Analysis Report: Air Conditioning System (Japanese Market)
Changes in the supply chain map due to the electrification of air conditioning systems
List of Suppliers
Introduction
Domestic car sales in Japan in 2024 were affected by Daihatsu's suspension of sales due to certification fraud, and were 4,415,000 units for mini- and non-mini vehicles, reflecting a decrease of 359,000 units, or 7.5%, compared to 2023. The proportion of sales of electrified vehicles (BEV, PHEV, and HEV) among this Japan domestic total increased slightly to 53.6%. The shift to electrified vehicles (xEVs) is progressing in Japan, albeit more gradually than in Europe, the U.S., and China.
Correspondingly, the automotive air conditioner market is also undergoing continuous changes in terms of technology and supplier selection.
This report provides an overview of the above changes in the Japanese market over the past year and analyzes the relationships between OEMs and air conditioner suppliers. The subject areas are HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) units and compressors.
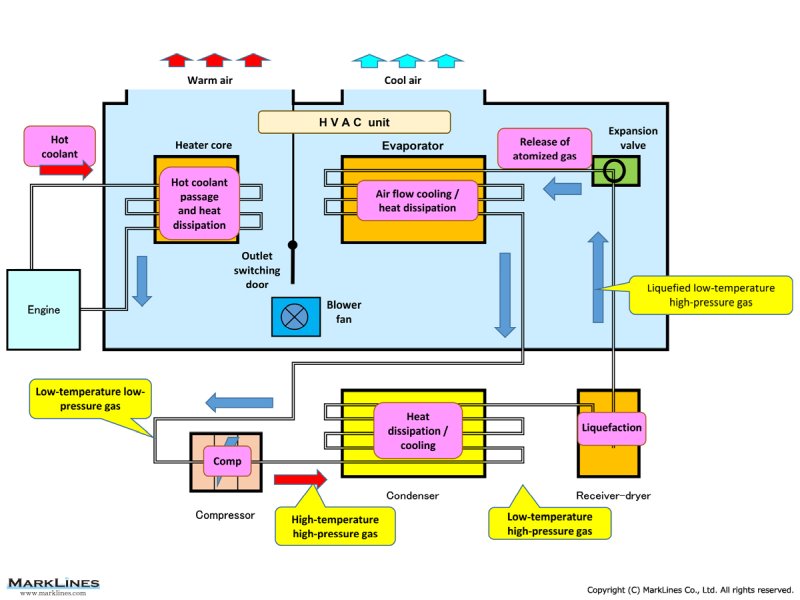
Conventional system configuration, principles and functions of air conditioners
- When the air conditioner switch is turned on, the compressor runs.
The compressor compresses the low-temperature, low-pressure refrigerant gas to convert it into a high-temperature, high-pressure semi-liquid refrigerant.
In engine-equipped vehicles, the engine drives the compressor by transmitting power through a belt, but in hybrid, and other electrified vehicles, electric power runs the compressor. - The refrigerant compressed by the compressor is then sent to the condenser.
Here, the high-temperature, high-pressure refrigerant releases heat as it passes through the condenser, in which many rows of thin tubes are arranged, and is transformed into a low-temperature, high-pressure liquid refrigerant.
The condenser is made of aluminum with excellent thermal conductivity and has many fins to improve cooling performance. - Next, in the receiver-dryer, low-temperature, high-pressure liquid refrigerant cooled by the condenser is temporarily stored. This part is also called the "receiver," "receiver tank," or "liquid tank." The receiver-dryer also has the function of serving as afilter and removes excess moisture and impurities in the refrigerant.
- The expansion valve installed at the inlet of the evaporator expands the high-pressure refrigerant sent from the receiver-dryer at once and sprays it into mist.
As the refrigerant expands as it passes through the expansion valve, thermal energy is lost and the temperature drops. - The refrigerant vaporized and cooled by the expansion valve also takes heat from the air around the evaporator. The cool air generated at this time is blown by a blower fan to cool the inside of the vehicle. Like the condenser, the evaporator is made of aluminum with fins affixed to remove heat efficiently.
- For heating, heated engine coolant is circulated through a heater core, which is a separate heat exchanger from the evaporator, via a separate circuit, and the warm air generated at this time is blown into the vehicle interior by a blower fan.
If you register as a free member, you can read the rest of this article for a limited time.
In addition, you can also enjoy the following content for free:

 AI Navigator
AI Navigator











 Japan
Japan USA
USA Mexico
Mexico Germany
Germany China (Shanghai)
China (Shanghai) Thailand
Thailand India
India