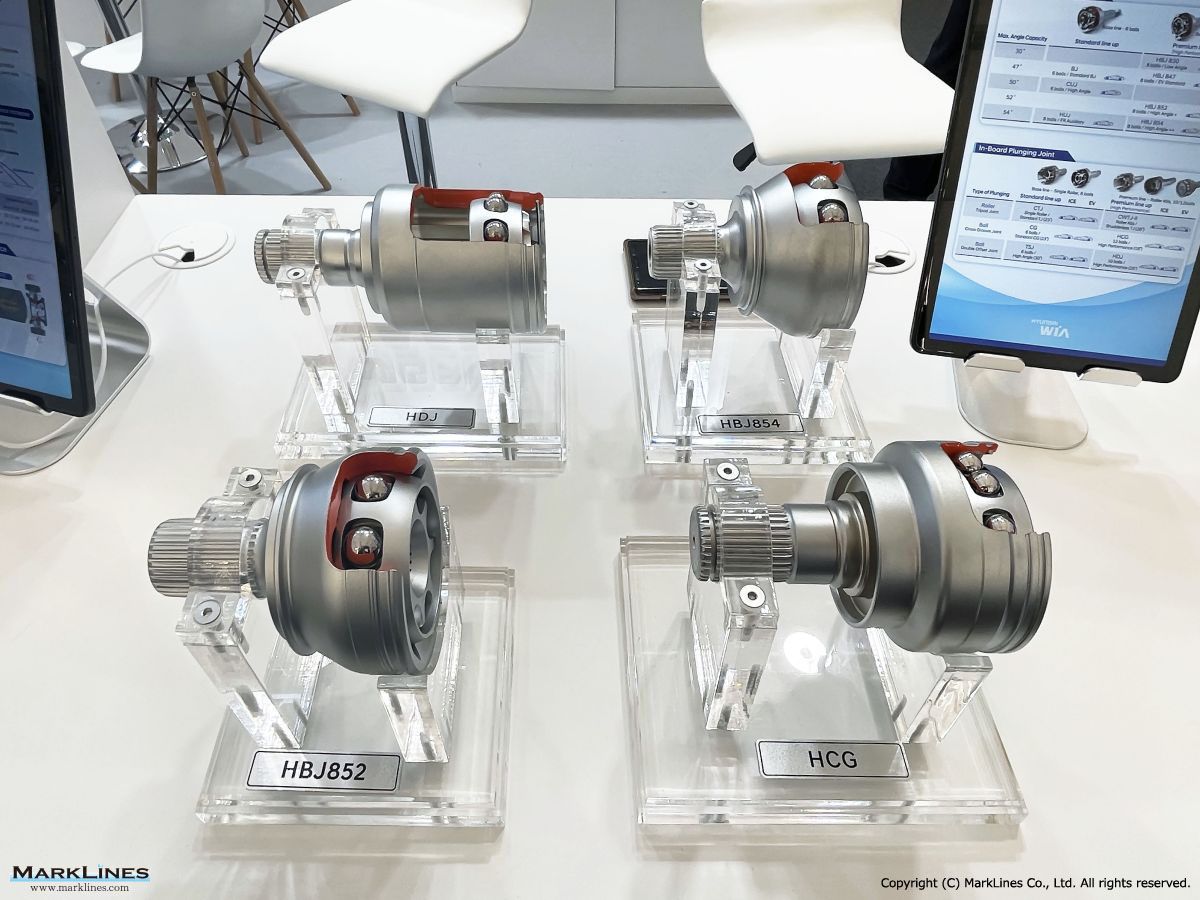
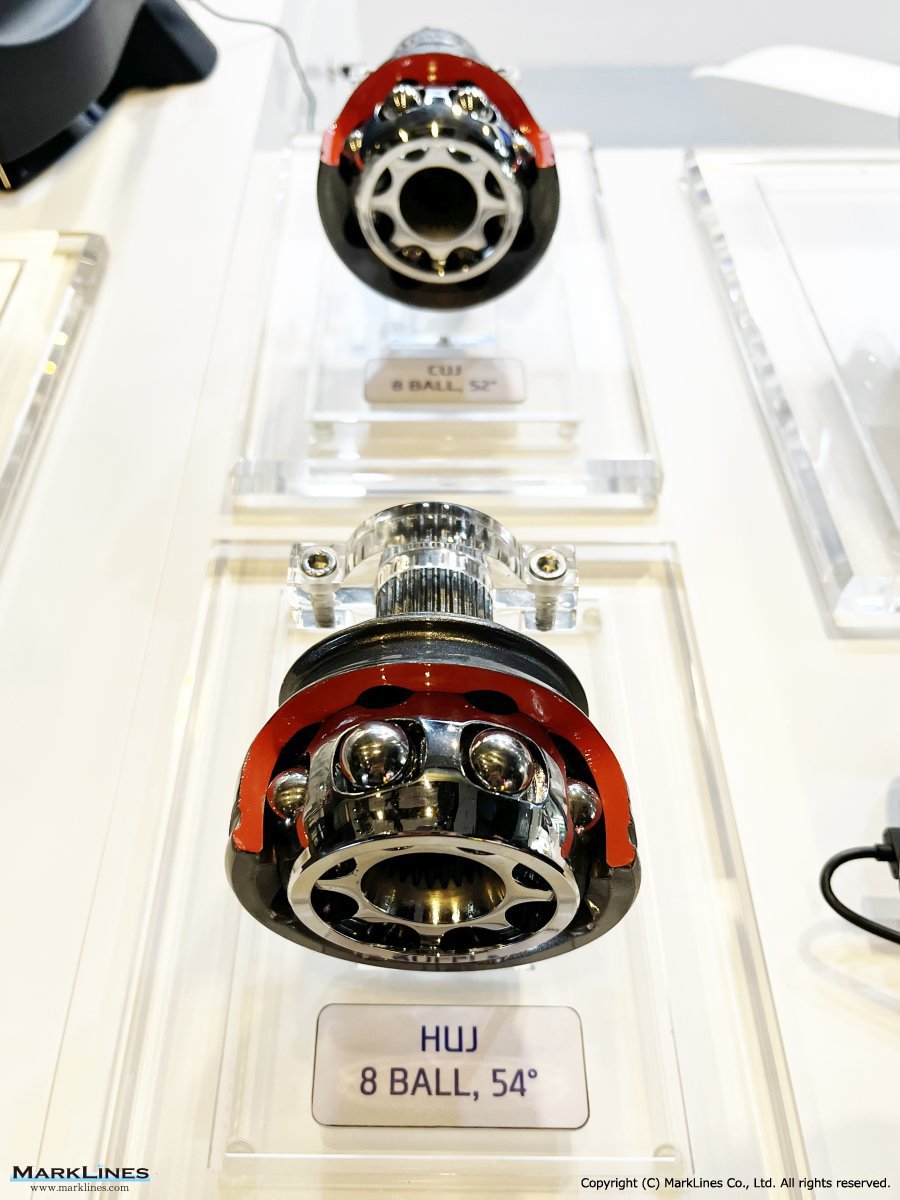
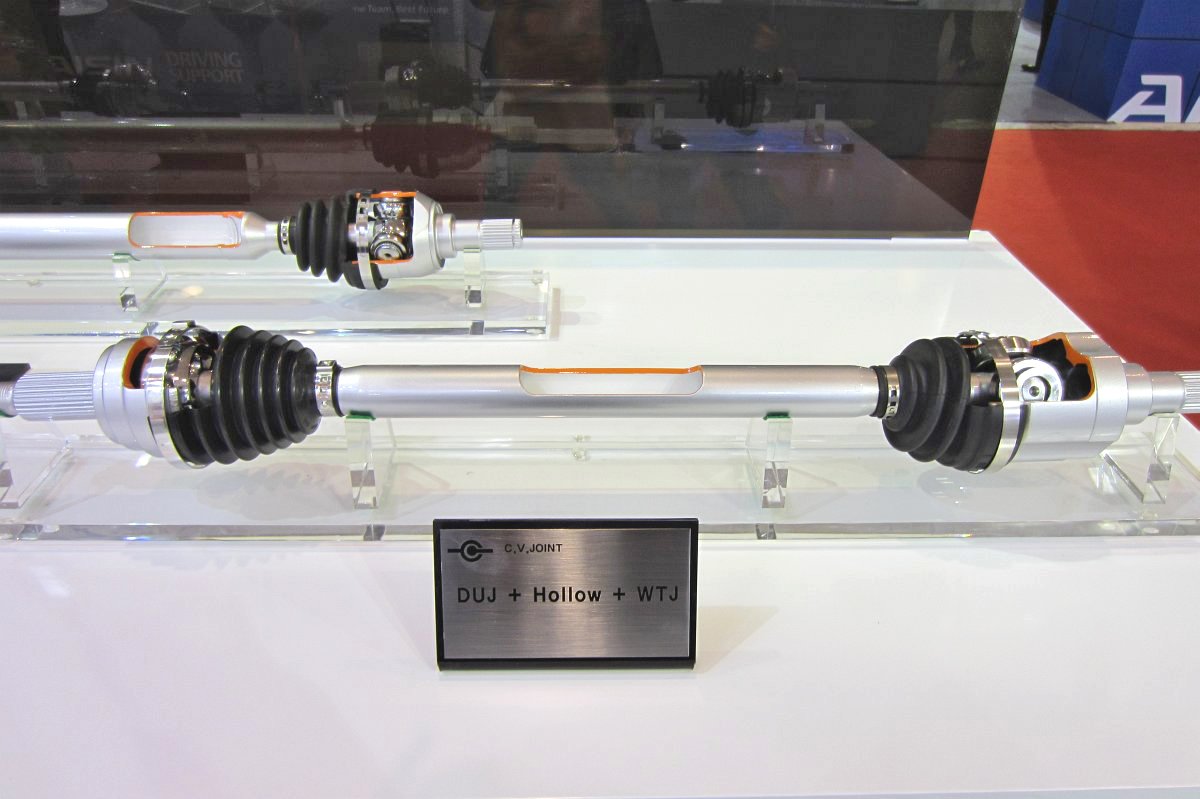
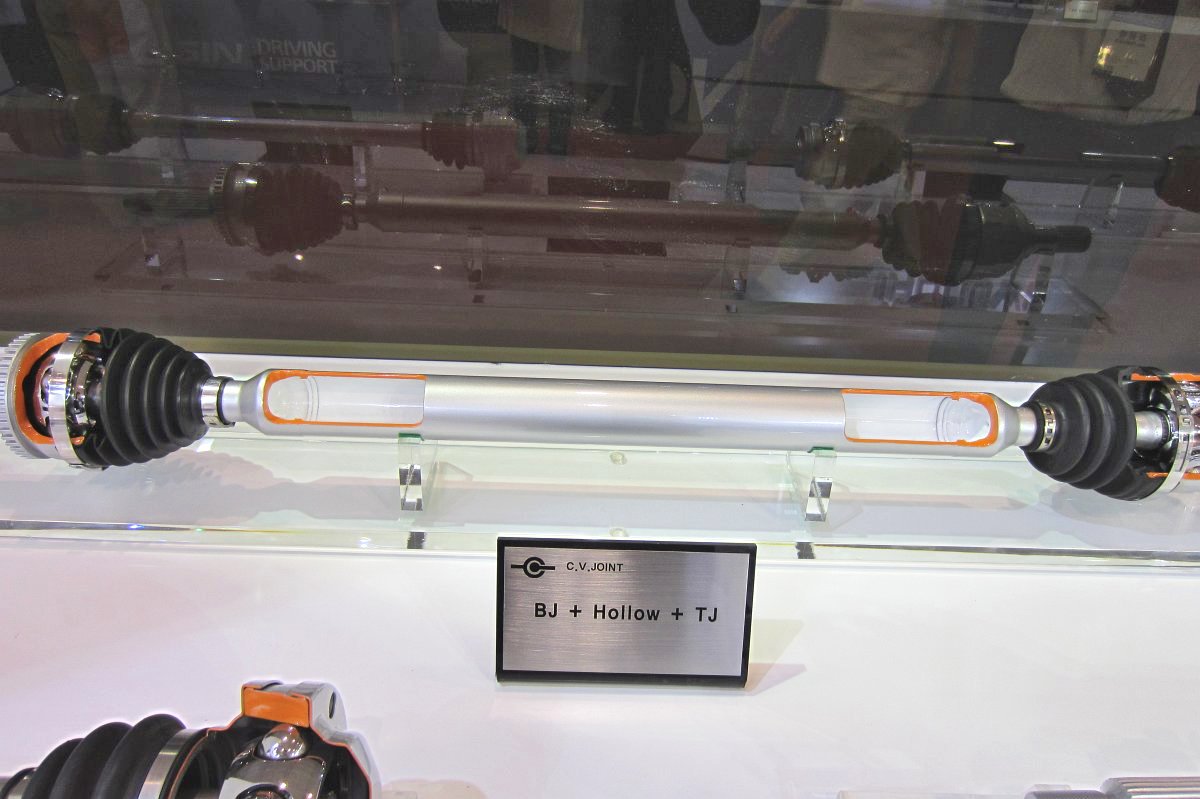
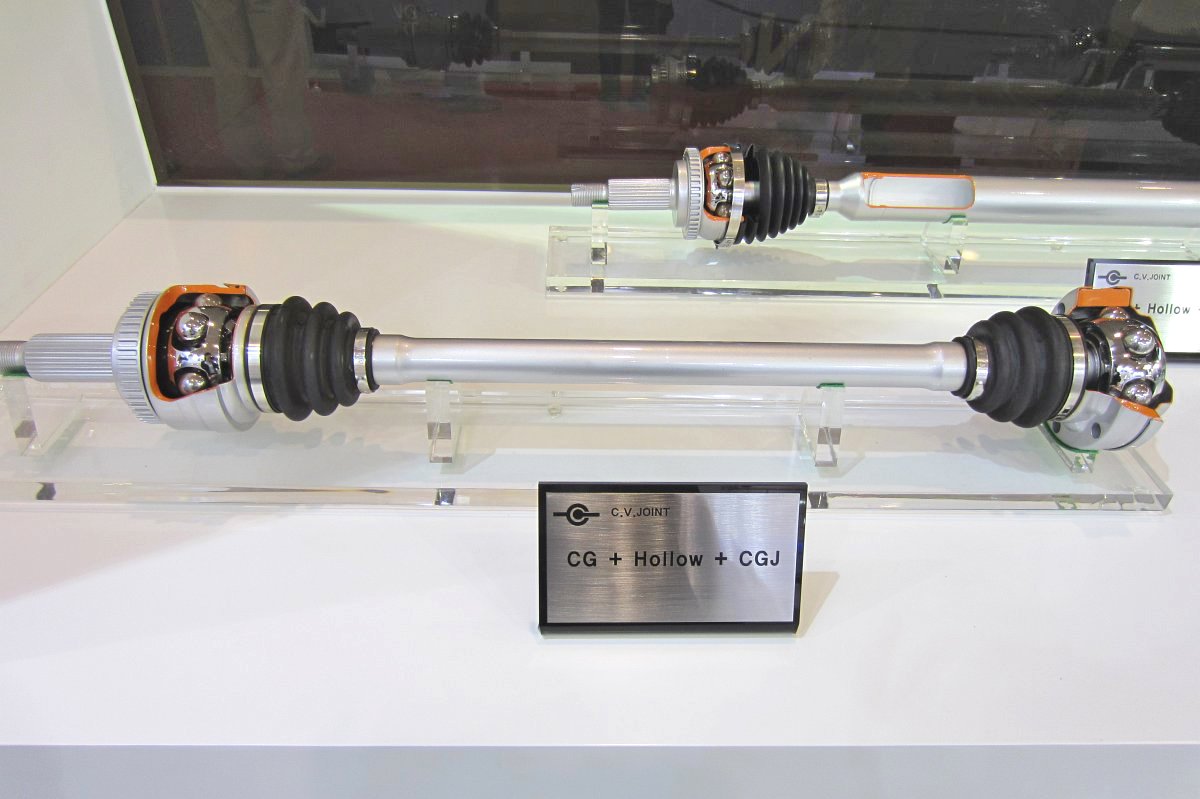
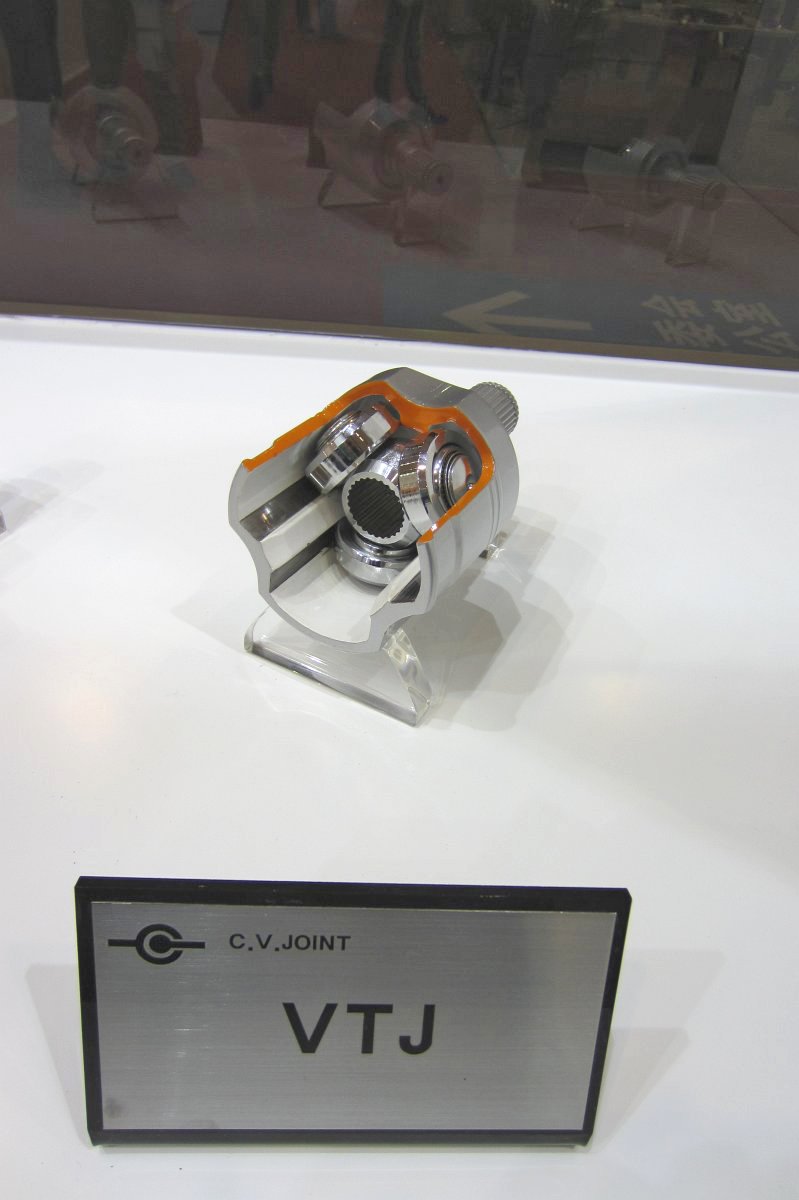
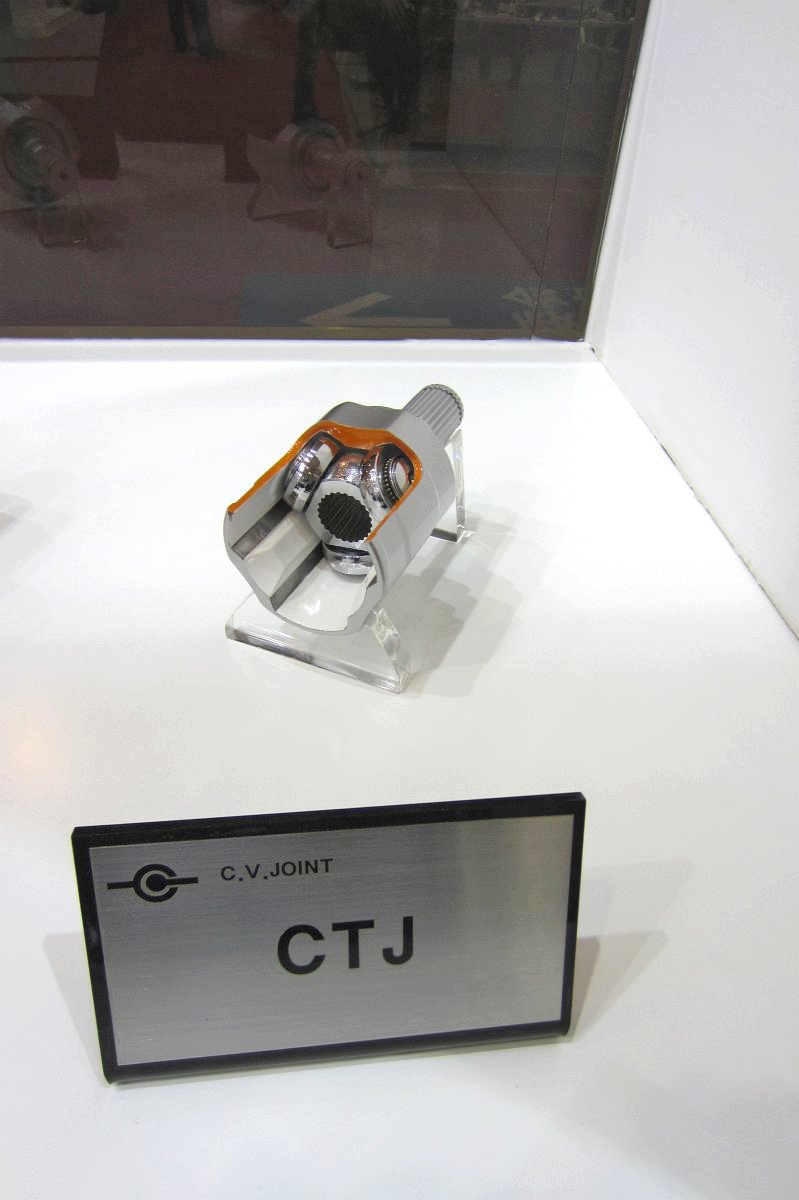
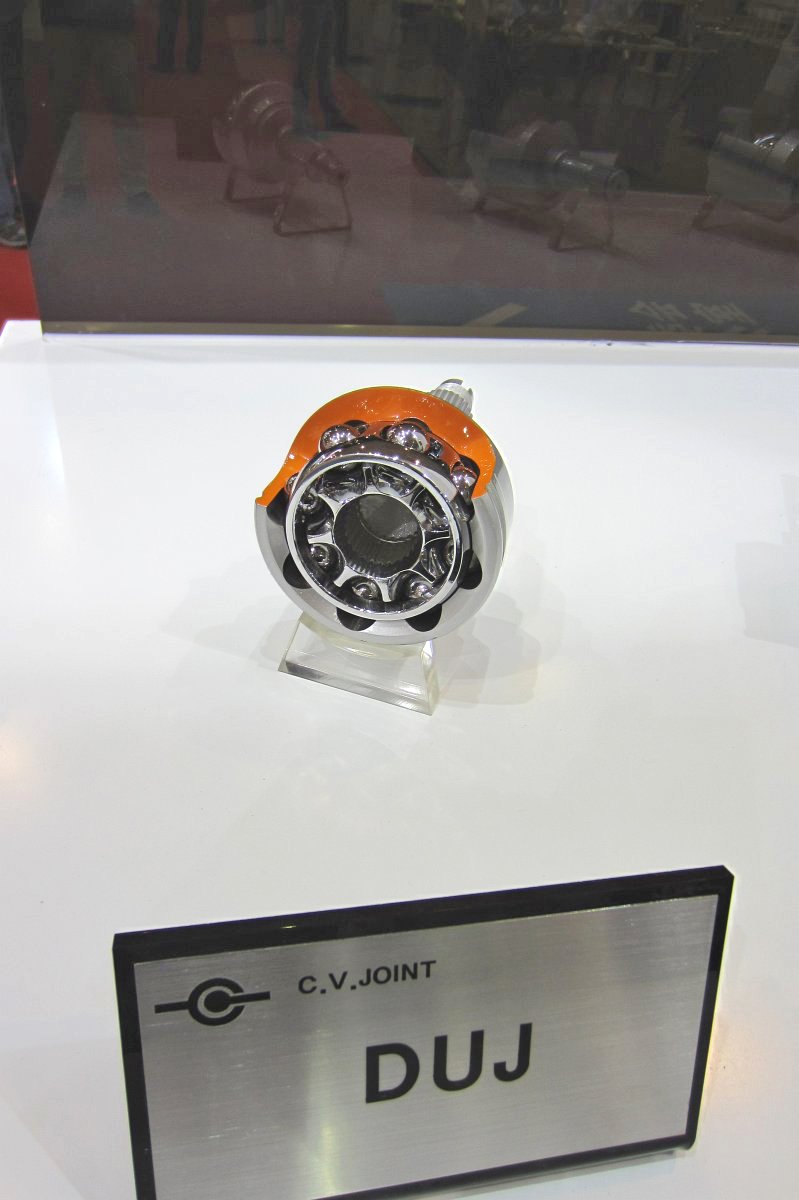
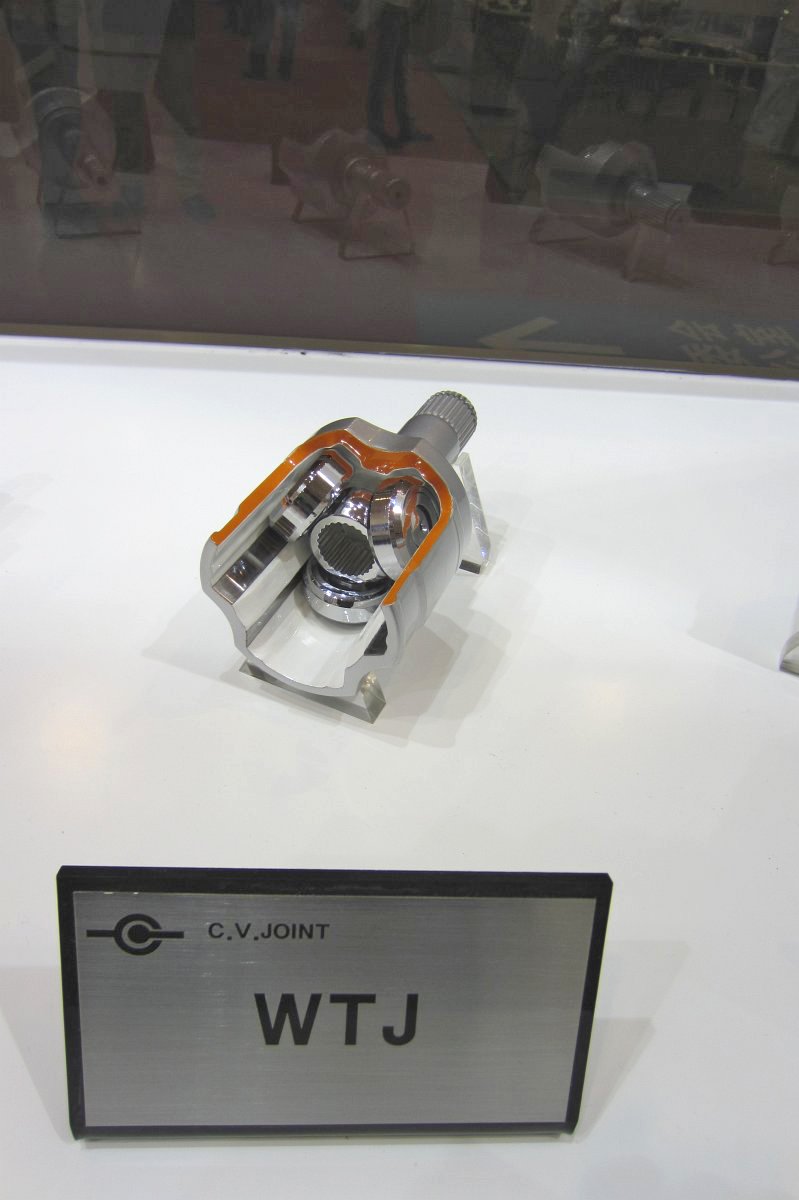
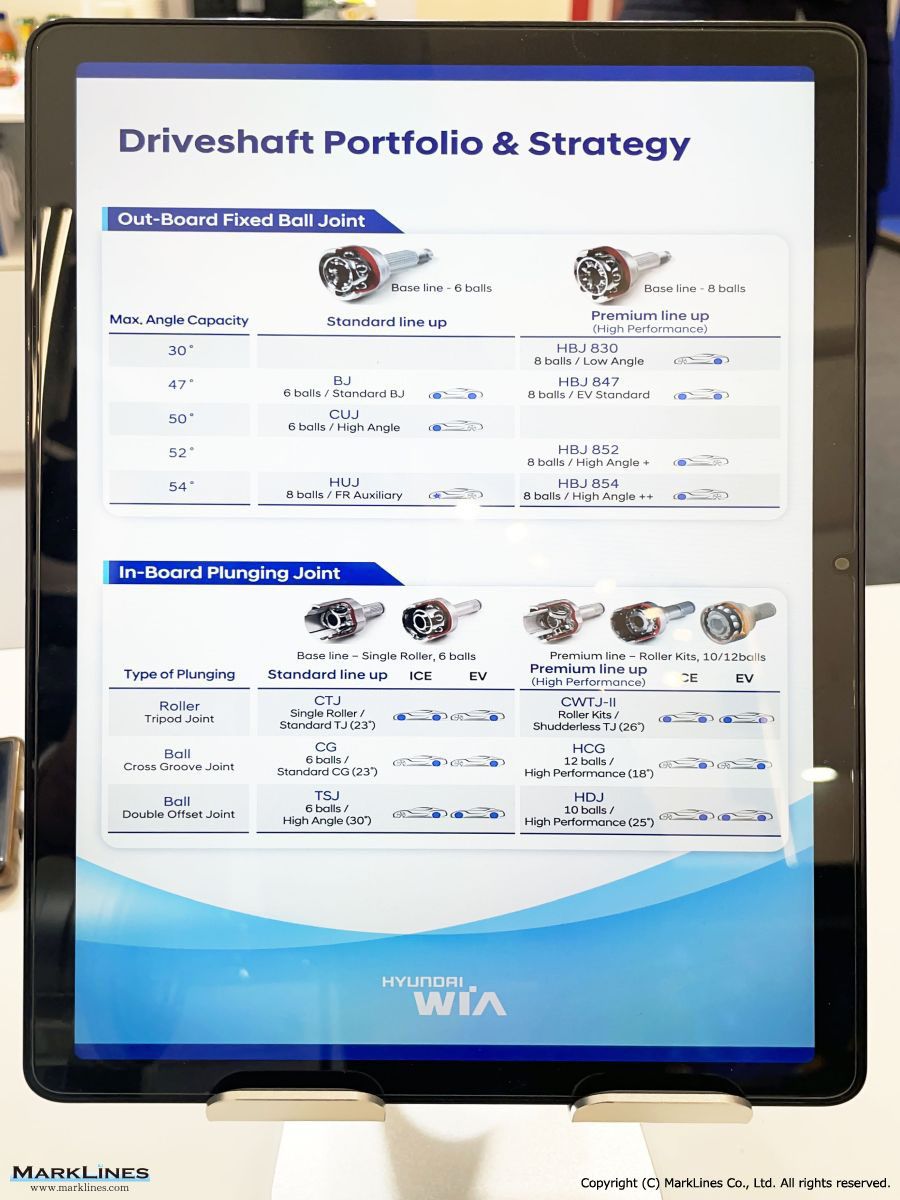
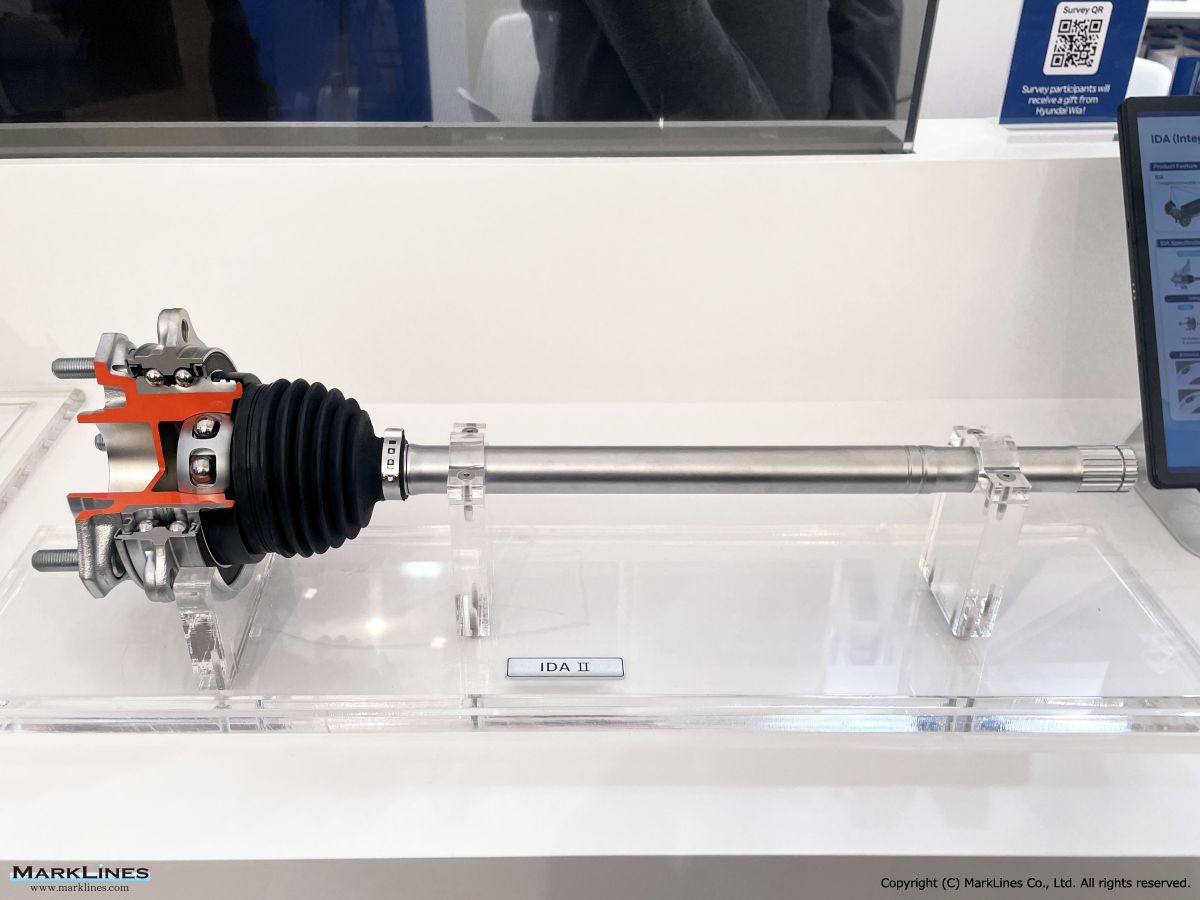
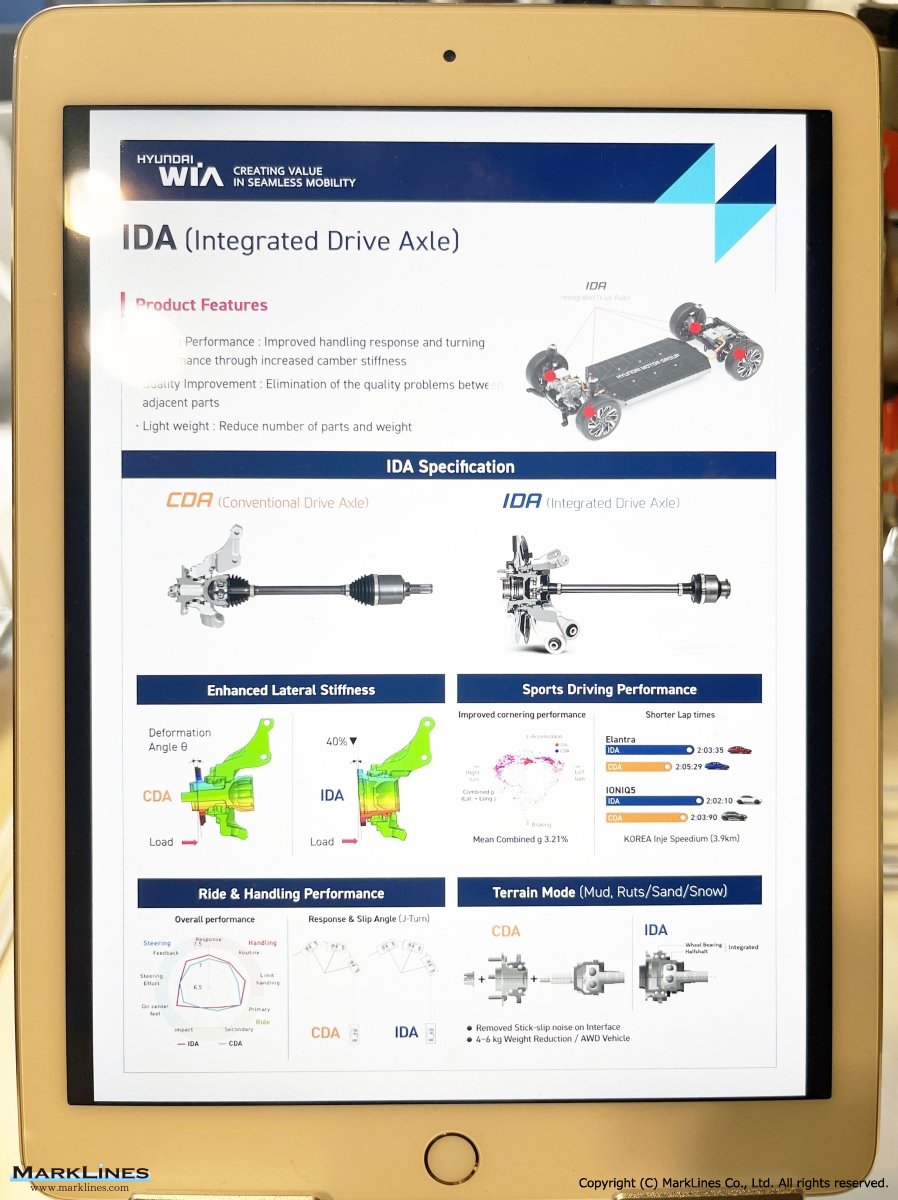
CVJ:Constant Velocity Joints
Constant velocity joint
Outboard Joint
- Rzeppa Ball Joint
- Lean-manufacturing Ball Joint
- Compact Ball Joint
- Compact Undercut-free Joint
- High Performance Undercut Joint
Inboard Joint
- Tripod Joint
- Lean-manufacturing Tripod Joint
- Compact Tripod Joint
- Compact Wrinkled Tripod Joint, Anti-Shudder
- Tri-Spherical Joint
- Cross Groove Joint
- High-Efficiency Cross Groove
Shaft
History
| Mar. 1976 | The Company was established. |
| Mar. 1979 | The Company started manufacturing automotive transmission systems. |
| Oct. 1986 | The Changwon Plant and Namsan Plant were completed. |
| Apr. 1988 | A testing and prototyping facility was completed. |
| May. 1989 | The Company established a U.S subsidiary. |
| Jan. 1990 | The Ansan Plant and Banwol Plant were completed. |
| Apr. 1993 | The Gwangju Plant was completed. |
| Dec. 1993 | The Company manufactured its 1 millionth transmission system for commercial vehicles, recording the largest production volume among transmission manufacturers in Korea. |
| Jan. 2000 | The Company adopted a new company name, WIA Corporation. |
| Jun. 2000 | The Company manufactured its 3 millionth constant velocity joint. |
| Aug. 2000 | The Company was spun off from the Hyundai Group. |
| Apr. 2001 | The Company became a group company of the the Hyundai Motor Group. |
| Dec. 2001 | The Company received QS9000 and ISO14001 certifications. |
| Mar. 2004 | The Company increased its production capacity to make 1.5 million CV joints per year. |
| Jul. 2004 | The Company launched commercial production of automotive chassis modules. |
| Dec. 2004 | The Company increased production capacity to make 2 million CV joints per year. |
| Jan. 2005 | The Company established Wia Automotive Parts Co.,Ltd. (Zhangjiagang) in Jiangsu Province, China. |
| Feb. 2005 | The Company obtained ISO/TS16949 certification. |
| Jun. 2005 | The Company and Fuji Univance Corporation formed a technical alliance in the area of electronic control transfers for front-engine, rear-drive-wheel vehicles. |
| Oct. 2005 | The Company started producing manual transmissions for passenger vehicles. |
| Oct. 2005 | The Company entered the automotive engine market. |
| Nov. 2006 | The Company established WIA Automotive Engine (Shangdong) Co., Ltd. in Shangdong Province. |
| Jan. 2007 | Jointly with Dymos and Hyundai Powertech, which are members of the Hyundai Motor Group, the Company established Hwaseong Drivetrain R&D Center in Hwaseong, Korea. |
| Apr. 2007 | A new engine plant was completed in Shandong Province, China. |
| Jan. 2008 | The Company completed new CVT plant in Jiangsu Province, China. |
| Sep. 2008 | The Company completed engine plant No.2 in Shandong Province, China. |
| Jan. 2009 | The Company established WIA Magna Powertrain jointly with Magna Powertrain AG of Austria, entering the electronic control coupling business for all-wheel-drive vehicles. |
| Aug. 2009 | The Company adopted a new name, Hyundai WIA Corporation. |
| Sep. 2009 | WIA Automotive Parts Co.,Ltd. (Zhangjiagang) adopted a new corporate name, Jiangsu Hyundai WIA Co., Ltd. |
| Mar. 2010 | The Company established Hyundai WIA India Pvt. Ltd. in India. |
| Sep. 2010 | Production of the Kappa engine started at the Pyeongtaek Plant. |
| Dec. 2010 | The Company manufactured its 20 millionth CVJ. |
| Feb. 2011 | The Company was listed on Korea Exchange. |
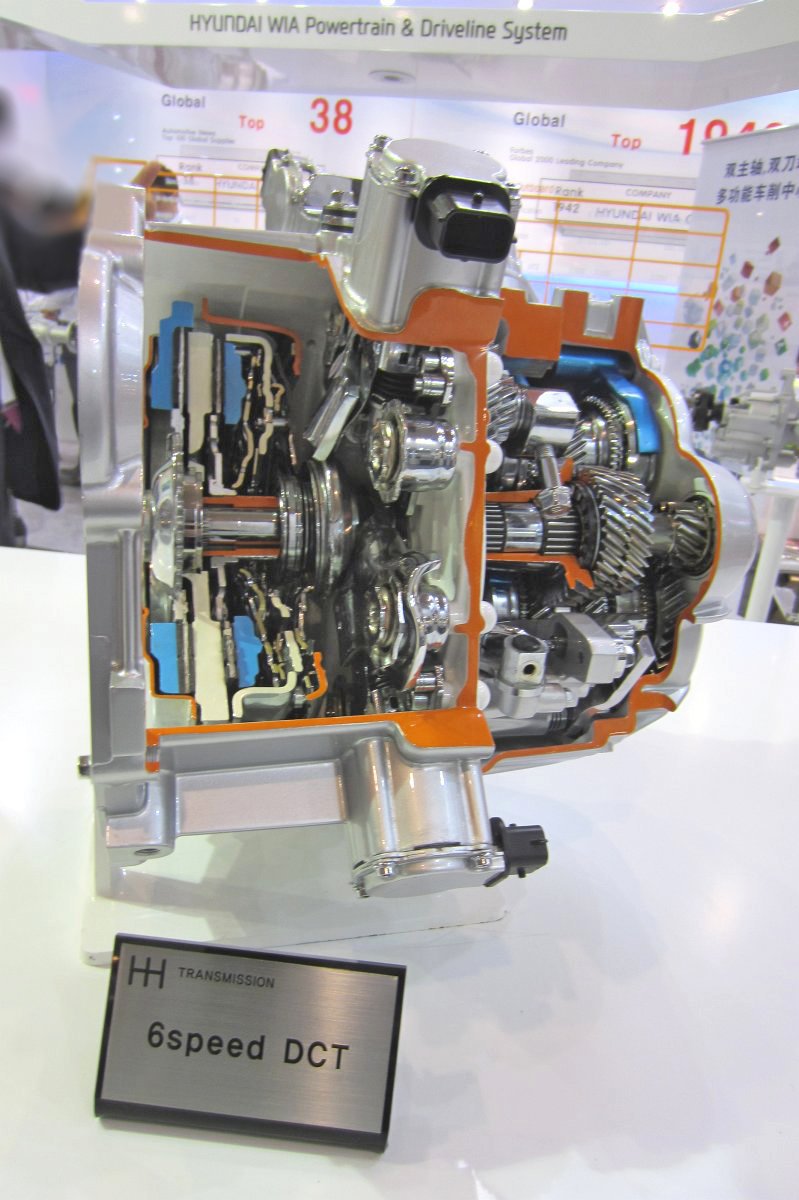
| Jun. 2011 | Mass production of dual clutch transmissions (DCTs) started at the Changwon Plant. |
| Aug. 2013 | The Company and IHI of Japan have jointly established Hyundai WIA IHI Turbo Co., Ltd. in Korea |
| Jul. 2014 | The Company established Beijing WIA Turbocharger Co., Ltd. in China. |
| Sep. 2014 | The Company established Hyundai WIA Mexico S. DE R.L. DE in Mexico. |
| Apr. 2015 | The Company produced 5 millionth transfer. |
| Jul. 2015 | Opened a training center at Shandong Hyundai Wia Automotive Engine Company. |
| Mar. 2016 | The Company completed a plant in Mexico. |
| Mar. 2016 | The Company produced 100 millionth CVJ. |
| Jul. 2016 | Increased production lines producing CVJs at production plant in Jiangsu Province, China |
| Mar. 2017 | Started production of diesel engines at the Seosan Plant in Korea |
| Sep. 2021 | Completed construction of an engine plant in St. Petersburg, Russia. |
| Sep. 2021 | Established Hyundai-Wia Alabama, Inc. |
| Feb. 2023 | Established Wia Slovakia s.r.o. |
| Dec. 2023 | Established two subsidiaries: MOVIENT, a modular production company; and TECZEN, a parts manufacturer. |
Supplemental Information 1
The Hyundai Motor Group's Ratio of Shareholding in Automotive Companies |
(As of Dec. 31, 2024) |
|
Name of group company
Company in which the company holds shares |
Hyundai Motor |
Kia Corporation |
Hyundai Mobis |
Hyundai WIA |
Hyundai Transys |
Hyundai Kefico |
| Hyundai Motor | - | 34.53% | - | 25.35% | 41.13% | 100.00% |
| Kia Corporation | - | - | 17.66% | 13.44% | 40.43% | - |
| Hyundai Steel | - | - | 5.92% | - | - | - |
| Hyundai Mobis | 21.86% | - | - | - | 15.74% | - |
| Hyundai GLOVIS | - | - | 0.71% | - | - | - |
| Hyundai WIA | - | - | - | - | 1.88% | - |
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 31, 2013
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 31, 2014
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 31, 2015
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 31, 2016
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 31, 2017
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 31, 2018
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 31, 2019
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 31, 2020
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 31, 2021
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 31, 2022
>>>Business Report up until FY ended Dec. 31, 2023
Note: A figure in brackets ( ) indicates a loss

 AI Navigator
AI Navigator

















































































































 Japan
Japan USA
USA Mexico
Mexico Germany
Germany China (Shanghai)
China (Shanghai) Thailand
Thailand India
India