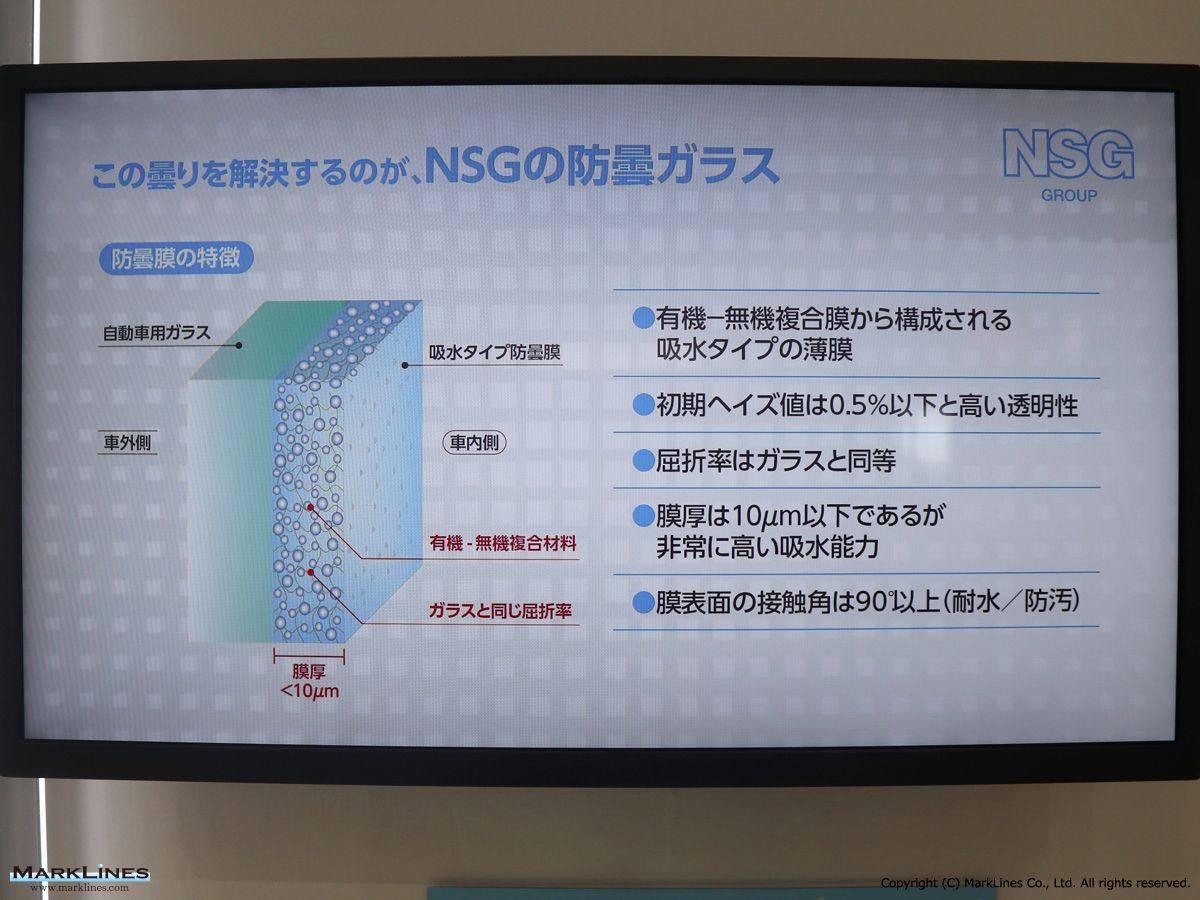
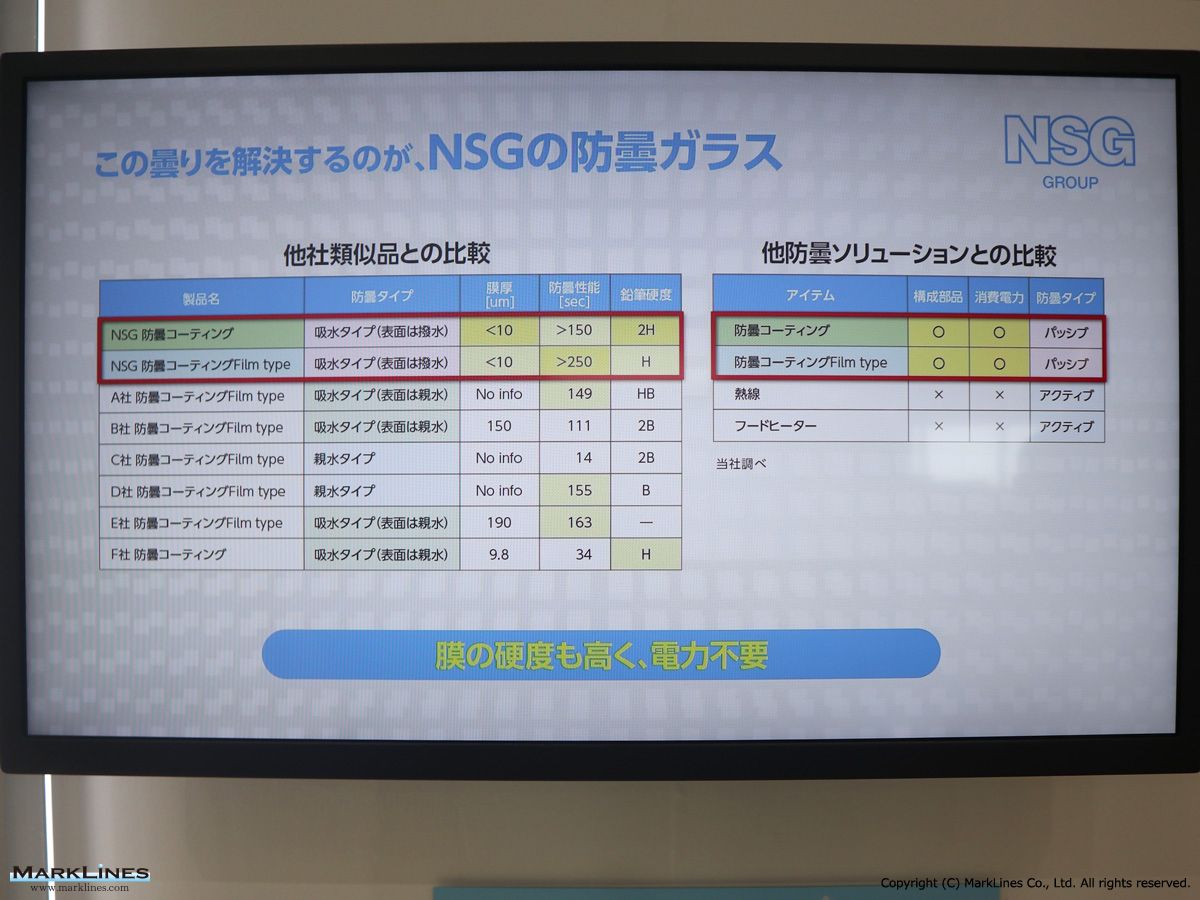
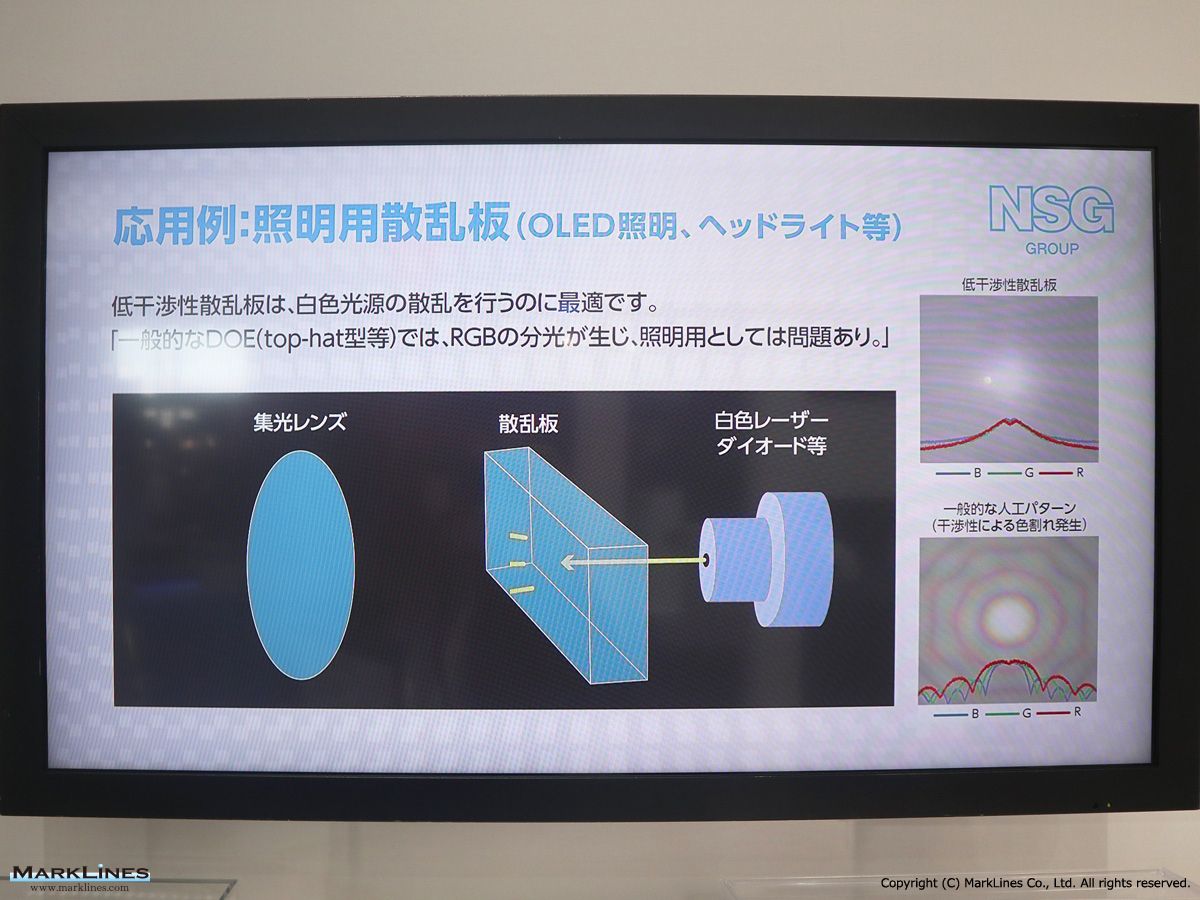
Nippon Sheet Glass Co., Ltd.
Company Profile
■URL
■Address
Business Overview
-The Company is one of the world's three leading glass suppliers for automotive industry. It supplies its products to all major global automakers.
Shareholders
| -Listed on the first section of the Tokyo Stock Exchange. | (As of Mar. 31, 2023) |
| Name or Company Name | Investment Ratio (%) |
| The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Ltd. (Trust Account) | 16.22 |
| Custody Bank of Japan, Ltd. (Trust Account) | 4.87 |
| Nomura Securities Co.,Ltd. | 3.94 |
| MSIP CLIENT SECURITIES | 2.76 |
| BNYM SA/NV FOR BNYM FOR BNYM GCM CLIENT ACCTS M ILM FE | 2.20 |
| MLI FOR CLIENT GENERAL OMNI NON COLLATERAL NON TREATY-PB | 2.04 |
| Customer share holding commission | 1.67 |
| JP JPMSE LUX RE BARCLAYS CAPITAL SEC LTD EQ CO | 1.41 |
| JP MORGAN CHASE BANK 385781 | 1.34 |
| Sumitomo Life Insurance Company | 1.00 |
| Total | 37.50 |
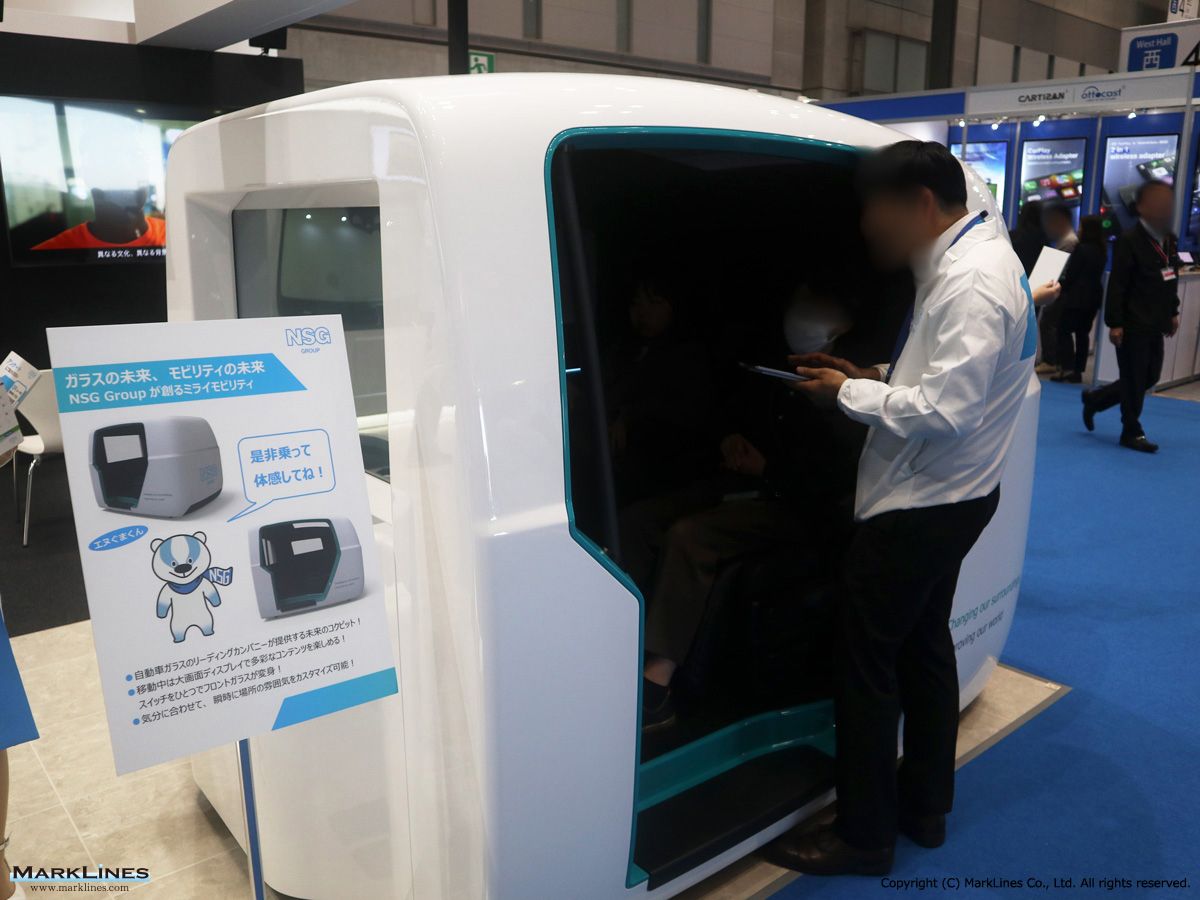
Products
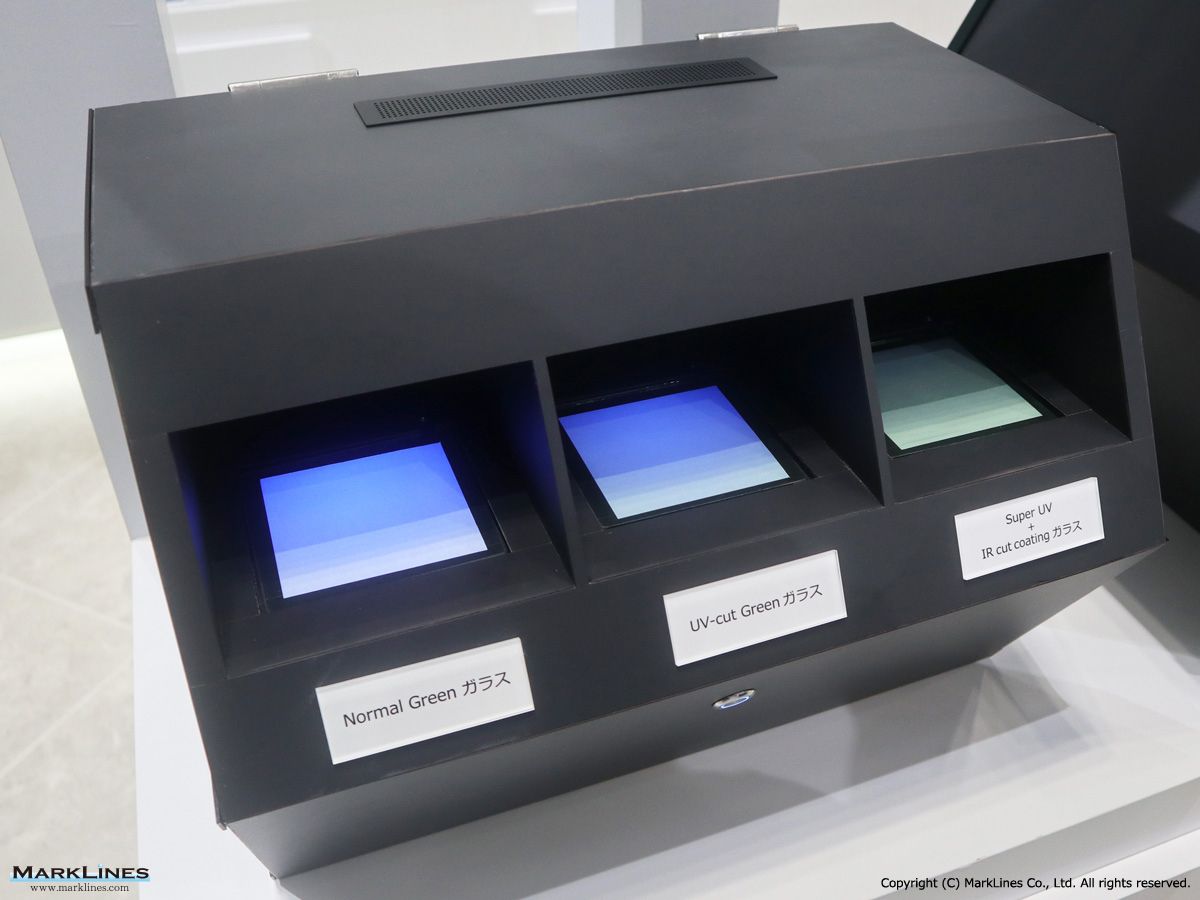
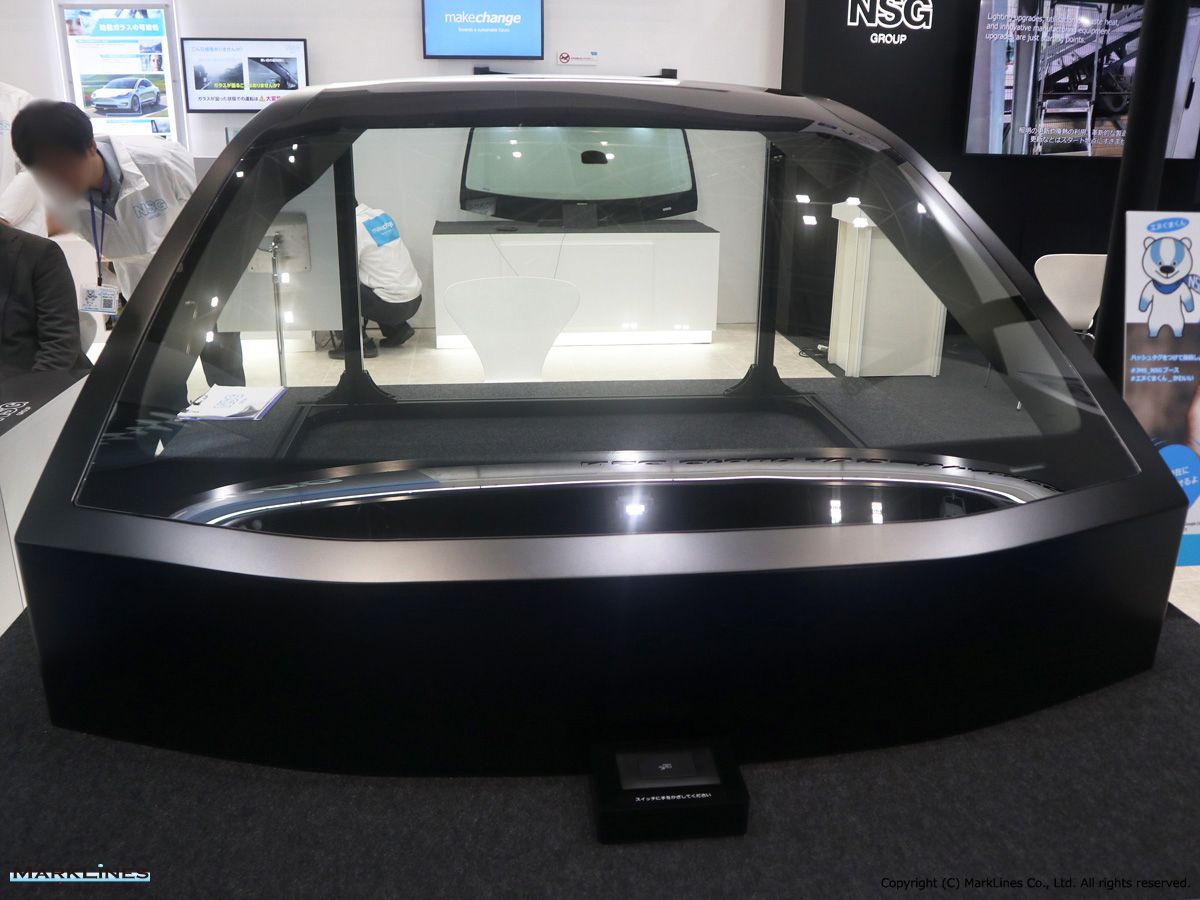
Automotive
-Front & Rear door glass
-Front & Rear quarter glass
-Front & Rear vent glass
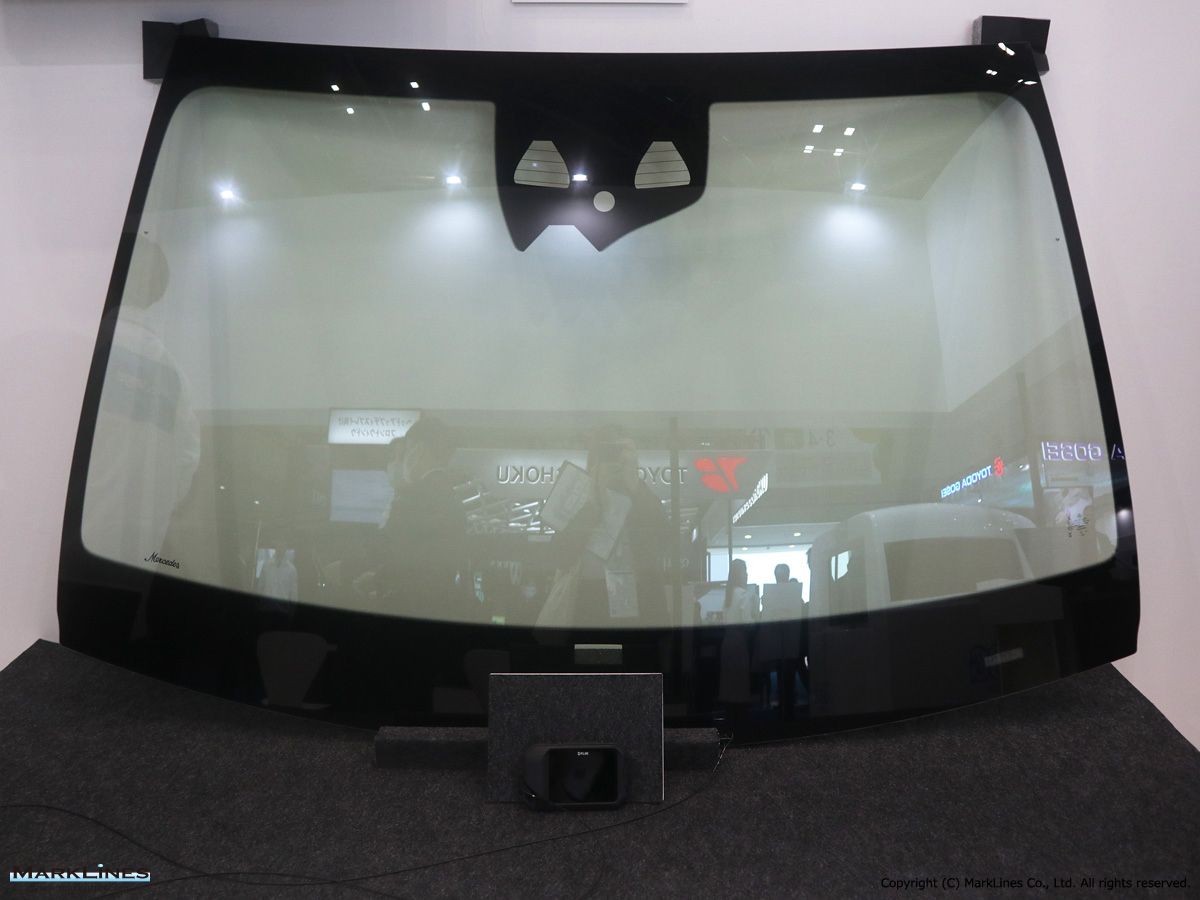
-Windshield glass
-Sunroof Glass
-Rear window glass
History
| Feb. 1919 | The Company was established as America Japan Sheet Glass Co., Ltd. |
| May 1919 | Set up Futashima plant. (the name of the plant was changed to Wakamatsu plant in July 1950) |
| Dec. 1927 | Established Isoraito Kogyo Co., Ltd. (currently a consolidated subsidiary) |
| Jan. 1931 | Adopted its current name. |
| Aug. 1935 | Established Yokkaichi plant. |
| Mar. 1941 | Merged Tokunaga Sheet Glass Manufacturing Co., Ltd. And set up Amagasaki plant. |
| Nov. 1944 | Closed the Amagasaki plant And transferred it to Sumitomo Kakozai Industry Co., Ltd. |
| Nov. 1949 | Established a research center in Amagasaki city. (transferred to Itami city in July 1968) |
| June 1950 | Listed on the Tokyo, Osaka, And Kobe Stock Exchanges. |
| Mar. 1951 | Established Maizuru plant. |
| Oct. 1961 | Isoraito Kogyo Co., Ltd. was listed on the second section of the Osaka And Nagoya Stock Exchanges. |
| Sept. 1963 | Established Chiba plant. |
| Feb. 1965 | Established floating method glass manufacturing facilities in Maizuru plant. |
| July 1968 | Established a new research center in Itami City. Later renamed the Kansai Research Center, Research Laboratory in April 1994. |
| Oct. 1970 | Merged Nippon Safety Glass Co., Ltd. And opened the Kawasaki Plant And Kyoto Plant. |
| Aug. 1971 | Established floating method glass manufacturing facilities in Chiba Plant. |
| Jan. 1973 | Acquired the trade right of window sash And other products from Nippon Sumi Sash Co., Ltd. |
| Dec. 1977 | Closed Wakamatsu plant. |
| June 1978 | Established additional floating method glass manufacturing facilities in Maizuru plant. |
| July 1979 | Acquired trade rights for glass fiber products from Nippon Glass Fiber Co., Ltd. And started selling glass fiber. |
| Dec. 1979 | Set up Tsuchiura factory at the site of Chiba plant. |
| July 1980 | Established Sagamihara factory at the site of Kawasaki plant. (the name of the plant was changed to Sagamihara plant in June 1990.) |
| Oct. 1983 | Established Tsukuba research center. |
| May 1987 | Transferred manufacturing And trade right of short glass fiber to Nippon Microsie Wool Co., Ltd. |
| Apr. 1988 | Transferred part of its trade right of the Environmental Division to Nippon Glass Sheet Environment Amenity Co., Ltd. (currently a consolidated subsidiary) |
| June 1990 | Closed Kawasaki plant. |
| Sept. 1991 | Isoraito Kogyo Co., Ltd. was listed on the first section of the Osaka And Nagoya Stock Exchanges. (formerly listed on the second section) |
| Nov. 1991 | Established Aichi plant. |
| Apr. 1999 | Merged with Nippon Glass Fiber Co., And Micro Optics Co., Ltd., which were previously consolidated subsidiaries. |
| Oct. 1999 | Epitax Inc., which was previously a consolidated subsidiary was handed over to JDS Uniphase Corporation through a stock transaction. |
| May 2000 | Formed a comprehensive business alliance with the UK's leading glass manufacturer, Pilkington, to achieve cooperative manufacturing worldwide in the area of automotive sheet glass. |
| Nov. 2000 | Took over 33.3% of Nippon Muki Co., Ltd.'s authorized shares from Hitachi Chemical Co., Ltd. |
| Dec. 2000 | Sold Osaka Headquarters building. |
| Mar. 2001 | Nippon Muki Co., Ltd. delisted from second section of the Tokyo Stock Exchange. |
| Apr. 2001 | Nippon Muki Co., Ltd. becomes a wholly owned subsidiary through a stock transaction. |
| Oct. 2001 | Pilkington plc becomes a affiliated company applicable to the equity method. |
| Aug. 2004 | Transferred a consolidated subsidiary, Isolite Insulating Products Co., Ltd., to Shinagawa Refractories Co., Ltd. through a public tender bid offered by Shinagawa. |
| Sep. 2004 | Closed down the Aichi plant. |
| Oct. 2004 | Took over the battery separator business from Nippon Muki Co. Ltd. opened the Tarui plant. The separator business was spun off from Nippon Muki. |
| Jun. 2006 | Pilkington plc. became its wholly owned subsidiary. |
| Feb. 2007 | Tokyo headquarters And the address for head office were moved to the current address (Mita, Minato-ku, Tokyo). |
| Jun. 2008 | Sold shares in Mag to Saint-Gobain K.K. (Mag was an affiliated company accounted for under the equity method of accounting.) |
| Oct. 2009 | Sold shares in Nippon Muki Co., Ltd. to Daikin Industries Ltd. |
| 2011 | Expanded production facility of automotive glass production plant in Poland |
| 2018 | Established the Business Innovation Center to accelerate the development and cultivation of new businesses. |
| 2021 | Announced its Mid-term Vision and its new mid-term management plan: Revival Plan 24 (RP24). Transferred the battery separator business to ENTEK based in the USA. |
| 2022 | Moved from the First Section of the Tokyo Stock Exchange to the Prime Market due to the TSE's reorganization. |
| The automotive glass business in China has been transferred to China SYP Kangqiao Autoglass Co., Ltd. |
Supplemental Information 1
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2008 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2009 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2010 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2011 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2012 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2013 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2014 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2015 Business Report
>>>FY ended Mar. 31, 2016 Business Report
>>>NGS's IR Information
>>>Financial Forecast for the Next Fiscal Year (Sales, Operating Income etc.)