Imasen Electric Industrial Co., Ltd.
Company Profile
Business Overview
-The Company is independently owned. It manufactures and sells automotive seat mechanisms, as well as electrical and electronic products.
-The automotive-parts business accounted for 95% of the Group's total sales in the fiscal year that ended in March 2025.
-The Company’s business is comprised of the automotive-seat, electrical-component, and electronics businesses, in addition to others.
-The breakdown of sales by business in the fiscal year that ended in March 2025 is as follows: Seating and electrical systems: 79.1%, electronics: 16.0%, and new businesses: 5.0%.
-The Company has a 16% share of the seat-adjuster market and a 17% share of the seat-recliner market in Japan, according to its own research.
-In 2020, the Company formed a capital and commercial alliance with TS Tech. The two companies plan to further expand their businesses based on joint sales promotions, taking advantage of TS Tech's expansive, global operations.
Shareholders
| -Listed on the Standard Market of the Tokyo Stock Exchange and the Premium Market of the Nagoya Stock Exchange. | (As of Mar. 31, 2025) |
| Name or Company Name | Investment Ratio (%) |
| TS TECH Co., Ltd. | 36.66 |
| Business partner share holding association | 4.47 |
| Employee stock holdings | 3.00 |
| INTERACTIVE BROKERS LLC (Standing proxy: Interactive Brokers Securities Japan Inc. Representative Director) | 2.44 |
| San Ju San Bank, Ltd. | 2.32 |
| Custody Bank of Japan, Ltd. (Trust Account) | 1.67 |
| MSIP CLIENT SECURITIES (Standing proxy: Morgan Stanley MUFG Securities Co., Ltd. Securities Management Chief) | 1.54 |
| LIM JAPAN EVENT MASTER FUND (Standing proxy: Tachibana Securities Co., Ltd.) | 1.52 |
| NHK Spring Co., Ltd. | 1.42 |
| Honda Motor Co., Ltd. | 1.33 |
| Total | 56.37 |
Products
Mechanical products
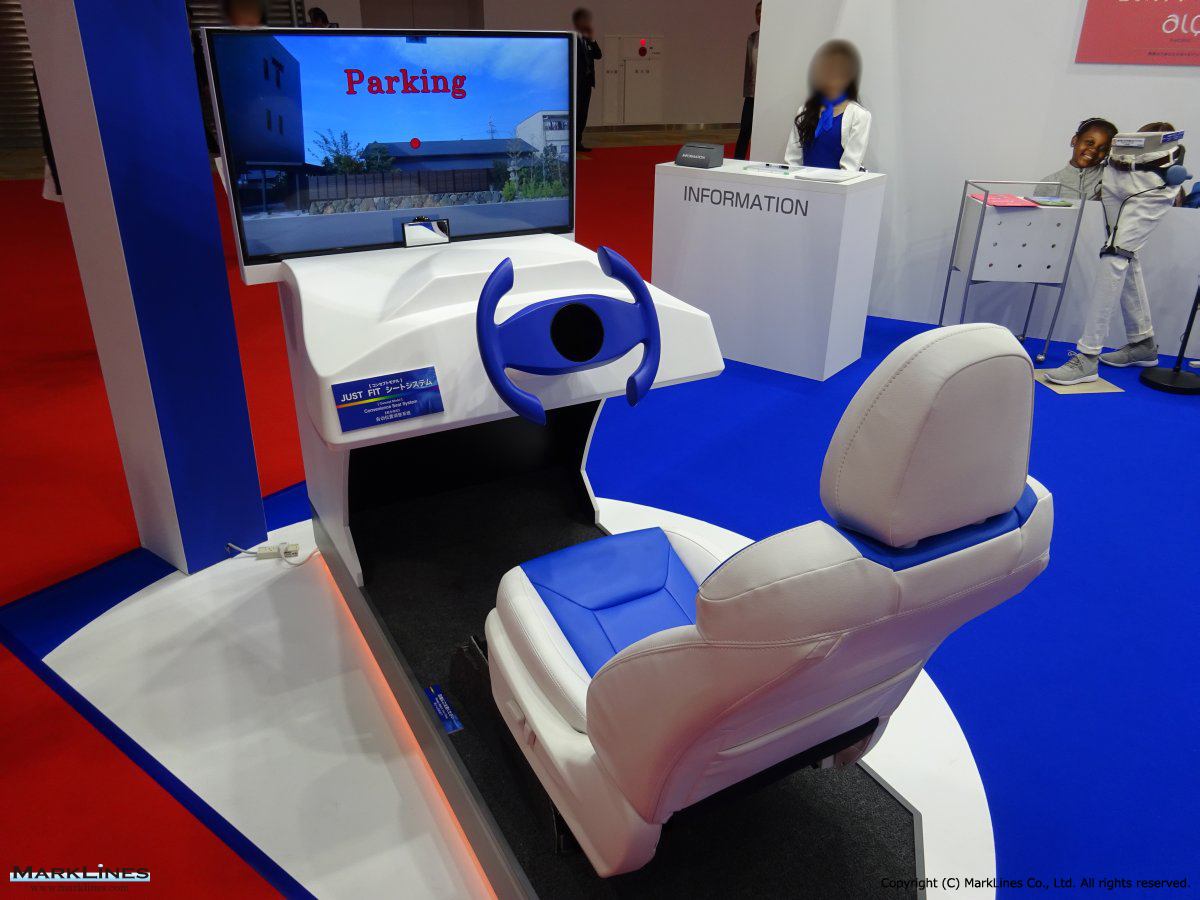
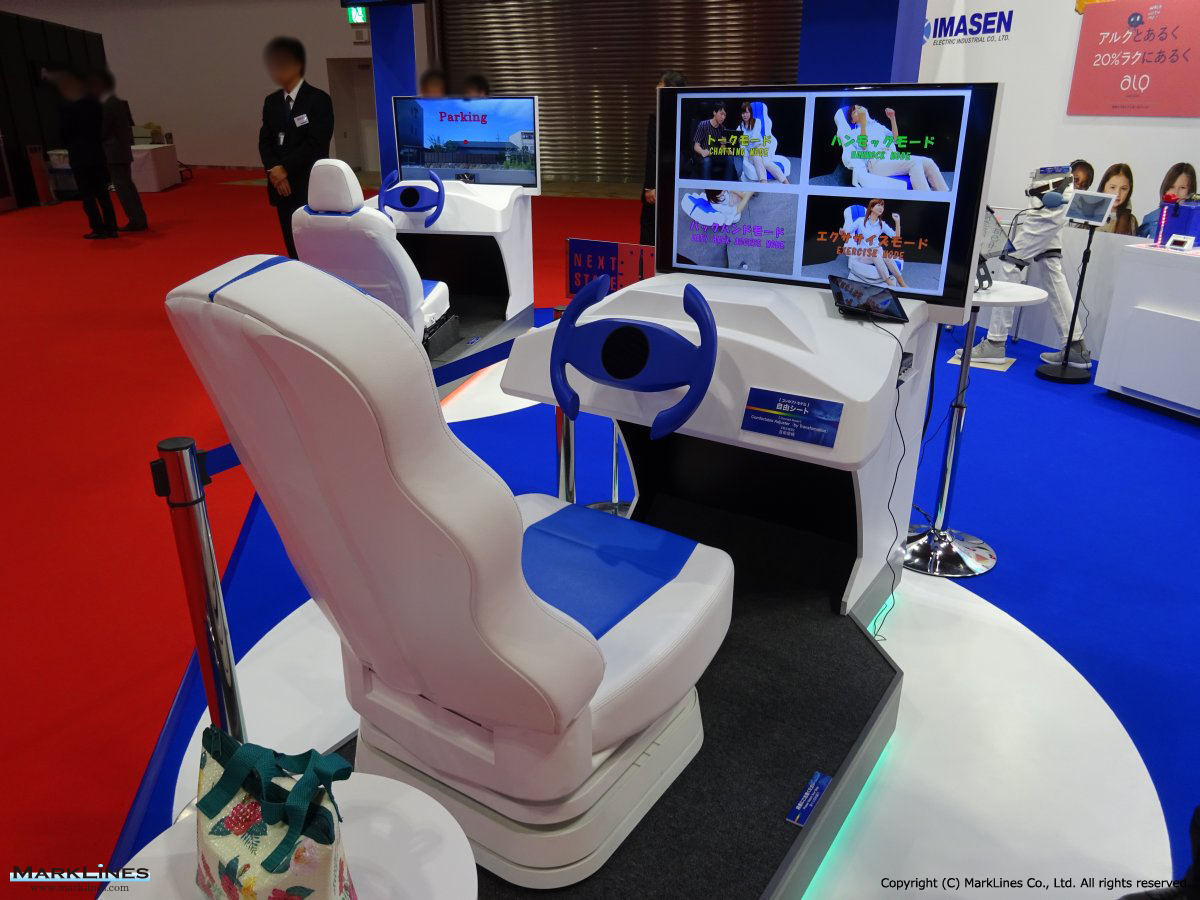
Seat adjusters
-Manual seat adjusters
-Power seat adjusters
-
- Lightweight power seat devices
- High strength power seat devices
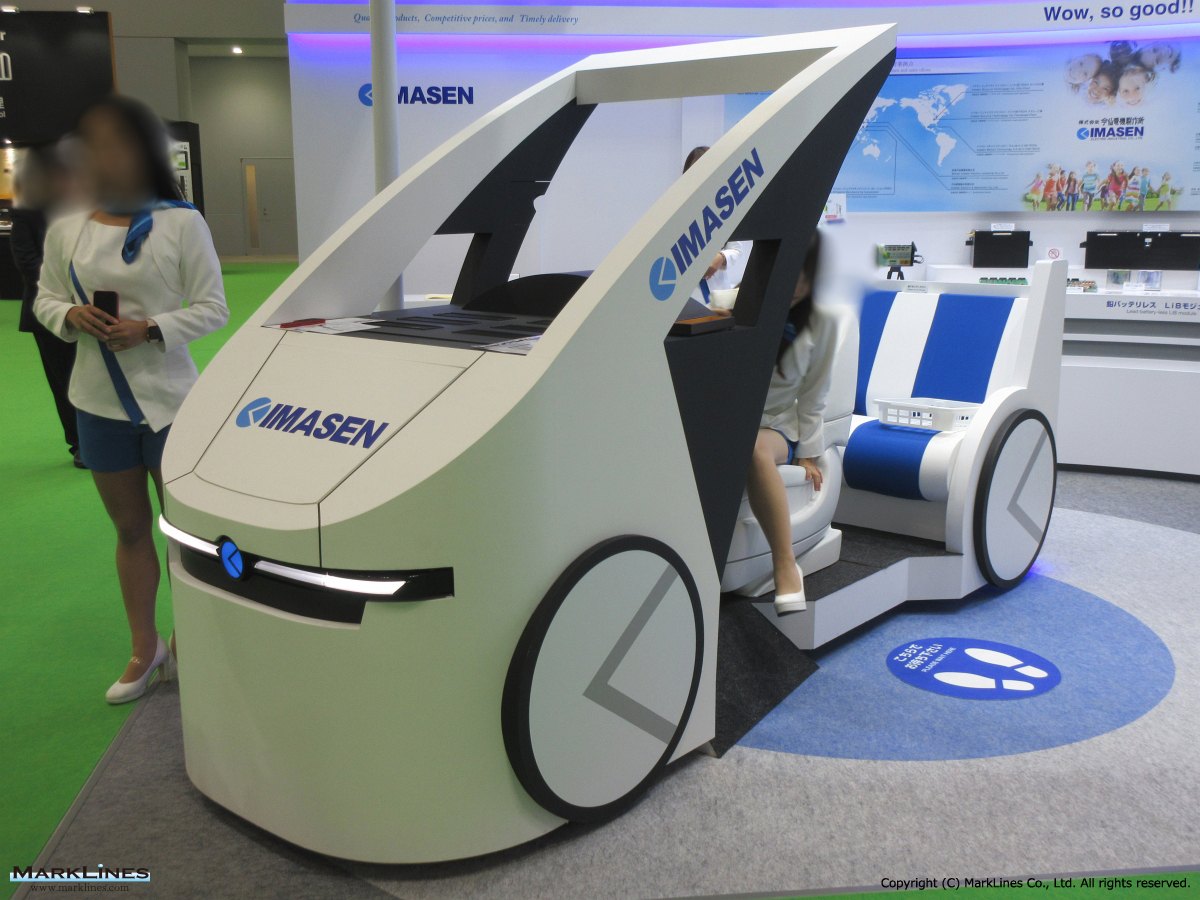
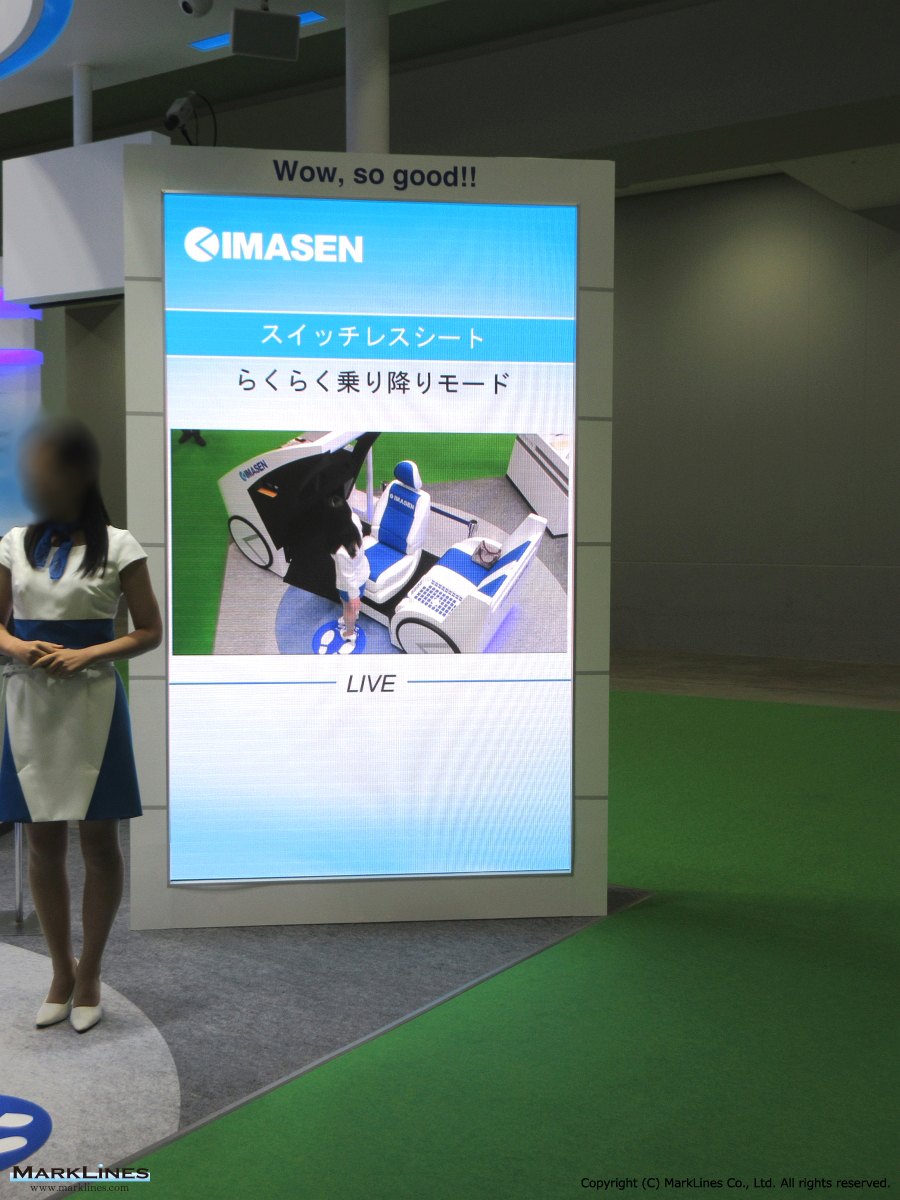
- Lift-up and rotation device for vehicles designed to carry physically challenged passengers
-Round units
-Slide adjusters
- Standard rails
- Long rails
-Height adjusters
-Brake units
-Recliner devices with automatic restoration function
Window regulators
-Wire type window regulators
-X-ray type power window regulators
- X-ray type power window regulators
- Mono-arm type power window regulators
Electric products
-Electric products and relays
- Electronic units
- Micro ISO relays
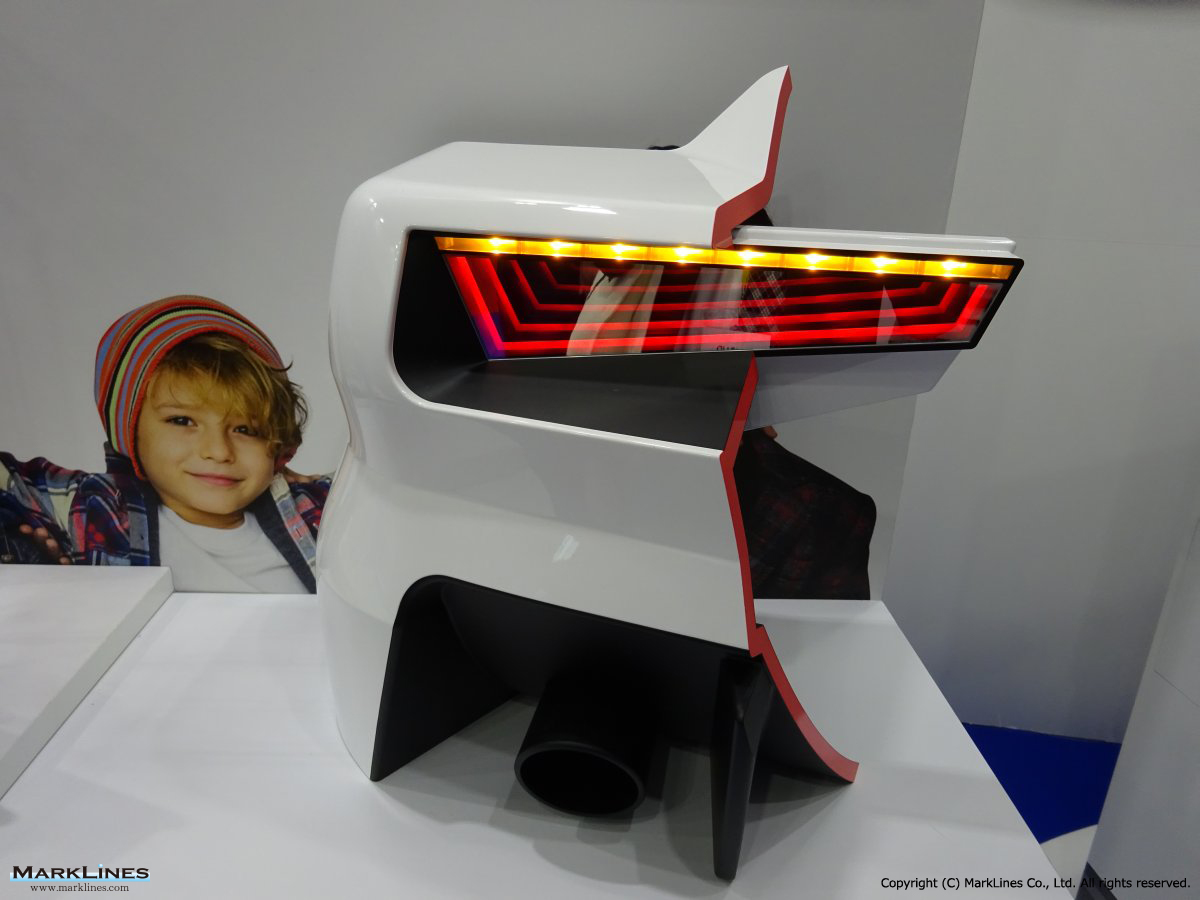
-Lamps
- Over head consoles
- Interior lamps
- High-mounted stop lamps
- Rear combination lamps
- LED lamps for illumination lighting
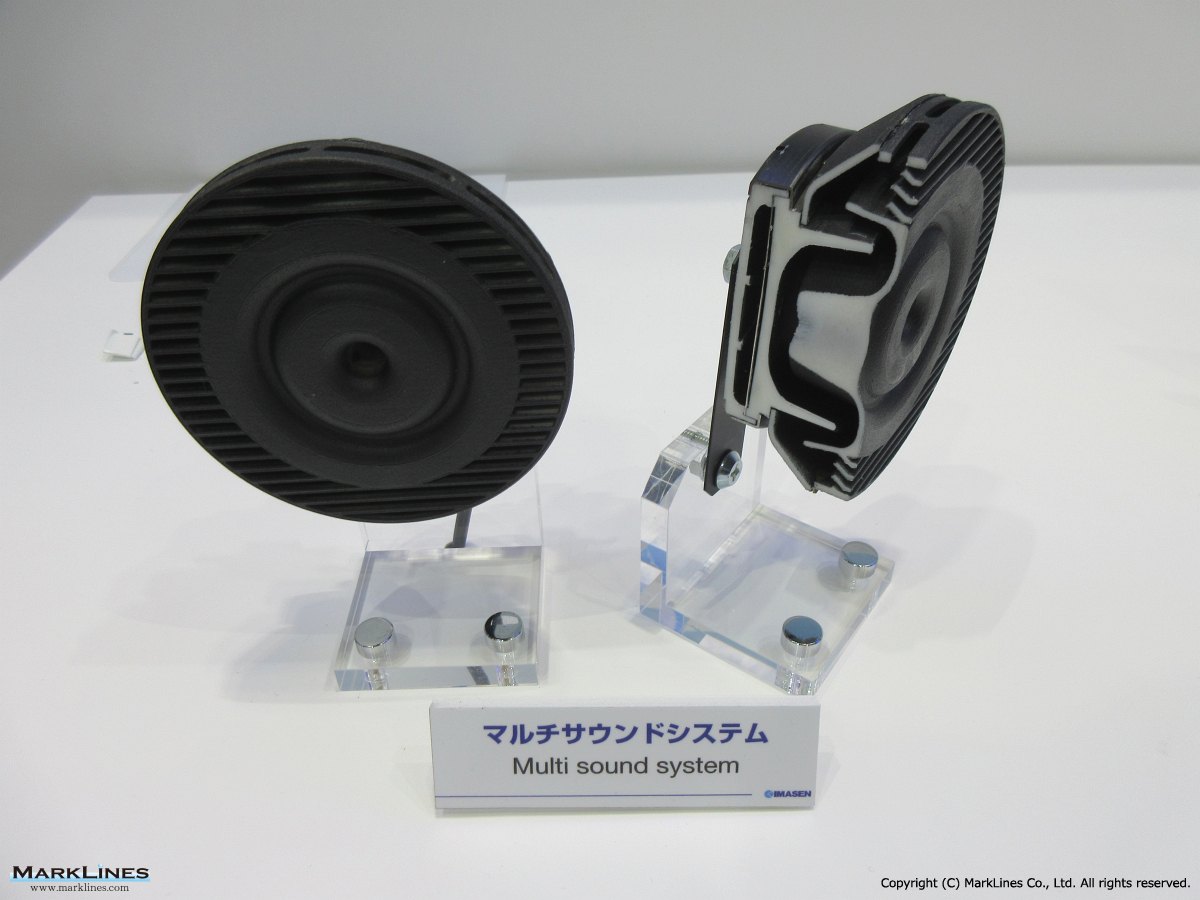
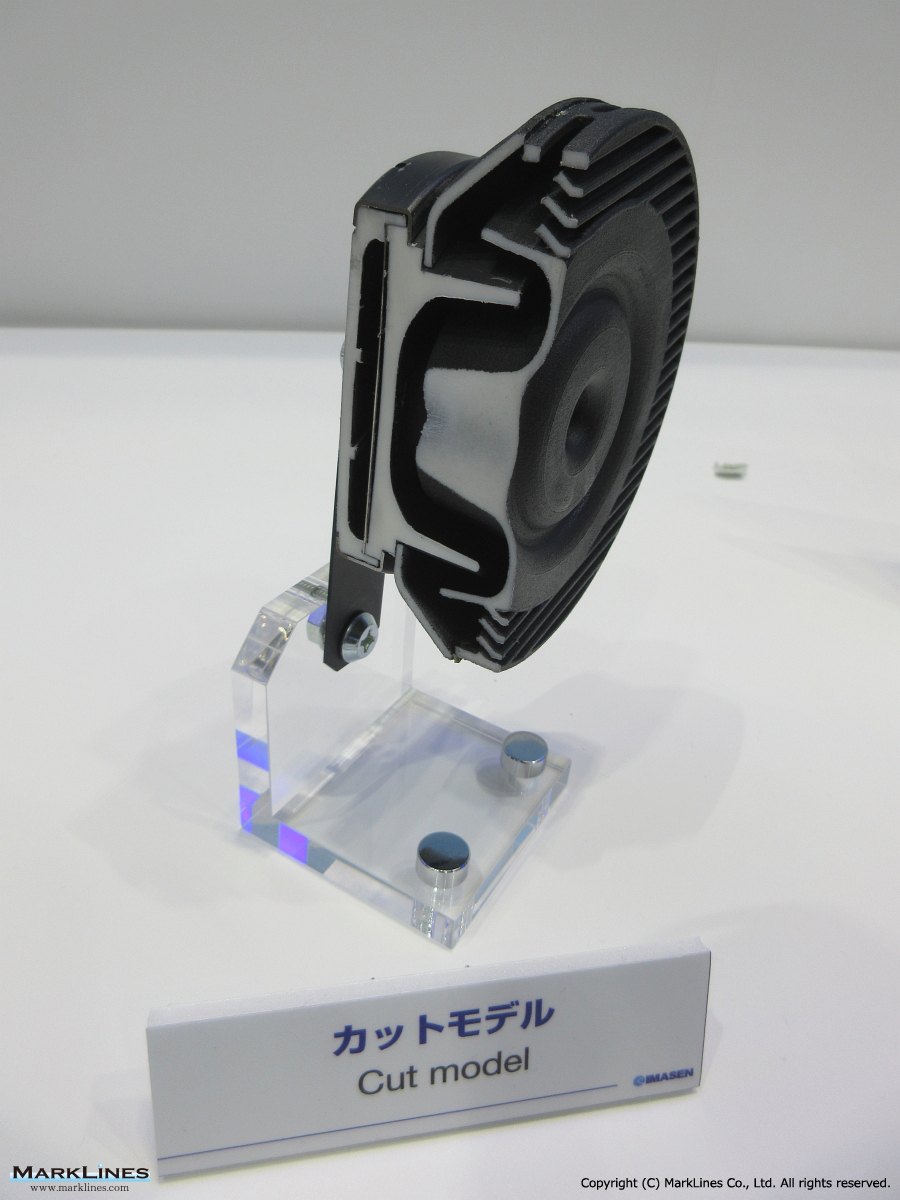
-Horns
- Flat horns
- Spiral horns
- Air horns
-Power electronics products
- DC-DC converters
- Control ECUs for air conditioning blower motors
-Body controlling products
- Control ECUs for power seats and seat heaters
- Body control modules
- Slide door control ECUs
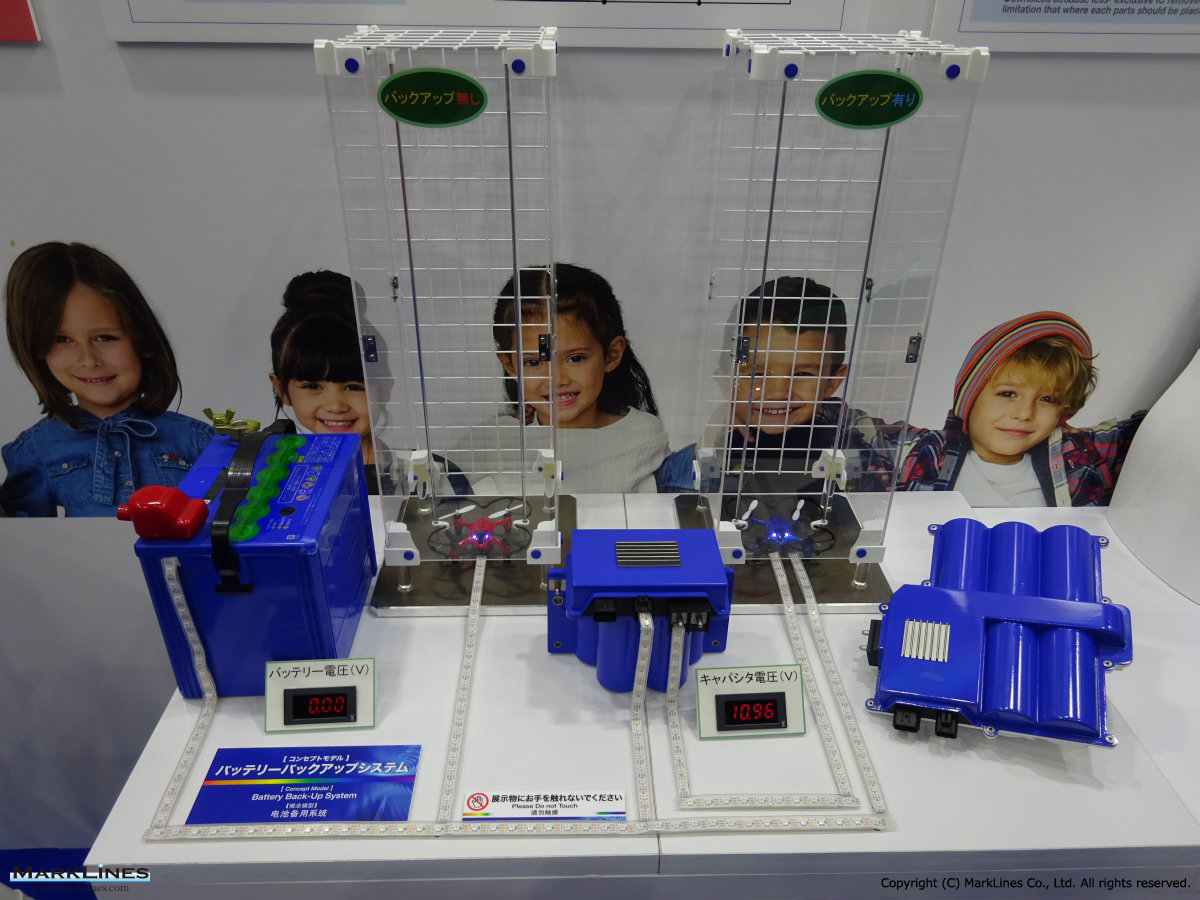
-Safety products
- Back-up batteries
- Image switchable ECUs
Others
-Speed sensors
-Damper actuators for car air conditioning systems
-Magnetic valves
-Ashtrays
History
| Feb. 1939 | Established Imasen Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. |
| Feb. 1947 | Established Inuyama Plant. |
| June 1954 | Started the production of lamps. |
| Mar. 1955 | Started the production of relays. |
| Jun. 1958 | Started the production of window regulators. |
| Nov. 1960 | Established Mizushima Plant. |
| Sep. 1962 | Established Knight Beam Co., Ltd. |
| Nov. 1962 | Established Knight Denso Co., Ltd. |
| Dec. 1963 | The Company built a plant in Nagoya. |
| Nov. 1965 | The Company started manufacturing automotive seat-reclining adjusters. |
| Nov. 1966 | The Company started manufacturing automotive slide adjusters for seats. |
| Jun. 1967 | Established a subsidiary, Toyo Koku Denshi Co., Ltd., which is (currently a consolidated subsidiary). |
| Sep. 1968 | The Company established Imasen Electric & Machinery Co., Ltd., which is (currently a consolidated subsidiary). |
| Aug. 1971 | The Company built a plant in Hiroshima. |
| Jun. 1973 | The Company built a plant in Shirakawa. |
| Feb. 1979 | The Company moved its headquarters to Inuyama City, Aichi Prefecture. |
| Jan. 1982 | The Company merged Night Seiki Co., Ltd., into its operations (This is currently the Kani Plant). |
| Apr. 1982 | Established a subsidiary, Imasen Engineering Corporation, which is (currently a consolidated subsidiary). |
| Nov. 1985 | The Company began manufacturing automotive power adjusters for seats. |
| Oct. 1993 | The Company merged Knight Denso Co., Ltd. into its operations. It was formerly called the Okayama Plant. |
| Apr. 1995 | The Company established a plant in Yaotsu Cho, Gifu Prefecture. |
| Jul. 1996 | The Company established Imasen Philippine Manufacturing Corporation, which is (currently a consolidated subsidiary). |
| Dec. 1996 | The Company's stock was registered as over-the-counter issues by Japan Securities Dealers Association. |
| Apr. 1997 | The Company established Imasen Bucyrus Technology Inc., which is (currently a consolidated subsidiary). |
| May 1999 | The Company built a new plant in Okayama. |
| Sep. 2001 | Listed on the Second Section of Nagoya Stock Exchange. |
| Dec. 2001 | Established an overseas subsidiary, Guangzhou Imasen Electric Industrial Co., Ltd., which is currently a consolidated subsidiary. |
| Sep. 2002 | Designated in the first section of Nagoya Stock Exchange. |
| Dec. 2002 | Obtained ISO 14001, the international standard for environmental management. |
| Jan. 2003 | Established an overseas subsidiary Imasen Manufacturing (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (currently a consolidated subsidiary) |
| Feb. 2003 | Listed on the first section of Tokyo Stock Exchange. |
| Feb. 2004 | Obtained ISO/TS16949: 2002 |
| Apr. 2004 | Absorbed a subsidiary, Knight Beam Co., Ltd. (This is currently the Harusato Plant.) |
| Apr. 2007 | Established a subsidiary, Kyushu Imasen Co., Ltd. (currently a consolidated subsidiary). |
| Nov. 2007 | Established a subsidiary in Indonesia, Imasen Manufacturing India Private Limited (currently a consolidated subsidiary). |
| Mar. 2011 | Established Wuhan Imasen Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. in Whuhan, Hubei Province, China. |
| Jul. 2012 | Established a subsidiary, Imasen Mexico Technology S.A. de C.V., in Mexico. |
| Aug. 2014 | Established a subsidiary, PT Imasen Parts Indonesia, in Indonesia (currently a consolidated subsidiary). |
| Apr. 2015 | Established Imasen Global Development and Training Center. |
| Jun. 2015 | Established German Branch office. |
| Nov. 2020 | Signed an agreement with TS Tech Co., Ltd. to form a capital-based business alliance. |
| Aug. 2022 | Established Mazda Imasen Electric Drive Co., Ltd. |
| Oct. 2023 | Moved from the Prime Market of the Tokyo Stock Exchange to the Standard Market. |
Supplemental Information 1
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2008 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2009 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2010 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2011 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2012 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2013 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2014 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2015 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2016 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2017 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2018 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2019 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2020 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2021 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2022 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2023 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2024 Business Report
Archives of Past Exhibits
Note: A figure in brackets ( ) indicates a loss






















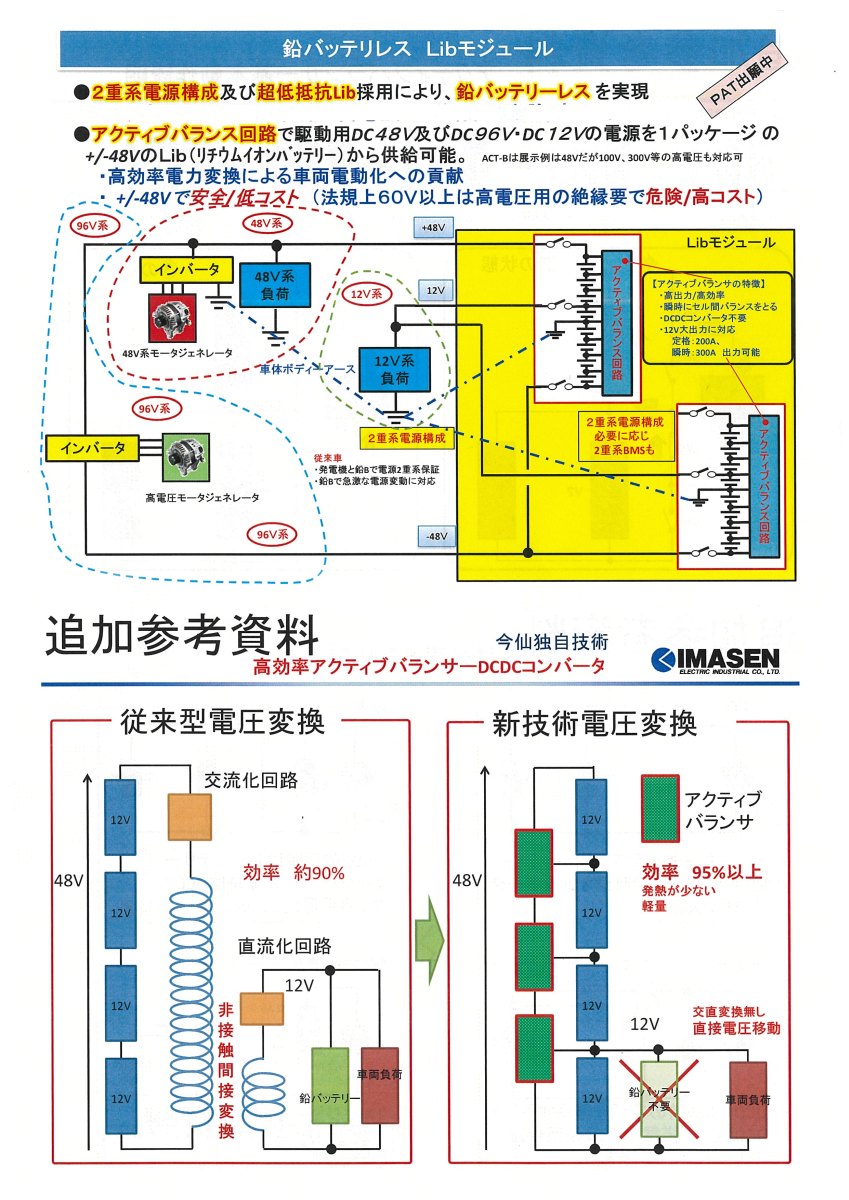
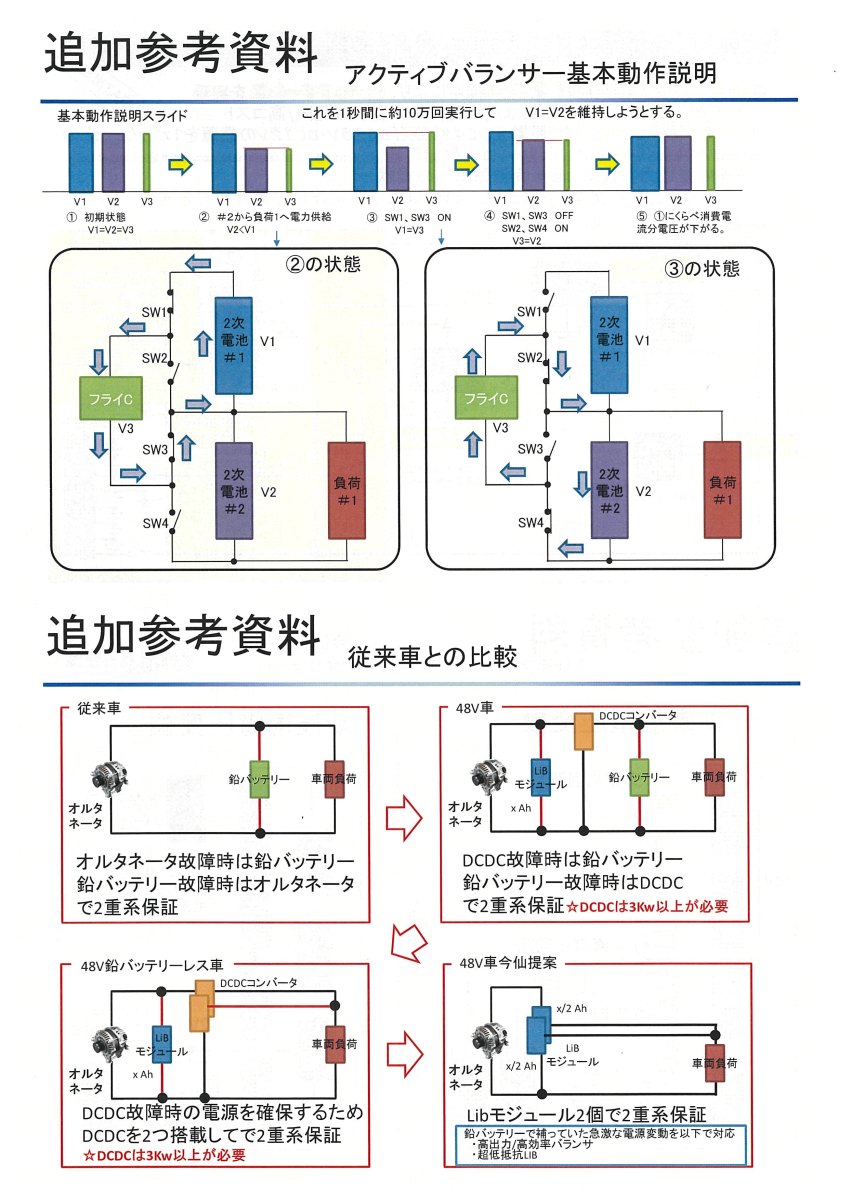

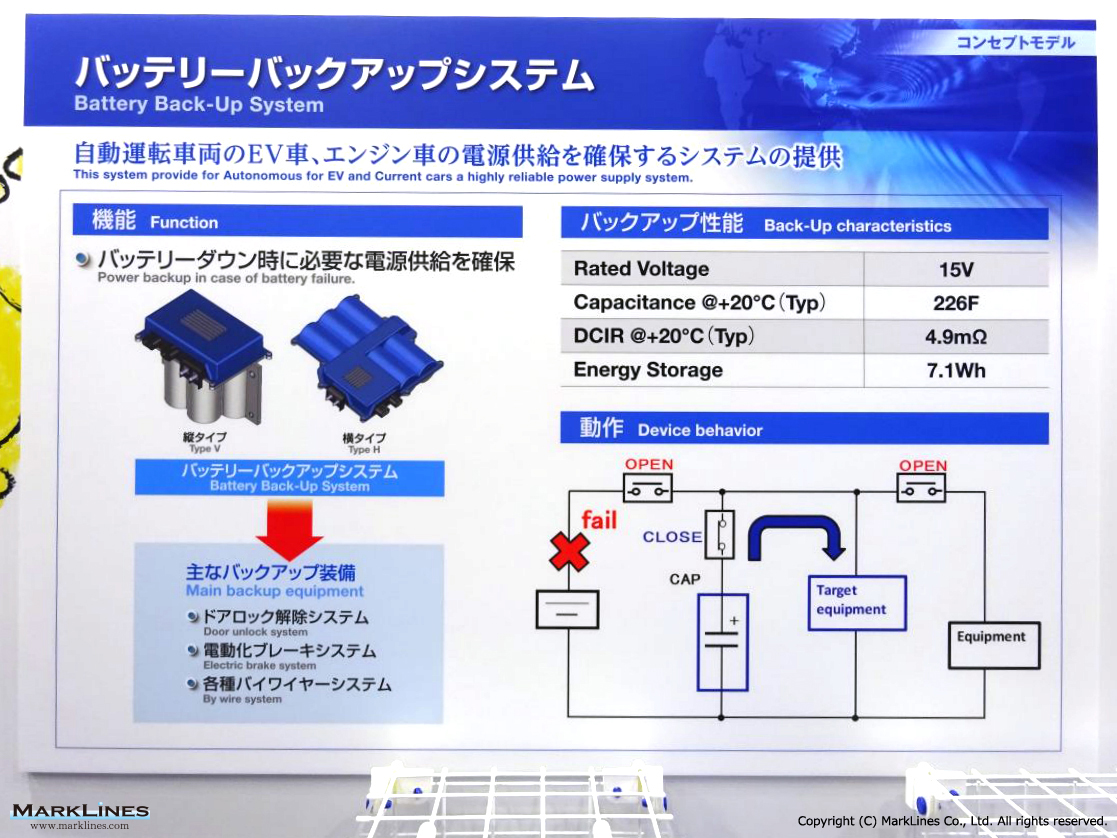

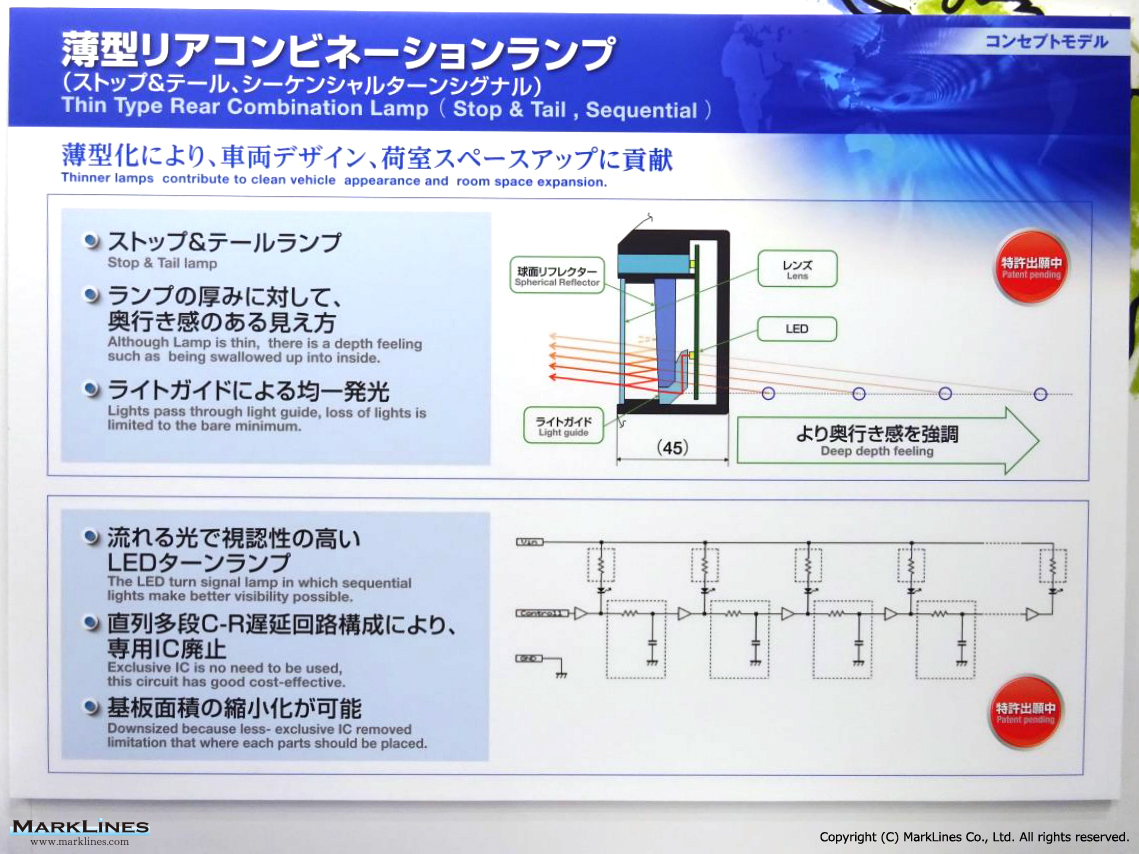

























 Japan
Japan USA
USA Mexico
Mexico Germany
Germany China (Shanghai)
China (Shanghai) Thailand
Thailand India
India